Backup n8n Workflows to Gitea: A Story of One Near-Miss
On a quiet Tuesday morning, Lena, a marketing operations manager at a fast-growing startup, opened her n8n dashboard and froze. The workflow that handled all lead routing from their website, CRM, and email platform was gone.
She had been tweaking a few nodes the night before. Somewhere between refactoring and testing, she had overwritten the wrong version. No backup, no Git history, no easy way back. The only option was to rebuild from memory.
That was the moment Lena decided this would never happen again.
The Problem: Fragile Automation Without Version Control
Lena was responsible for a growing network of n8n workflows. They synced leads, cleaned data, updated sales dashboards, and triggered campaigns. Every new experiment meant another tweak, another node, another risk of breaking something that used to work.
She knew Git could solve this. Her engineering teammates used Git daily for code, but her automations lived only inside n8n. No version history, no pull requests, no way to see what changed last week or last month.
She wrote a list of what she wanted for her n8n workflows:
- Version history for every workflow change
- Centralized storage with team access and permissions
- Automatic, scheduled backups so she did not have to remember
- Easy rollback if a workflow was deleted or misconfigured
Her team already hosted a self-managed Gitea instance for internal projects. If she could back up n8n workflows to Gitea automatically, she would get all the benefits of Git without manual exports.
That is when she discovered an n8n workflow template that did exactly that.
The Discovery: An n8n Template for Automated Gitea Backups
Late that afternoon, Lena found an n8n template titled “Backup n8n Workflows to Gitea.” It promised exactly what she needed: a scheduled backup process that would export all workflows from her n8n instance and push them into a Gitea repository.
Reading through the template description, she realized it was not just a simple export. It was a complete, automated backup strategy:
- Trigger on a schedule, for example every 45 minutes
- Fetch all workflows from the n8n API
- Check Gitea to see if each workflow file already existed
- Base64-encode workflow JSON and create or update files through the Gitea API
- Commit only when a workflow had actually changed
It sounded like the kind of safety net she wished she had the night before. She decided to set it up the same day.
Setting the Stage: How the Template Works Behind the Scenes
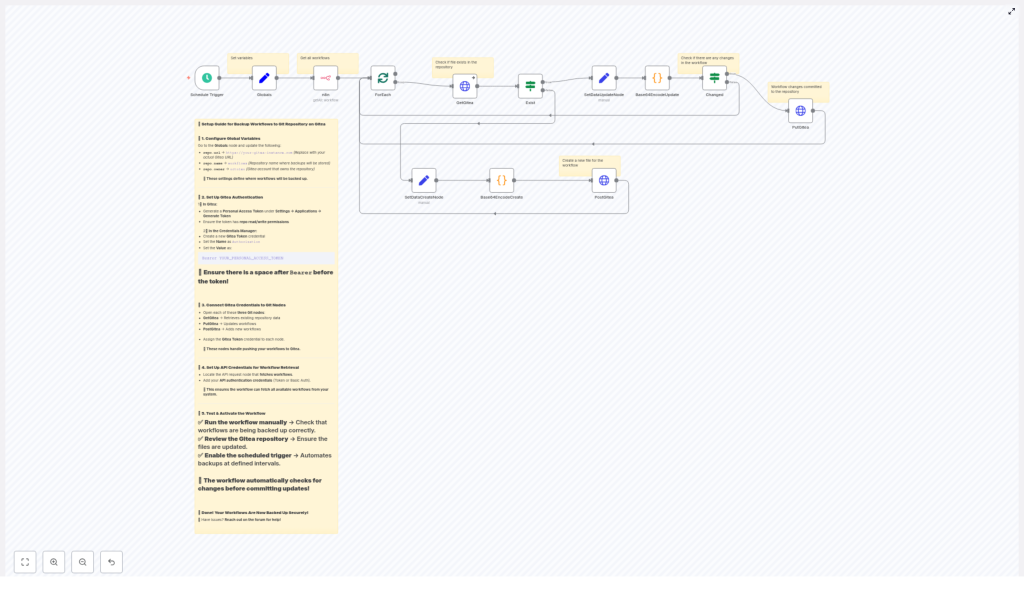
Before touching any settings, Lena wanted to understand the moving parts. The template was built from a handful of key n8n nodes, each playing a specific role in the backup story.
The Schedule Trigger: The Metronome
At the start of the workflow sat a Schedule Trigger node. It was the metronome of the system, kicking off a backup run every 45 minutes by default. She liked that she could change this interval later, maybe to hourly or daily, once she saw how often her workflows changed.
Globals (Set Node): The Single Source of Truth
Next was a Set node labeled Globals. This node stored the core configuration for the Gitea repository:
repo.url– for examplehttps://git.your-domain.comrepo.owner– the repository owner or organizationrepo.name– the repository name, such asworkflows
By centralizing these values, the rest of the workflow could reference them without hardcoding URLs or repo names in multiple places. If she ever moved the repository, she would only have to update this single node.
n8n API Node: The Archivist
Further down, Lena found the n8n (API node). This node authenticated against the n8n API and requested the list of workflows along with their JSON definitions. It was the archivist of her system, responsible for collecting the exact state of every workflow at the time of backup.
She noted that it needed valid n8n API credentials with permission to read and export workflows, either via an API key or Basic Auth, depending on how the server was configured.
ForEach / splitInBatches: The Workflow Loop
Once the workflows were fetched, the template used a combination of ForEach or splitInBatches logic. This allowed the workflow to process one n8n workflow at a time, which made it easier to check the corresponding file in Gitea, update it, or create it if it did not exist.
Instead of pushing everything in one huge request, it carefully walked through each workflow individually, which also helped with error handling and logging.
GetGitea, PutGitea, PostGitea: The Bridge to Git
The most critical pieces for Gitea integration were three HTTP Request nodes:
- GetGitea – checked if a file for the current workflow already existed in the repository
- PutGitea – updated an existing file, using the file’s SHA to create a correct commit
- PostGitea – created a new file if one was missing
These nodes talked to the Gitea REST API. Together, they allowed the template to behave like a careful Git user: look for the file, update it if present, or create it if it was new.
Code Nodes for Base64: The Translators
Finally, there were two Code nodes with names like Base64EncodeCreate and Base64EncodeUpdate. They took the raw workflow JSON, formatted it as pretty-printed JSON, and then converted it into a Base64 string.
This Base64 output was exactly what the Gitea API expected in its content field when creating or updating files. Encoding the content ensured binary-safe transfers and matched Gitea’s format requirements for these endpoints.
Now that Lena understood the architecture, she was ready to wire it to her own Gitea instance.
Rising Action: Turning a Template into a Lifesaver
With a clear goal and a working template, Lena started configuring the workflow. Each step moved her further away from fragile, manual backups and closer to automated version control for every n8n workflow.
1. Configuring Global Repository Settings
She opened the Globals node and filled in the fields:
- repo.url:
https://git.example.com - repo.owner: the internal organization that owned their repos
- repo.name:
workflows, a new repository she had created just for n8n backups
This single node now defined where every backup would be stored.
2. Creating a Gitea Personal Access Token
Next, she logged into Gitea and navigated to Settings → Applications → Generate Token. She created a new personal access token with repo-level read and write permissions, just enough to create and update files in the target repository.
She copied the token immediately, knowing she would not be able to view it again.
3. Storing Credentials Securely in n8n
Back in n8n, Lena created a new HTTP Header Auth credential. She set:
- Header Name:
Authorization - Header Value:
Bearer YOUR_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN(with a space afterBearer)
This ensured that all calls to the Gitea API would be authenticated securely, without exposing the token in plain text inside workflow nodes.
4. Wiring the Credentials to Gitea Nodes
She then opened each of the Gitea-related HTTP Request nodes: GetGitea, PutGitea, and PostGitea. In each one, she selected the new HTTP Header Auth credential she had just created.
Now every interaction with Gitea, from checking for existing files to pushing updates, would use the same secure token.
5. Configuring the n8n API Node
To complete the loop, Lena needed to make sure the n8n API node could actually read workflows. She created or selected an existing n8n API credential, configured it with an API key or Basic Auth, and tested the connection.
The test returned a list of workflows in JSON format. That was the confirmation she needed that the node could act as the archivist for her automations.
6. The First Manual Test
With everything wired, Lena ran the workflow manually. She watched the execution logs step by step:
- The Schedule Trigger was bypassed for manual execution, but the rest of the flow started.
- The n8n API node fetched all workflows successfully.
- The ForEach logic looped through each workflow.
- GetGitea returned a
404for each workflow, which made sense because the files did not exist yet. - The template recognized the
404as an expected case and used PostGitea to create new files. - The Code nodes encoded each workflow JSON into Base64 and passed it to the Gitea API.
When she opened the Gitea repository, there they were: every n8n workflow saved as a JSON file, each with its own commit. The near-miss from the night before suddenly felt like a turning point rather than a disaster.
The Turning Point: From One-Off Fix to Reliable System
Over the next few days, Lena let the Schedule Trigger take over. Every 45 minutes, the workflow ran quietly in the background, checking for changes and syncing them to Gitea.
She noticed something important: the template only committed when a workflow had changed. That meant no unnecessary noise in the Git history. Each commit actually represented a meaningful update, making it easier to track when and how workflows evolved.
With backups now running automatically, she started thinking not just about recovery, but about collaboration, security, and optimization.
Security Practices Lena Put in Place
Because the new system touched both automation and source control, Lena made sure it followed security best practices:
- She stored the Gitea token only in n8n credentials and never in plain text nodes or logs.
- The token had the minimum required scope, only repo read and write access.
- She restricted repository access using Gitea team and repo permissions so only the right people could see and modify workflow backups.
- For particularly sensitive workflows, she considered keeping them in a private repository and avoided storing secrets in the workflows themselves, using n8n credentials instead.
With these measures in place, she felt confident that automating backups did not mean compromising on security.
When Things Go Wrong: Troubleshooting in the Real World
Not everything was perfect from day one. A few issues popped up during the first week, but the template design and n8n logs made them manageable.
Common Issues She Encountered
- HTTP 401 / 403: When she accidentally used an old Gitea token, the Gitea nodes returned 401 and 403 errors. Updating the token and checking its permissions fixed it.
- 404 on GetGitea: At first, these errors looked alarming, but they were actually expected for new workflows. The template caught the 404 and used PostGitea to create the missing files.
- Encoding mistakes: During a test change to the Code node, she briefly broke the Base64 output. The result was that Gitea rejected the content. She reverted to the original logic, ensuring the Code nodes produced valid Base64 strings and that the
contentfield in the API calls used that value.
Each time, the combination of clear error messages, execution logs, and the predictable structure of the template helped her track down the issue quickly.
Optimizations: Making the Backup Flow Work for the Team
Once the system was stable, Lena started refining it to better fit her team’s workflow.
- Adjusting frequency: Since most workflows only changed a few times a day, she increased the backup interval to reduce API calls and repository noise.
- Commit messages: She extended the HTTP body parameters in the Gitea nodes to include descriptive commit messages, like “Update workflow: Lead Routing (2025-03-10 14:30 UTC)”. It made the Git history easier to read.
- Diff and audit ideas: For future iterations, she considered saving diffs in a separate directory or enabling more verbose change logs for auditing, especially for workflows tied to compliance-sensitive processes.
Looking Ahead: Advanced Options She Is Planning
With the core backup system running smoothly, Lena started exploring more advanced options that the template could support.
- Environment branches: She planned to introduce a branch per environment, such as
dev,staging, andproduction, so each n8n instance would push its workflows to the correct branch in the same repo. - Webhook-triggered backups: Instead of relying solely on a fixed schedule, she considered triggering backups whenever a workflow changed, using webhooks for near-real-time backups.
- Compression or encryption: For particularly sensitive setups, she thought about compressing or encrypting workflow JSON before pushing to Gitea, while still keeping secrets in n8n credentials rather than in the workflows themselves.
The template had become more than a safety net. It was now part of a broader strategy for how her team managed automation as a first-class asset.
Resolution: From Panic to Confidence
Weeks later, someone on Lena’s team accidentally changed a critical workflow and broke a key integration. In the past, that would have meant hours of guesswork. This time, Lena calmly opened the Gitea repository, browsed the workflow’s history, and restored the last known good version.
What used to be a crisis was now just another small task.
By backing up n8n workflows to a Gitea repository, she had gained:
- A robust, versioned history of every workflow
- An easy recovery path for accidental deletions or bad edits
- Team visibility and collaboration through Git
- Confidence that her automation logic was as safe as the application code her engineers wrote
All of it powered by a single n8n template that automated the entire process: fetching workflows, encoding them, checking for existing files, and creating or updating them only when needed.
Take the Next Step: Secure Your Own n8n Workflows
If you are running n8n in production, you are one unexpected change away from the same panic Lena felt that Tuesday morning. You do not have to wait for a near-miss to fix it.
Import the n8n template, configure the Globals node with your Gitea URL, owner, and repo name, set up your credentials, run a manual test, and then enable the scheduled trigger. From that point on, your workflows will quietly back themselves up to Gitea.
Need help customizing it for branches, commit messages, or multiple environments? Reach out to your team, contact support, or post a question in the n8n community forum. Share this guide with your teammates so everyone’s automations are backed up reliably and versioned like any other critical part of your stack.