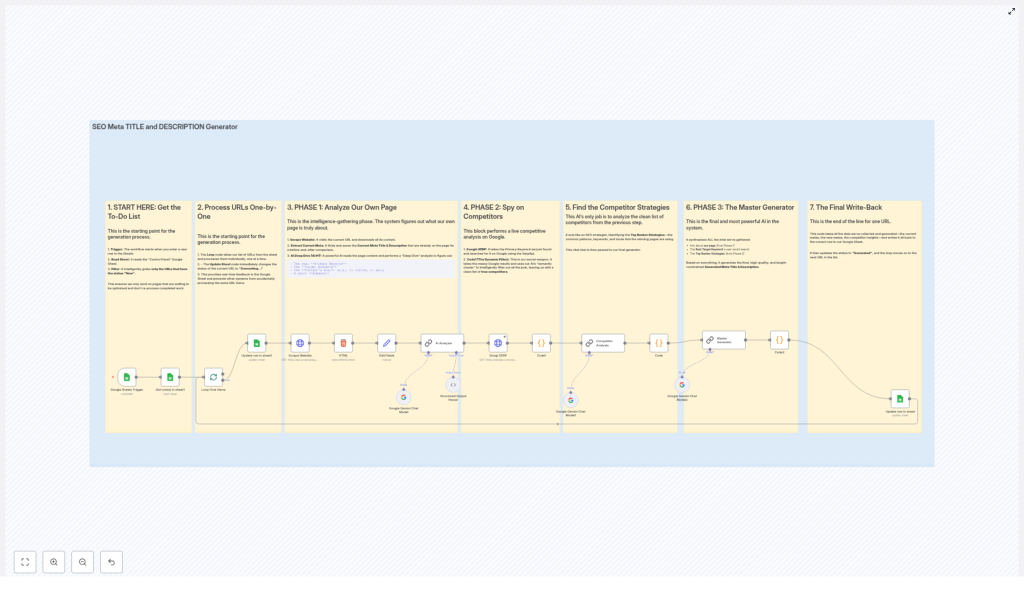
Automated SEO Meta Title & Description Generator Workflow
Overview
The Automated SEO Meta Title and Description Generator is an n8n workflow template that programmatically generates optimized meta titles and descriptions for web pages at scale. It reads URLs from a Google Sheet, crawls each page, performs AI-assisted content and keyword analysis, evaluates search competitors, then outputs SEO-friendly meta tags back into the sheet.
The workflow is designed for technical SEO specialists, growth teams, and automation engineers who want a repeatable pipeline for meta tag optimization that integrates:
- Google Sheets as a control panel and data store
- A smart scraping API for dynamic content retrieval
- Google Gemini Chat Model for semantic and competitive analysis
- SerpApi for Google SERP data
- n8n Code nodes for filtering, validation, and control flow
High-Level Architecture
At a high level, the workflow follows this sequence:
- Trigger & Input – A Google Sheets Trigger monitors a “Control Panel” sheet for new URLs with status
New. - Item-by-item Processing – URLs are processed sequentially, and each row’s status is updated to indicate that meta generation is in progress.
- Page Analysis – The workflow scrapes the target URL, extracts existing meta data, and uses AI to derive primary and secondary keywords, search intent, audience, and content angle.
- Competitor Research – Using SerpApi, the workflow queries Google for the primary keyword, filters relevant competitors, and analyzes their titles and snippets with AI.
- Meta Generation – A “master” AI prompt combines page insights and competitor patterns to produce optimized meta titles and descriptions that respect SEO length constraints.
- Validation & Output – Code validation ensures the AI response is valid JSON and within character limits, then writes the final meta tags and completion status back to the original Google Sheet row.
Data Flow Summary
- Input source: Google Sheet rows with URLs and a status column.
- Intermediate data: Scraped HTML, extracted current meta tags, AI-generated semantic analysis, SERP results, competitor lists, and AI pattern analysis.
- Output: Optimized meta title and description plus updated status in the same Google Sheet row.
Node-by-Node Breakdown
1. Google Sheets Trigger – Detect New URLs
The workflow begins with a Google Sheets Trigger node that monitors a designated “Control Panel” spreadsheet. It is configured to:
- Poll the sheet at a regular interval (every minute).
- Identify rows where the
statuscolumn is set toNew.
Only these “New” rows are passed forward as items in the workflow. This approach ensures:
- Existing or previously processed URLs are not reprocessed.
- New URLs can be added at any time without manual intervention.
2. Loop Control – Process URLs One at a Time
Once the trigger collects all rows marked New, the workflow loops through them sequentially. This can be implemented using standard n8n item-by-item processing or explicit loop constructs, depending on how the template is structured.
For each URL:
- The workflow immediately updates the corresponding row’s status to
Generating - wait for a few minutes. - This real-time status update helps prevent concurrent or duplicate processing of the same URL.
- Team members viewing the sheet can see that the URL is currently in progress.
If the workflow is run with concurrency or multiple parallel executions, this status update acts as a simple coordination mechanism to avoid double work. The template assumes that status changes are respected and that only rows with status New are picked up by the trigger node.
3. Page Analysis Stage
The next group of nodes focuses on understanding the target page itself: its content, current meta tags, and semantic structure.
3.1 Scrape Website Content
A Scrape Website node (using a smart scraping API) retrieves the HTML content of the URL. The scraper is configured to:
- Handle dynamic or JavaScript-rendered pages.
- Return a fully rendered HTML document suitable for parsing.
Typical parameters include:
- Target URL from the current Google Sheet row.
- Any required headers or API keys (configured via credentials).
If the target page fails to load or returns an error, the workflow behavior depends on your n8n error handling settings (for example, “Continue on Fail”). The template assumes successful retrieval and does not define additional custom recovery logic in this description.
3.2 Extract Existing Metadata
After the HTML is available, a subsequent node (often a Code node or HTML extractor) parses the document and extracts:
- The current
<title>tag (meta title). - The
<meta name="description">content (meta description), if present.
These values are:
- Stored as part of the item data for comparison.
- Available for use in prompts to the AI model, if desired.
3.3 AI Semantic Analysis of the Page
A Google Gemini Chat Model node is used to analyze the scraped content in depth. The prompt instructs the model to read the page and return a structured JSON payload that contains:
- Primary keyword that best represents the page’s main topic.
- Semantic cluster of 5 to 7 related secondary keywords.
- Search intent, for example:
- Informational
- Transactional
- Other intent types, depending on the page
- Target audience that the content is aimed at.
- Content angle, such as:
- How-to guide
- Listicle
- Other common content formats
- One-sentence summary of the page content.
The node output is structured JSON, which downstream nodes can reference using n8n expressions. This semantic information is critical for both competitor analysis and meta tag generation.
4. Competitor Research Stage
Once the primary keyword is identified, the workflow evaluates competing pages on Google for that keyword.
4.1 Google SERP Query via SerpApi
A SerpApi node performs a Google search using the primary keyword returned by the Gemini analysis node. Configuration typically includes:
- SerpApi API key (stored as credentials).
- Search engine set to Google.
- Query parameter bound to the primary keyword.
The node returns a structured set of SERP results, including:
- Page titles
- Snippets
- URLs
4.2 Dynamic Filtering of Competitors
A Code node processes the raw SERP results to isolate genuine competitors. The logic typically:
- Iterates over SERP items.
- Checks whether each result’s title or snippet includes any of the secondary keywords from the semantic cluster.
- Filters out pages that do not match any of these related terms.
The outcome is a “clean” list of competitor URLs, titles, and snippets that are:
- Semantically aligned with the target page.
- More likely to represent direct competition for the same search intent.
This node is also the right place to add optional guardrails, such as:
- Excluding your own domain to avoid self-competition.
- Limiting the number of competitors passed downstream.
The template description focuses on filtering based on semantic cluster keywords and does not introduce additional exclusions by default.
4.3 AI Analysis of Competitor Patterns
Another Google Gemini Chat Model node receives the filtered competitor titles and snippets. The prompt guides the model to:
- Identify recurring SEO patterns in titles and descriptions.
- Analyze tone and style (for example, formal vs. casual, benefit-driven vs. feature-driven).
- Detect formatting trends among top-ranking pages, such as:
- Use of brackets or parentheses
- Inclusion of numbers or power words
- Brand mentions
The AI output encapsulates these patterns in a structured format that the final meta generator can use to align your meta tags with what currently works in the SERPs, while still remaining unique to your page.
5. Meta Title & Description Generation
5.1 Master AI Meta Generator
A dedicated Google Gemini Chat Model node acts as the “master generator” for meta titles and descriptions. It aggregates:
- Insights from your own page (primary keyword, secondary keywords, search intent, audience, angle, summary).
- Competitor patterns derived from the previous AI analysis.
- Optionally, the current meta title and description for context or comparison.
The prompt instructs the model to output:
- An SEO-optimized meta title that:
- Accurately reflects the page content.
- Targets the primary keyword and relevant semantic terms.
- Respects a hard limit of under 60 characters.
- An SEO-optimized meta description that:
- Supports the same keyword strategy and search intent.
- Encourages clicks with a clear value proposition.
- Stays under 160 characters.
The node is configured to return its response in valid JSON format, which simplifies downstream parsing and validation.
5.2 Code Validation & Constraint Enforcement
A Code node performs final validation of the AI output before writing anything back to the sheet. Its responsibilities include:
- Parsing the AI response as JSON and handling parse errors.
- Verifying that both the title and description fields exist.
- Checking that:
- Meta title length is less than 60 characters.
- Meta description length is less than 160 characters.
If any of these checks fail, the node can:
- Trim the strings to the required length, or
- Flag the item as invalid, depending on how you configure the logic.
The template description emphasizes that this validation step prevents invalid or oversized meta tags from being used, giving you more reliable output without manual review for every row.
6. Final Write-back to Google Sheets
Once the meta tags are validated, a Google Sheets node updates the original row for the current URL. This node:
- Writes the new meta title into the designated column.
- Writes the new meta description into its corresponding column.
- Updates the status column to
Generated.
This creates a closed feedback loop:
- Rows move from
NewtoGenerating - wait for a few minuteswhile they are in progress. - They end at
Generatedonce the workflow completes for that URL.
The sheet now serves as a live dashboard for:
- Tracking which URLs have been optimized.
- Reviewing generated meta titles and descriptions.
- Re-running or adjusting specific rows if needed by changing their status (subject to your own process rules).
Configuration & Integration Notes
Credentials & External Services
- Google Sheets: Configure OAuth or service account credentials with read/write access to your “Control Panel” spreadsheet.
- Scraping API: Set the API key or token in n8n credentials and reference it in the Scrape Website node.
- SerpApi: Add your SerpApi API key via n8n credentials and configure the search parameters in the corresponding node.
- Google Gemini Chat Model: Ensure the Gemini model is correctly configured and available in your n8n instance, with appropriate API credentials.
Sheet Structure Expectations
The workflow expects a Google Sheet with, at minimum:
- A column containing the URL to analyze.
- A status column with values like:
New– ready for processing.Generating - wait for a few minutes– currently being processed.Generated– successfully processed.
- Columns for Meta Title and Meta Description where the workflow will write the final results.
Error Handling Considerations
The template description assumes a straightforward happy path. In practice, you may want to configure:
- Continue on Fail for non-critical nodes (such as scraping or SERP queries) to avoid stopping the entire batch.
- Optional status updates for error cases (for example,
ErrororNeeds Review) if a node fails or the AI output is unusable.
These adjustments can be made directly within n8n without changing the core logic described here.
Advanced Customization Ideas
While the template already provides a full end-to-end pipeline, technical users can extend it in several ways:
- Additional Filters in the competitor Code node, such as excluding specific domains or limiting to a certain number of SERP results.
- Custom Prompts for Gemini to enforce stricter brand voice or compliance rules.
- Multi-language support by adjusting prompts and SERP locale parameters (if your site targets multiple regions).
- Versioning of meta tags in the sheet, for example by adding columns for “old” vs “new” titles and descriptions.
All of these can be implemented while preserving the core flow: sheet trigger, page analysis, competitor research, AI meta generation, validation, and write-back.
Conclusion
This n8n workflow template provides a robust, repeatable system for automated SEO meta title and description generation. By combining Google Sheets, web scraping, AI-driven content understanding, competitive SERP analysis, and strict validation, it helps you scale meta tag optimization without sacrificing quality or control.
If you want to improve search visibility and click-through rates across many URLs at once, this kind of automated pipeline offers a practical solution that still respects SEO best practices and technical constraints.
Ready to optimize your website meta titles and descriptions with AI automation? Start building your workflow now and watch your SEO performance grow.