Build a Production KPI Dashboard with n8n & Vector Search
This reference guide describes a complete n8n workflow template for building a Production KPI Dashboard pipeline. The workflow accepts incoming KPI events via webhook, converts free-text notes or incident logs into embeddings, persists them in a Weaviate vector database, retrieves similar incidents on demand, augments analysis with an LLM, and logs agent output to Google Sheets.
The implementation combines webhook ingestion, text splitting, Cohere embeddings, Weaviate vector storage and search, an OpenAI-based chat agent with memory, and a Google Sheets audit log. The result is a production-ready KPI monitoring and analysis pipeline that supports semantic search and LLM-assisted reasoning.
1. Solution Overview
1.1 Objectives
The workflow is designed for production operations teams that need more than traditional time series dashboards. It enables:
- Context-aware analysis of KPI anomalies using historical incident data
- Similarity search across past events and incident notes
- LLM-powered summarization and root-cause hypotheses
- Lightweight, auditable logging of all automated analyses
1.2 Core Components
The architecture leverages the following services and n8n nodes:
- n8n for low-code orchestration of the entire pipeline
- Cohere (or another embedding provider) to generate vector embeddings from text
- Weaviate as a vector database for fast similarity search
- OpenAI Chat (or a compatible LLM) to reason over retrieved context and current events
- Google Sheets for append-only audit logs and lightweight reporting
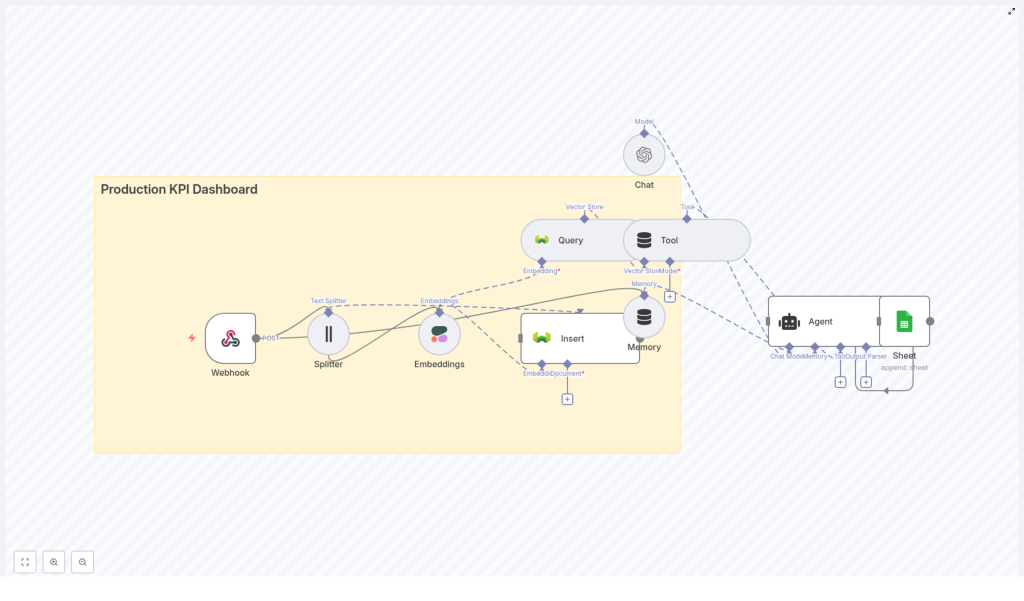
2. High-Level Architecture
The n8n workflow implements the following logical sequence:
- Webhook receives KPI events or free-text notes via HTTP POST.
- Text Splitter breaks longer notes or logs into overlapping chunks.
- Embeddings node calls Cohere to transform each chunk into a dense vector.
- Weaviate Insert node writes vectors and metadata into the
production_kpi_dashboardindex. - Weaviate Query node retrieves semantically similar incidents when analysis is requested.
- Tool node exposes vector search as a callable tool to the LLM Agent.
- Memory node maintains a buffer of recent interactions for multi-turn context.
- Chat node (OpenAI) provides the LLM used by the Agent.
- Agent orchestrates tool calls, uses memory, and composes responses.
- Google Sheets node appends an audit log of each analysis and recommendation.
This architecture supports both continuous ingestion of KPI events and on-demand querying of historical incidents, with the LLM acting as a reasoning layer over vector search results and current event data.
3. Data Flow and Payload Structure
3.1 Inbound KPI Payload
The entry point is an n8n Webhook node that accepts JSON payloads via HTTP POST on a dedicated path. Example payload:
{ "timestamp": "2025-10-15T14:23:00Z", "source": "line-7-packaging", "kpi": "throughput", "value": 420, "notes": "Line slowed due to jam; manual restart at 14:18"
}
Key fields:
timestamp– ISO 8601 timestamp for the event.source– Identifier for the machine, line, or subsystem.kpi– KPI name such as throughput, scrap rate, OEE, etc.value– Numeric KPI value at the given time.notes– Free-text description or incident log associated with the event.
The workflow assumes the presence of these fields for metadata enrichment. If your schema differs, you can adapt the mapping in the nodes that follow, especially the Embeddings and Weaviate Insert nodes.
4. Node-by-Node Breakdown
4.1 Webhook Node
Purpose
Expose an HTTP endpoint that receives KPI events in JSON format and triggers the pipeline for each POST request.
Key Configuration
- HTTP Method:
POST - Path:
production_kpi_dashboard(for example/webhook/production_kpi_dashboard) - Response: Typically a simple acknowledgment (for example a JSON success flag) to confirm receipt.
Behavior & Edge Cases
- Ensure the webhook is set to production mode in n8n before exposing it externally.
- On upstream retries (for example from monitoring systems), you may receive duplicate payloads. Idempotency considerations are handled later via metadata or document IDs in Weaviate.
- Validate JSON structure at this stage if your downstream nodes assume specific fields. You can add a simple validation or IF node between Webhook and Splitter for stricter schemas.
4.2 Text Splitter Node
Purpose
Chunk free-text notes or incident logs into segments that are suitable for embedding and vector search.
Suggested Configuration
- Splitter type: Character-based text splitter
- chunkSize:
400 - chunkOverlap:
40
These values keep each chunk compact for embedding model limits while preserving local context via overlap. Adjust them based on your typical note length and embedding provider constraints.
Input & Output
- Input text: Typically the
notesfield from the webhook payload. - Output: An item per chunk, each containing the chunk text and any copied metadata (for example timestamp, source, kpi).
Considerations
- If
notesis empty or very short, the splitter will yield a single chunk. The workflow still proceeds, and vector search remains valid, just with fewer documents. - For multi-paragraph incident reports, character-based splitting avoids splitting mid-word but may still split mid-sentence. Increase overlap if sentence continuity is critical for your use case.
4.3 Embeddings Node (Cohere)
Purpose
Transform each text chunk into a dense vector representation using Cohere or another supported embedding provider.
Key Configuration
- Provider: Cohere (via the n8n Embeddings node)
- Model: Choose a Cohere embedding model that fits your cost and quality requirements.
- Input: Chunk text from the Splitter node.
Metadata Handling
Alongside the embedding vector, store the following metadata for each chunk:
timestampsourcekpioriginal_text(full notes or original content if needed)chunk_index(position of the chunk in the original text)
This metadata is critical for downstream filtering in Weaviate. It enables queries such as:
- Filter by machine or line (
source) - Filter by KPI type (
kpi) - Restrict to a time window (
timestamp)
Error Handling
- Embedding API calls may fail due to rate limits or transient errors. In n8n, configure retry logic or wrap the Embeddings node with error handling to implement backoff.
- If an embedding call fails for a single chunk, you can either drop that chunk or mark it with an error flag in metadata and continue processing others.
4.4 Weaviate Insert Node
Purpose
Persist embeddings and associated metadata in a Weaviate vector index for later similarity search.
Index Configuration
- Target class / index name:
production_kpi_dashboard - Mode: Insert (create new objects)
Schema Considerations
In Weaviate, define a class that includes at least the following properties:
source– stringkpi– stringtimestamp– date/timeraw_text– string (optional if you choose to store raw text)chunk_index– integer
Enable text plus vector search as appropriate for your Weaviate deployment. The n8n Insert node will map embeddings and metadata fields into this schema.
Idempotency & Duplicates
- To avoid inserting the same event multiple times (for example due to webhook retries), consider including a deterministic
documentIdor checksum in the metadata and use it as a unique identifier in Weaviate. - If you do not enforce uniqueness, repeated inserts will create multiple similar objects that may appear in search results.
4.5 Weaviate Query Node & Tool Node
Purpose
Provide semantic search over stored incidents and expose this search capability as a tool to the LLM Agent.
Weaviate Query Node
- Input: A search query or vector, typically derived from the current KPI event or user prompt.
- Operation: Similarity search against the
production_kpi_dashboardindex. - Filters: Optional filters on metadata such as
source,kpi, ortimestamp.
Example usage scenario: A user or automated system asks, “Why did throughput drop on line 7 yesterday?”. The query node retrieves historical incidents with similar descriptions or metrics from line 7 around the relevant time window.
Tool Node
- Purpose: Wrap the Weaviate query capability as a tool so that the Agent can invoke it dynamically during reasoning.
- Integration: The Tool node is configured to call the Weaviate Query node and return results in a format the LLM can consume (for example JSON text with relevant fields).
Behavior
- The Agent decides when to call the tool based on the prompt and its internal reasoning.
- Retrieved passages (such as
raw_textand associated metadata) are included in the Agent context for final answer generation.
4.6 Memory Node
Purpose
Maintain short-term conversational context for multi-turn analysis and follow-up questions.
Configuration
- Memory type: Buffer window memory (commonly used for recent message history).
- Scope: Store recent user queries, Agent responses, and relevant tool outputs.
Usage
- When operators ask follow-up questions like “Compare that with last week” or “What changed after the last maintenance?”, the Memory node provides the necessary context so the Agent does not lose track of previous steps.
4.7 Chat Node & Agent
Chat Node (OpenAI)
- Provider: OpenAI Chat (or compatible LLM)
- Role: Base language model used by the Agent for reasoning and response generation.
Agent Orchestration
The Agent sits on top of the Chat node and coordinates:
- Calls to the Weaviate Tool for vector search
- Use of Memory for recent context
- Construction of the final natural language response
Typical Agent Capabilities
- Query the vector store for similar incidents given a new KPI event
- Summarize retrieved incidents and highlight patterns
- Propose root-cause hypotheses and remediation steps
- Generate human-friendly summaries for shift handovers or reports
Example Prompt Template
A simplified system and user prompt configuration might look like:
System: You are an operations analyst. Use the provided context to explain KPI anomalies.
User: Analyze the following KPI event and find similar incidents. Provide root-cause hypotheses and an action list.
Context: {{weaviate_results}} \nEvent: {{event_json}}
In the actual n8n configuration, {{weaviate_results}} and {{event_json}} are populated using expression syntax, pulling data from the Weaviate Query node and the original webhook payload.
4.8 Google Sheets Logging Node
Purpose
Append an audit record for each Agent response so that operations teams and stakeholders can review historical analyses and recommendations.
Configuration
- Mode: Append
- Target: A dedicated Google Sheet used as an audit log
Suggested Columns
timestamp– Time of the analysis or Agent responsequery– Original user query or event descriptionsummary– Agent-generated summary of the situationrecommended_actions– Proposed remediation stepsevent_linkorraw_event– Reference to the original KPI event
Google Sheets is suitable for lightweight reporting and can be easily integrated with BI tools or exported for further analysis.
5. Configuration & Deployment Notes
5.1 Credentials & Secrets
- Store all API keys (Cohere, Weaviate, OpenAI, Google) in n8n Credentials, not in node parameters or code.
- Restrict access to credentials to only the workflows and users that require them.
5.2 Weaviate Schema
- Define a class (for example
production_kpi_dashboard) with fields forsource,kpi,timestamp,raw_text, andchunk_index. - Enable hybrid or vector search as supported by your Weaviate deployment to combine metadata filtering with vector similarity.
5.3 Chunking Strategy
- Start with
chunkSize = 400andchunkOverlap = 40, then adjust based on average note length and embedding token limits. - For very long incident logs, consider smaller chunk sizes to reduce per-request token usage at the cost of slightly more fragmentation.
5.4 Rate Limiting & Retries
- Embedding and LLM APIs may throttle requests. Configure n8n retry policies or add dedicated error-handling branches