Automated Grant Application Routing with n8n & RAG
Grant programs have the power to unlock innovation, support communities, and fuel growth. Yet behind every successful grant initiative is a mountain of applications that someone has to review, categorize, and route. At scale, this work can feel overwhelming, repetitive, and vulnerable to human error.
If you have ever stared at a backlog of grant submissions and thought, “There has to be a better way,” this guide is for you.
In this article, you will walk through a complete journey: from the pain of manual triage to the possibility of intelligent automation, and finally to a practical, ready-to-use n8n workflow template that uses RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), OpenAI embeddings, Supabase vector storage, and LangChain tools to route, summarize, and log incoming applications.
Think of this template as a starting point, not a finished destination. It is a foundation you can build on, customize, and expand as your grant operations grow.
The problem: manual routing slows down impact
Nonprofits, research offices, and grant-making teams often share the same challenges:
- Applications arrive from multiple forms, portals, or systems.
- Staff spend hours reading, tagging, and routing each submission.
- Important details can be missed or inconsistently categorized.
- Reviewers struggle to find context or past similar applications.
As volume grows, this manual approach does not just cost time, it delays decisions, slows funding, and limits the impact your organization can have.
Automation is not about replacing your expertise. It is about freeing you and your team from repetitive triage so you can focus on what truly matters: evaluating quality, supporting applicants, and driving outcomes.
The mindset shift: from reactive to proactive with automation
Before diving into nodes and configuration, it helps to adopt a different mindset. Instead of asking, “How do I keep up with all these applications?” start asking, “How can I design a system that does the heavy lifting for me?”
With n8n and a RAG-powered workflow, you can:
- Turn every incoming application into structured, searchable data.
- Automatically suggest routing decisions with rationale and confidence scores.
- Log results in tools your team already uses, like Google Sheets and Slack.
- Continuously refine the workflow as you learn what works best.
Instead of reacting to a flood of submissions, you build a proactive, always-on assistant that learns from your data and supports your process every day.
The vision: an intelligent routing pipeline with n8n & RAG
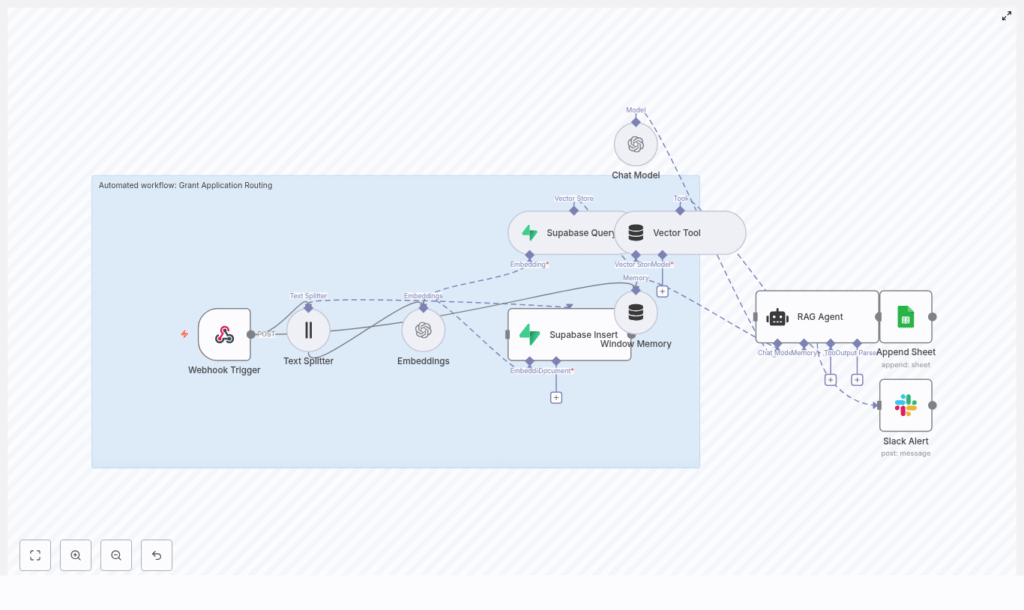
The workflow you are about to explore is built on top of n8n, OpenAI, Supabase, and LangChain. At a high level, it works like this:
- Webhook Trigger receives incoming grant application payloads.
- Text Splitter breaks long application text into manageable chunks.
- Embeddings (OpenAI) converts those chunks into vector embeddings.
- Supabase Insert stores embeddings and metadata in a vector index.
- Supabase Query + Vector Tool retrieves relevant context for the RAG agent.
- Window Memory maintains short-term context for the agent’s reasoning.
- Chat Model (OpenAI) powers the language understanding and generation.
- RAG Agent summarizes the application and decides where it should go.
- Append Sheet records all outputs in Google Sheets.
- Slack Alert notifies your team when something goes wrong.
This is not a theoretical diagram. It is a working, reusable n8n template you can plug into your stack and adapt to your own grant programs.
Step-by-step journey: building the workflow in n8n
Let’s walk through each piece of the workflow. As you follow along, imagine how you might customize each part for your own application forms, review process, or internal tools.
1. Receive applications with a Webhook Trigger
Your journey starts with a simple entry point: an HTTP POST webhook.
Create a Webhook node in n8n and configure it as:
- HTTP Method: POST
- Path:
/grant-application-routing
External forms or APIs can now send application JSON directly into n8n. This might be a custom form on your website, a submission portal, or another system in your stack.
Protect this gateway. Use a shared secret header, IP allowlisting, or network-level validation so only trusted sources can send data into your workflow.
2. Prepare the text with a Text Splitter
Grant applications are often long and detailed. To make them usable for embeddings and retrieval, you split them into smaller, overlapping chunks.
Add a Text Splitter node and configure it with approximately:
- Chunk size: 400 characters
- Chunk overlap: 40 characters
This overlap preserves context across boundaries so the meaning of the text remains intact when you later search or reconstruct it. It is a small detail that makes your RAG agent more accurate and reliable.
3. Turn text into vectors with OpenAI Embeddings
Next, you transform each chunk of text into a vector representation. This is what allows your workflow to search and compare text semantically instead of relying on simple keyword matching.
Add an Embeddings node and select an OpenAI embedding model optimized for this task, such as text-embedding-3-small.
For each chunk, store useful metadata alongside the embedding, for example:
- Application ID
- Chunk index
- Original text
This metadata will later help you trace back decisions, debug issues, or rebuild context for reviewers.
4. Store context in Supabase as a vector index
Now you need a place to keep those embeddings so they can be searched efficiently. Supabase provides a managed vector store that integrates nicely with SQL-based querying.
Add a Supabase Insert node and point it to a vector index, for example:
- Index name:
grant_application_routing
Insert each embedding along with its metadata and original chunk. Over time, this index becomes a rich knowledge base of your grant applications, policies, and related documents that your RAG agent can learn from.
5. Retrieve relevant context with Supabase Query + Vector Tool
When a new application is processed, the agent should not work in isolation. It should be able to look up similar past cases, policy excerpts, or any stored context that might inform routing decisions.
Use a Supabase Query node together with a Vector Tool node to:
- Query the vector store for nearest neighbors to the incoming text.
- Expose the retrieved documents as a tool that the RAG agent can call when needed.
This step turns your Supabase index into a dynamic knowledge source for the agent, so it can reference past applications or internal guidelines while making decisions.
6. Maintain short-term context with Window Memory
Complex applications may involve multiple pieces of text or related messages. To help the agent reason across them, you add a memory component.
Use a Window Memory node to maintain a short-term buffer of recent messages and context. Configure the memory size to balance two goals:
- Enough context for the agent to understand the full picture.
- Controlled cost so you are not sending excessive text to the model.
This memory makes the agent feel more coherent and “aware” of the current application flow.
7. Combine Chat Model and RAG Agent for intelligent routing
Now you are ready to bring everything together. The RAG agent is the brain of your workflow, powered by an OpenAI chat model and connected to your vector tools and memory.
Add a Chat Model node and configure it to use an appropriate OpenAI chat model for your needs. Then connect it to a RAG Agent node that orchestrates:
- Incoming application data.
- Vector Tool calls to Supabase for context.
- Window Memory for recent conversation history.
Use a focused system message to set expectations, for example:
You are an assistant for Grant Application Routing.Then design a prompt template that instructs the agent to:
- Summarize key application fields, such as project summary, budget, and timeline.
- Assign a routing decision, for example Program A, Review Committee B, or Reject for incomplete.
- Provide a short rationale and a confidence score.
This is where your process knowledge shines. You can refine the prompt over time to match your organization’s language, categories, and decision logic.
8. Log every decision in Google Sheets with Append Sheet
Automation is powerful, but only if you can see and audit what it is doing. To keep everything transparent, you log the agent’s output to a central spreadsheet.
Add an Append Sheet node for Google Sheets and map columns such as:
- Application ID
- Routing decision
- Summary
- Raw RAG response or notes
This gives coordinators and reviewers a simple, familiar view of what the workflow is doing. They can spot check results, override decisions, and use the data to refine prompts or routing rules.
9. Protect your workflow with Slack error alerts
Even the best workflows occasionally hit errors. Instead of silently failing, your automation should actively ask for help.
Connect the onError output of the RAG Agent node to a Slack node configured as an alert channel. When something goes wrong, send a message to a dedicated #alerts channel that includes:
- A brief description of the error.
- Optional stack traces or identifiers for debugging.
This keeps your engineering or operations team in the loop so they can quickly triage issues and keep the pipeline healthy.
Configuration and security: building on a solid foundation
As your workflow becomes a critical part of your grant operations, security and reliability matter more than ever. Keep these practices in mind:
- Secrets management: Store all API keys (OpenAI, Supabase, Google, Slack) in n8n credentials, not directly in nodes or code.
- Input validation: Validate the webhook payload schema so malformed or incomplete applications do not break the pipeline.
- Rate limiting: Batch or throttle embedding requests to manage OpenAI costs and avoid hitting rate limits.
- Access control: Use dedicated service accounts for Google Sheets and Supabase, with write access restricted to this workflow.
- Monitoring: Combine Slack alerts with n8n execution logs to track failure rates and overall performance.
These guardrails help your automation stay dependable as you scale.
Scaling and cost: growing smart, not just big
Embedding and model calls are typically the main cost drivers in a RAG-based workflow. With a few thoughtful choices, you can scale efficiently.
- Embed only what matters: Focus on the fields that influence routing or review. Avoid embedding large binary data or repeated boilerplate text.
- Use tiered models: Rely on smaller, cheaper embedding models for indexing, and call higher quality models only when you need deeper summarization or analysis.
- Cache and optimize queries: Cache frequent Supabase queries and keep a compact memory window to reduce repeated calls.
By tuning these levers, you keep your workflow sustainable and ready to handle growing application volumes.
Testing and validation: building trust in your automation
Before you rely on the workflow for live grant cycles, take time to test and validate. This stage is where you build confidence, both for yourself and for your team.
Run end-to-end tests with real or representative application samples and confirm that:
- The entire pipeline executes without errors from webhook to Google Sheets.
- Routing decisions align with expected labels or your existing manual process.
- Summaries capture the essential fields reviewers need for intake.
Use what you learn to refine prompts, adjust thresholds, or tweak routing logic. Each iteration makes the workflow more aligned with your real-world needs.
Example prompts to guide your RAG Agent
Clear, structured prompts help your RAG agent produce consistent, actionable outputs. Here is a simple starting point you can adapt:
System: You are an assistant for Grant Application Routing.
Extract the project summary, funding amount requested, key timelines,
and assign a routing decision.
User: Process the following application data: {{application_text}}.
Return JSON with keys: routing_decision, confidence (0-1), summary, notes.
As you gain experience, you can refine this prompt with your own categories, risk flags, or eligibility checks.
Your next step: turn this template into your automated ally
You now have a complete picture of how this n8n-based workflow works, from raw application text to routed decisions, summaries, and logs. More importantly, you have a starting point for transforming how your organization handles grant applications.
This pipeline combines Webhooks, OpenAI embeddings, Supabase vector storage, LangChain tools, and a RAG agent into a scalable, auditable foundation for automated grant application routing. It reduces manual triage, creates searchable context for reviewers, and gives you space to focus on strategy and impact instead of repetitive sorting.
Do not feel pressure to make it perfect on day one. Start small, connect your data, run test payloads, and improve as you go. Each iteration is an investment in a more focused, automated workflow.
Call to action: experiment, adapt, and grow with n8n
Ready to see this in action?
Import the n8n template, connect your OpenAI and Supabase accounts, and send a few sample grant applications through the workflow. Watch how they are summarized, routed, and logged. Then adjust prompts, categories, or thresholds until it feels like a natural extension of your team.
If you want a deeper walkthrough or a tailored implementation plan, reach out to our team. Use this template as your stepping stone toward a more automated, focused, and impactful grant review process.