Build a Notion Knowledge Base Assistant with n8n
Use n8n, the Notion API, and an AI language model to deliver a fast, reliable knowledge base assistant on top of your existing documentation. This guide explains the architecture of the n8n template, its key nodes and integrations, and the configuration steps required to deploy an AI chat assistant that answers questions directly from your Notion workspace.
Why automate a Notion knowledge base with n8n?
Notion has become a standard repository for internal documentation, product specs, and operational runbooks. As these spaces grow, manual search and human support do not scale. An n8n-powered assistant built on top of Notion enables you to:
- Provide fast, consistent answers from canonical documentation
- Reduce repetitive questions to support, IT, and operations teams
- Deliver context-aware responses that reference specific Notion pages
- Expose the same knowledge layer across Slack, email, or web chat
By orchestrating Notion queries and an AI model through n8n, you get a controllable, auditable automation workflow instead of a black-box chatbot.
Solution architecture at a glance
The template implements a deterministic pipeline that receives a user question, retrieves relevant content from Notion, and returns an AI-generated answer grounded in that content. At a high level, the workflow consists of:
- A public chat webhook that triggers the workflow
- Metadata retrieval from the target Notion database
- Schema normalization for consistent downstream processing
- An AI agent node that coordinates tool calls and reasoning
- Dedicated tools for searching the Notion database and reading page content
The following sections walk through these components in a logical sequence, then cover setup, optimization, and troubleshooting.
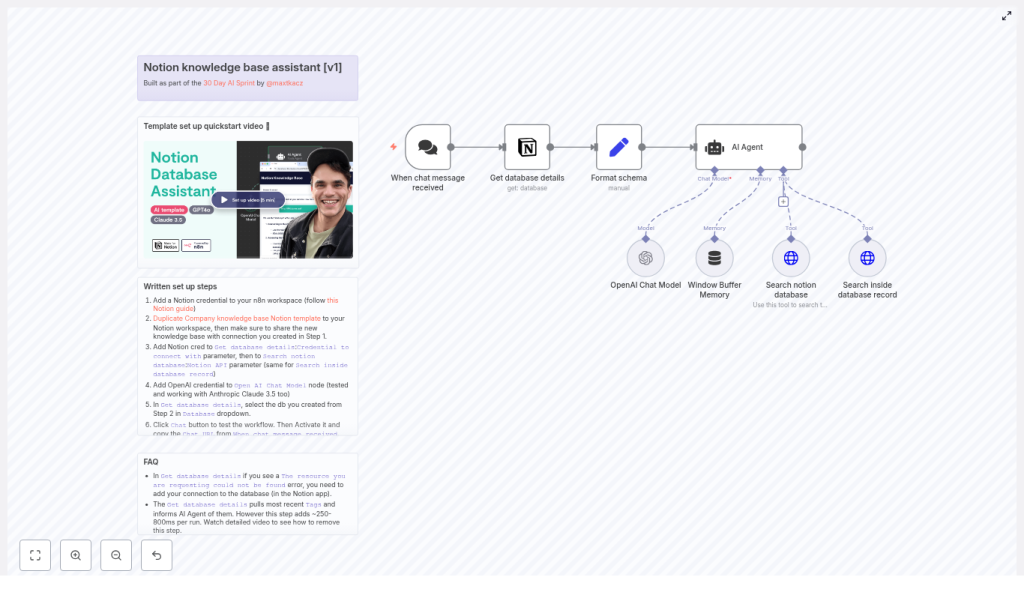
Core workflow components in n8n
1. Chat trigger – entry point for user questions
The workflow begins with a public chat webhook. This node exposes a URL that can be called from a frontend chat widget, Slack command, or any internal tool. It receives the raw user input and passes it into the automation pipeline as the primary question payload.
2. Notion database metadata retrieval
The next stage queries Notion for database metadata. The Get database details node fetches information such as:
- Database ID
- Available properties and tags
- Structural details that inform filtering strategies
This metadata allows the AI agent to understand which fields it can filter on and how the knowledge base is organized. Although this step can be cached for performance, the template runs it on each execution to ensure up-to-date context.
3. Schema formatting and normalization
Before the agent receives the request, a transformation step standardizes the data structure. The Format schema logic ensures that fields such as:
- Session ID
- Action type
- User message text
- Database ID
- Tag options and other metadata
are normalized into a predictable schema. This reduces complexity in the agent node and makes the overall workflow more robust to future changes or additional integrations.
4. AI agent – orchestration and reasoning layer
The central component of the template is an AI agent node that manages when and how to call Notion tools. It receives:
- The normalized user question
- Database metadata and tag information
- Access to two tools:
- Search Notion database
- Search inside database record
The agent is instructed via system prompts to:
- Only answer using content retrieved from Notion
- Be concise and fact-based
- Avoid hallucinating or inventing information
- Include the source Notion page URL when relevant
Based on the question, the agent decides when to search the database, which records to inspect, and how to synthesize the final answer from the retrieved content.
5. Searching the Notion database
The Search Notion database tool interacts with the Notion API to locate candidate pages. In the template, the search strategy typically includes:
- Keyword matching on the question text
- Tag-based filters derived from the database metadata
- An OR relationship between text and tags to allow partial matches
The search returns a ranked or sorted list of relevant pages. The agent then selects the most promising candidates for deeper inspection.
6. Retrieving content from a specific Notion page
Once a candidate record is identified, the Search inside database record tool fetches the full page content, including blocks and child elements. The agent uses this rich text to:
- Extract precise steps or policies
- Build an evidence-based answer
- Attach the direct Notion URL to the response
This approach ensures that the AI output is traceable back to a specific source document, which is critical in enterprise environments.
Step-by-step setup in n8n
To deploy the template in your environment, follow these steps:
- Create a Notion integration
In Notion, create a new integration and grant it access to the database that will serve as your knowledge base. Store the integration token securely, as it will be required for n8n credentials. - Prepare or duplicate the Notion database
If you are using the provided example, duplicate the Notion knowledge base template into your workspace. Confirm that the integration created in step 1 has explicit access to this duplicated database. - Import the n8n workflow template
In your n8n instance, import the Notion knowledge base assistant workflow. Configure Notion credentials for the following nodes:- Get database details
- Search notion database
- Search inside database record
Ensure that all these nodes reference the correct Notion integration and database.
- Connect the AI model
Add an OpenAI or compatible LLM credential to the chat model node used by the agent. The template is designed for GPT-style models. Adjust:- Timeout values to accommodate expected latency
- Temperature to control determinism and creativity (lower values are recommended for knowledge base use cases)
- Test the full chat flow
Use the test chat functionality in n8n to send sample questions. Validate that:- Notion database searches return relevant pages
- Page content is retrieved correctly
- Responses include Notion page URLs when they are used as sources
- Activate and integrate the webhook
Once validated, activate the workflow. Copy the public chat URL from the webhook node and integrate it into your preferred interface, for example:- A custom web chat UI
- Slack or Microsoft Teams bots
- Internal portals or tools
Configuration strategies and best practices
Controlling hallucination and enforcing source grounding
For a production-ready knowledge base assistant, controlling hallucination is essential. In this template:
- System prompts are written to explicitly forbid inventing facts
- The agent is instructed to answer only using content retrieved from Notion
- Responses should always reference the underlying Notion page when a page is used
Periodically review prompts and logs, and refine the system messages if you observe off-source or speculative answers.
Optimizing Notion search filters
Search configuration has a direct impact on answer quality. Recommended practices include:
- Start with broad keyword matching on the question text
- Layer in tag filters or updated date ranges for precision
- Use an OR combination of text and tags, as in the template, to handle partial or imperfect queries
- Iterate filters based on real query logs and missed results
The template provides a baseline search implementation that you can adapt to your specific schema and naming conventions.
Managing performance and cost-sensitive steps
Certain operations can introduce latency or additional cost. In particular:
- Get database details runs on every execution and typically adds around 250-800 ms
- Notion API calls for large pages can be relatively slow
- LLM calls are often the most expensive and time-consuming step
To optimize performance:
- Cache database metadata if live tag updates are not required
- Consider a scheduled workflow to periodically refresh metadata into a static store
- Use lower temperature and appropriate timeouts on the LLM
- Limit the number of pages the agent inspects per query
Example: how the agent responds to a real query
Consider a user asking: “How do I request hardware?”
- The agent triggers a Notion database search for the term “hardware” and any related tags.
- The search tool returns candidate pages, such as a procurement or IT equipment policy document.
- The agent selects the top result and calls the page content tool to retrieve the detailed steps.
- Using the retrieved text, the agent summarizes the process and includes a direct link to the relevant Notion page.
Example (shortened) response:
To request hardware, follow the steps outlined in our procurement process: Notion: Procurement Process. The request form is linked under “Request Hardware” on that page. If needed, I can guide you through the form fields or help you contact the procurement team.
Common errors and troubleshooting
“Resource not found” in Get database details
This error typically indicates that the Notion integration does not have permission to access the target database. To resolve:
- Open the database in Notion
- Share it with the integration used in n8n
- Re-run the workflow and confirm the node can read metadata
No matching records returned from Notion
If the agent cannot find relevant pages:
- Test alternative keywords, including plural and singular forms
- Add synonyms or alternative phrasing to your Notion content and tags
- Review the database filters configured in the search tool
The agent includes fallback strategies, such as trying closely related terms, but high-quality tagging and content structure remain critical.
Slow or inconsistent response times
When performance issues arise, identify which node contributes most to the latency:
- If Get database details is slow, consider caching metadata
- If Notion API calls are slow, review page size and structure
- If the LLM is slow, adjust timeout settings or use a more performant model tier
Monitoring execution times per node in n8n will help you target optimizations effectively.
Extending and hardening the assistant
Once the baseline assistant is stable, you can extend it to cover more use cases and governance requirements:
- Multi-channel access: Connect the chat webhook to Slack, Microsoft Teams, or a custom web interface.
- Role-based access control: Incorporate user identity and permissions so that responses only reference pages the user is allowed to see.
- Analytics and observability: Log queries, response times, top search terms, and unanswered questions to guide documentation improvements.
- Rich content support: Include images or file attachments from Notion pages in responses where appropriate.
Content and operations best practices
- Keep Notion pages concise and structured using headings, lists, and clear sections to improve extractability.
- Apply tags consistently across the database to improve search relevance and filtering.
- Use explicit versioning and updated dates so the agent can prioritize the most recent information.
- Continuously log queries and collect human feedback to refine prompts, filters, and documentation quality.
Conclusion
By combining Notion, n8n, and an AI language model, you can deliver a practical, extensible knowledge base assistant that answers questions with documented facts and verifiable links. The template described here provides a production-ready foundation, including a chat webhook trigger, Notion search tools, schema formatting, and an AI agent that composes grounded responses.
To get started quickly, duplicate the Notion database template if available, connect your Notion and OpenAI credentials in n8n, and test the chat webhook with real queries. Over time, iterate on prompts, search filters, and your Notion structure based on analytics and user feedback.
Next steps
Ready to deploy your Notion AI assistant in production?
- Import the n8n workflow template into your environment
- Connect your Notion and LLM credentials
- Activate the chat webhook and integrate it into your preferred channels
If you require support customizing prompts, adding new integrations such as Slack or email, or implementing analytics, reach out to your automation team or subscribe to ongoing workflow tutorials and best practices.