Build a Flight Price Drop Alert with n8n, Weaviate, and OpenAI
If you have ever refreshed a flight search page so many times that your browser started to feel judged, this guide is for you. Manually monitoring flight prices is the digital equivalent of watching paint dry, except the paint sometimes gets more expensive.
Instead of wasting hours checking fares, you can let an automated flight price drop alert do the boring work for you. In this walkthrough, you will use n8n, OpenAI embeddings, and a Weaviate vector store to build a workflow that:
- Receives flight price updates from your scraper or API
- Stores historical prices in a vector database
- Uses a lightweight agent with memory to decide when a drop is worth shouting about
- Logs everything to Google Sheets for easy auditing and trend analysis
You get the fun part (catching deals), and your workflow gets the repetitive part (staring at numbers all day).
Why bother with a flight price drop alert?
Whether you are a frequent flyer, a travel agency, or that friend who always finds suspiciously cheap flights, timing is everything. A good flight price monitoring system helps you:
- Catch price drops fast so you can book before the deal disappears
- Keep historical context and see how prices move over time
- Automate notifications and logging instead of doing manual spreadsheet gymnastics
- Avoid missed opportunities because you forgot to check prices for one day
In short, you trade in repetitive manual checks for a smart n8n workflow that quietly works in the background.
What this n8n workflow does (high-level overview)
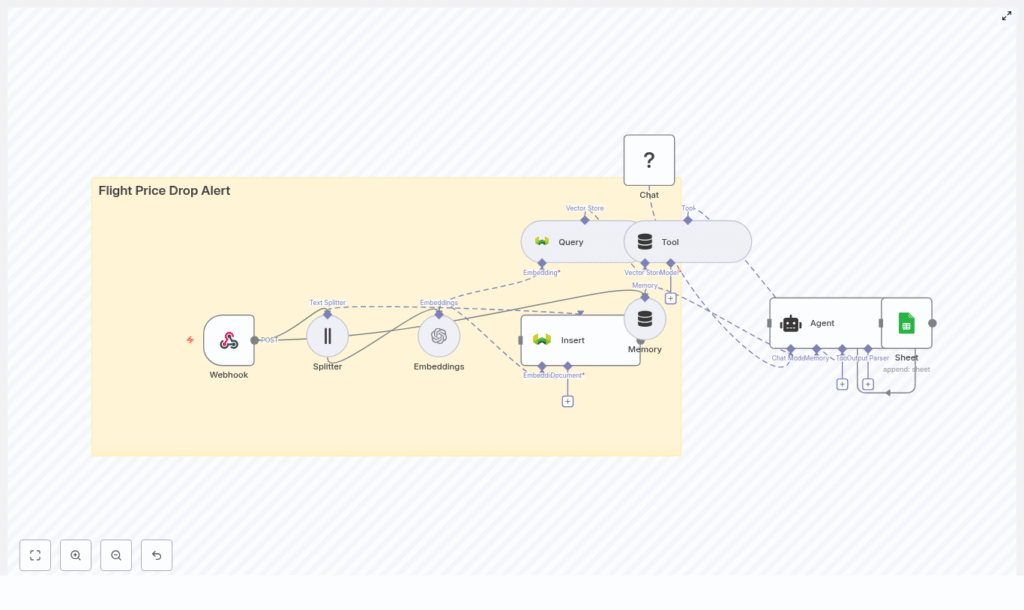
This template uses n8n as the orchestrator that connects all the moving parts. Here is the basic architecture of your flight price drop alert:
- Webhook – receives flight price updates via POST from your scraper or a third-party API
- Text Splitter – breaks longer text into chunks that are easier to embed
- OpenAI Embeddings – converts text into numeric vectors for similarity search
- Weaviate Vector Store – stores and queries those vectors efficiently
- Memory + Agent – maintains short-term context and decides when to trigger alerts
- Google Sheets – logs alerts and events for auditing and analysis
This combo lets you quickly prototype a robust flight price monitoring workflow in n8n, then scale it later without changing the core logic.
Core automation flow in plain English
Here is what happens when a new price comes in:
- Your scraper or API sends a JSON payload with flight details to an n8n Webhook.
- The workflow normalizes and splits any longer text fields into chunks.
- Each chunk goes through OpenAI embeddings, turning text into vectors.
- The vectors get stored in Weaviate under an index like
flight_price_drop_alert. - The workflow queries Weaviate for similar past entries on the same route.
- An agent, using short-term memory and query results, decides if the new price counts as a meaningful drop.
- If yes, the workflow logs the alert in Google Sheets and can later be extended to send messages via email, SMS, Slack, and more.
You get an automated, data-backed decision system instead of guessing whether a $20 drop is actually a good deal.
Keywords to keep in mind
If you care about SEO or just like buzzwords, this workflow revolves around:
flight price drop alert, n8n workflow, Weaviate vector store, OpenAI embeddings, flight price monitoring, webhook automation, travel alerts
Step-by-step setup in n8n
Let us walk through the main steps to build this flight price alert n8n template. You will keep all the original logic but in a more human-friendly order.
Step 1 – Receive flight price updates via Webhook
First, you need a way to get flight data into n8n.
- Create a Webhook node in n8n.
- Set it to accept POST requests with JSON payloads.
- Configure your scraper or third-party API to send flight metadata to that webhook URL.
Your payload might look like this:
{ "origin": "JFK", "destination": "LHR", "departure": "2025-09-01", "price": 432, "currency": "USD", "airline": "ExampleAir", "url": "https://booking.example/flight/123"
}
This is the raw material that everything else in the workflow uses to detect price drops.
Step 2 – Normalize and split content for embeddings
Next, you prepare the data for vectorization. If your payload includes longer descriptions or extra metadata, you do not want to embed a giant blob of text in one go.
- Add a Text Splitter node after the Webhook.
- Configure it to break text into chunks, for example:
- Chunk size: around 400 characters
- Overlap: around 40 characters
This keeps enough overlap so context is preserved, while keeping vectors compact and efficient for the Weaviate vector store.
Step 3 – Generate OpenAI embeddings
Now you turn text into something your vector database can understand.
- Add an OpenAI Embeddings node.
- Pass each chunk from the splitter into this node.
- Include key fields alongside the text, such as:
- Route (origin and destination)
- Price
- Timestamp or departure date
The embeddings represent your text as vectors, which makes similarity search fast and flexible. This is the backbone of your flight price monitoring automation.
Step 4 – Insert and query data in Weaviate
With embeddings ready, you can now store and compare them using Weaviate.
- Add an Insert operation to your Weaviate node.
- Use an index name like
flight_price_drop_alertto keep things organized. - Store:
- The embedding vectors
- Route identifiers
- Timestamps
- Raw prices and any other useful metadata
To figure out whether the latest price is a bargain or just mildly less disappointing, you:
- Run a Query on the same Weaviate index.
- Filter by route and a relevant time window, for example the last 30 days.
- Retrieve similar historical records so you can compare current prices against past ones.
Weaviate returns similar entries quickly, which lets your agent make smarter decisions instead of just reacting to every tiny fluctuation.
Step 5 – Use short-term memory and an agent to decide when to alert
Now comes the brain of the operation. Instead of hard-coding every rule, you combine:
- A small in-memory buffer that stores recent interactions and context
- An agent (LM-driven) that uses:
- Current price
- Historical prices from Weaviate
- Defined thresholds
The agent can apply logic such as:
- Compare the current price with the average and minimum over the last 30 days
- Only trigger an alert if the drop meets a minimum threshold, for example at least 10 percent lower
- Enrich the alert message with route details and booking links
The result is a more intelligent n8n flight alert workflow that avoids spammy notifications and focuses on meaningful price drops.
Step 6 – Log alerts to Google Sheets
Once the agent decides that a price drop is worth celebrating, you log it for future reference.
- Add a Google Sheets node.
- Configure it to append a new row whenever an alert is triggered.
Your sheet might include columns such as:
- Timestamp
- Route (origin and destination)
- Previous lowest price
- Current price
- Percent change
- Booking link
This gives you a simple audit log and a handy resource for trend analysis without manually updating spreadsheets at odd hours.
Decision logic and best practices for fewer false alarms
Not every tiny drop deserves an alert. You do not want your workflow pinging you every time a fare moves by a few cents.
Use meaningful thresholds
Combine absolute and relative rules so your alert system behaves like a calm adult, not a panicked stock trader. For example:
- Require at least a $50 drop
- And at least a 10 percent lower price than the recent average
This reduces noise and ensures alerts highlight genuinely interesting deals.
Compare prices over time windows
Flight prices are seasonal and sometimes chaotic. To keep things realistic:
- Compare prices across configurable windows, such as:
- 7 days
- 14 days
- 30 days
This helps your flight price monitoring workflow adapt to normal fluctuations and typical fare swings.
Store rich metadata with vectors
When inserting data into Weaviate, do not store just the vectors. Include:
- Route identifiers (origin, destination)
- Timestamps or departure dates
- Raw prices and currency
This makes filtering by route and date faster and keeps your queries flexible as you refine your alert logic.
Scaling your flight price monitoring workflow
If your use case grows from a few routes to a full-blown travel analytics system, the same architecture still works. You just need a few upgrades.
- Batch insert embeddings and use asynchronous workers to handle large volumes of price updates
- Shard vector indices by region or market to speed up lookups
- Apply rate limiting and retries for upstream scrapers and APIs so you do not break anything during peak times
- Use persistent storage like Postgres or S3 to keep raw payloads alongside your vector store
With these in place, your n8n flight price drop alert can comfortably handle larger workloads without falling apart.
Testing and validation before trusting the bot
Before you let automation loose on real bookings, you should test the workflow with controlled data.
- Create synthetic price histories that include:
- Clear price drops
- Slow, gradual declines
- Sudden spikes
- Log intermediate outputs such as:
- Similar records returned by Weaviate
- Computed averages
- Percent changes
This lets you verify that your thresholds and agent logic behave as expected before you rely on it for real travel decisions.
Security and cost considerations
Automation is great until someone pastes an API key into the wrong place. A few simple precautions go a long way:
- Sanitize incoming webhook data so you do not process unexpected or malicious input
- Store API keys securely using n8n credential stores or environment variables
- Monitor OpenAI embedding usage and Weaviate storage so costs do not quietly creep up
- Cache frequent queries if you notice repeated patterns in your searches
This keeps your flight price alert automation stable, secure, and budget friendly.
Example n8n node flow at a glance
If you like to see the big picture, here is how the main nodes line up in the template:
- Webhook (POST) – receives incoming price updates
- Splitter – chunks payload text for embeddings
- Embeddings – converts text chunks into vectors with OpenAI
- Insert – stores embeddings in Weaviate using the
flight_price_drop_alertindex - Query – searches recent similar vectors for the same route
- Tool or Agent – uses memory and query results to decide whether to trigger an alert
- Sheet – appends an audit row to Google Sheets when an alert fires
This is the full loop that turns raw price data into actionable alerts.
Example alert message
When the agent decides a price drop is worth your attention, it can generate a message like:
Price drop: JFK → LHR on 2025-09-01
Now: $432 (was $520, -17%)
Book: https://booking.example/flight/123
Short, clear, and straight to the point, so you can book quickly instead of decoding a cryptic log entry.
Next steps and customization ideas
Once you have the core n8n flight price drop alert workflow running, you can level it up with a few extras:
- SMS or email notifications using Twilio or SendGrid so you get alerts on the go
- Slack or Telegram integration for team travel deals and shared alerts
- User preference management with custom thresholds per user or route
- Dashboards and KPIs to visualize trends and monitor performance
The underlying architecture with n8n, OpenAI embeddings, and Weaviate is flexible, so you can keep extending it as your needs grow.
Wrapping up
By combining n8n, vector embeddings, and a Weaviate vector store, you get a powerful, extensible system for flight price drop alerts. The workflow balances fast similarity search with LM-driven decision making, which is ideal for catching fleeting fare opportunities without drowning in noise.
Ready to stop manually refreshing flight pages? Export the n8n workflow template, plug in your OpenAI and Weaviate credentials, and point your scraper to the webhook. In a short time, you will have a fully automated travel alert system quietly working in the background.
Call to action: Export the workflow, test it with around 50 synthetic entries, and fine tune your thresholds until the alerts feel just right. If you want a ready-made starter or hands-on help, reach out for a walkthrough or a custom integration.