Build a Visa Requirement Checker with n8n, LangChain & Weaviate
This guide walks you through building a practical, AI-powered Visa Requirement Checker using n8n as the automation layer, Cohere for embeddings, Weaviate as a vector database, an LLM chat model for reasoning, and Google Sheets for logging. You will learn how to go from raw visa policy documents to a working workflow that answers traveler questions and keeps an auditable history of responses.
What You Will Learn
By the end of this tutorial, you will be able to:
- Design an n8n workflow that responds to visa questions via a webhook
- Split long visa policy documents into chunks suitable for embeddings
- Create and store Cohere embeddings in a Weaviate vector store
- Query Weaviate to retrieve relevant policy snippets using semantic search
- Use an LLM-based agent with memory to generate clear, policy-backed answers
- Log every query and answer to Google Sheets for audits and analytics
- Apply best practices for metadata, chunking, security, and scaling
Why Build a Visa Requirement Checker?
Visa rules change frequently and depend on many variables, such as:
- Traveler nationality
- Destination country
- Passport type
- Reason for travel
- Planned length of stay
Manually checking embassy websites or internal documents does not scale, especially for support teams that handle many similar questions. An automated Visa Requirement Checker built on n8n helps you:
- Provide consistent, fast answers to travelers and internal agents
- Reduce repetitive manual research
- Maintain a clear audit trail of what was answered and why
- Combine structured filters (such as nationality) with semantic understanding of policy text
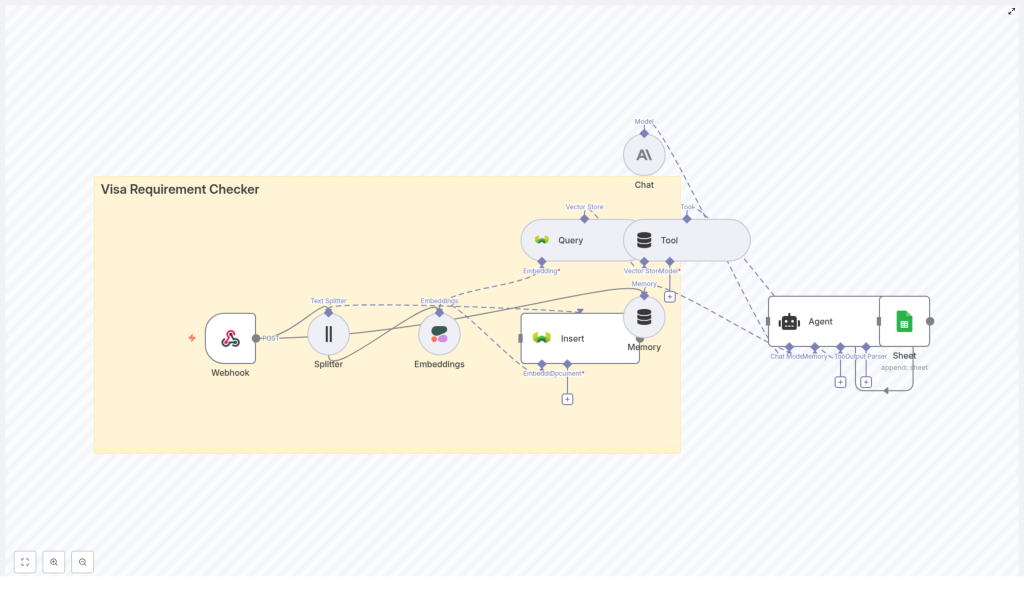
Conceptual Architecture
Before we configure nodes in n8n, it helps to understand how the main components work together. At a high level, the system follows this flow:
- A client (UI or API) sends a POST request with traveler details to an n8n webhook.
- Policy documents are preprocessed: split into chunks, embedded with Cohere, and stored in Weaviate with metadata.
- For each incoming question, the workflow embeds the query and searches Weaviate for relevant chunks.
- An LLM-based agent receives the retrieved context, uses memory for multi-turn conversations, and crafts an answer.
- The workflow logs the query and response to Google Sheets for compliance and analytics.
Main Components
- Webhook (n8n) – entry point that receives POST requests from your application or frontend
- Text Splitter – breaks long visa policy documents into manageable chunks
- Embeddings (Cohere) – converts text chunks into numerical vectors
- Weaviate Vector Store – stores vectors with metadata and supports semantic and hybrid search
- Agent + Chat model (Anthropic or similar) – uses retrieved context to reason and answer questions
- Memory – keeps short-term conversation history for multi-step interactions
- Google Sheets – append-only log of questions, answers, and key details
Step-by-Step n8n Workflow Guide
In this section, we will walk through the main workflow in n8n, from the incoming request to the final logged response.
Step 1 – Configure the Webhook Node
The webhook is the public entry point into your Visa Requirement Checker.
- Node: Webhook
- Method: POST
- Path:
visa_requirement_checker
The payload should include all the attributes the model needs to reason about visa rules. A typical JSON body might look like:
{ "nationality": "India", "destination": "Germany", "passport_type": "Regular", "travel_reason": "Tourism", "stay_duration_days": 10
}
You can add more fields as needed, but avoid sending sensitive identifiers like passport numbers into the vector database or logs.
Step 2 – Prepare and Split Visa Policy Documents
Before you can answer questions, you must ingest your policy sources (for example embassy pages, official PDFs, or internal guidelines). This is usually done in a separate preprocessing workflow, but the logic is the same:
- Collect raw text from policy documents.
- Send the text into a Text Splitter node.
Typical configuration for the splitter:
- chunkSize: 400 characters
- chunkOverlap: 40 characters
Chunking helps:
- Stay within embedding token limits
- Improve retrieval quality by focusing on smaller, relevant passages
- Avoid missing context by keeping a small overlap between chunks
Step 3 – Generate Embeddings with Cohere
Each chunk from the splitter is passed to an Embeddings node.
- Node: Embeddings
- Model: cohere (configure with your Cohere API key)
The node converts each text chunk into a vector representation. Along with the vector, it is crucial to attach metadata that will help with filtering later. Typical metadata fields include:
- Country or region (for example
Germany) - Traveler nationality or group, if applicable
- Document type (for example embassy policy, bilateral agreement)
- Source URL or document ID
- Effective date or last updated date
- Language
This metadata is stored together with the vector in Weaviate and becomes very important for precise retrieval.
Step 4 – Insert Vectors into Weaviate
Once you have embeddings and metadata, you can store them in a Weaviate index.
- Node: Weaviate Insert
- indexName:
visa_requirement_checker
Weaviate acts as your semantic knowledge base. It supports:
- Similarity search using embeddings
- Metadata filters (for example
country = "Germany") - Hybrid queries that combine keyword and semantic search
For a visa checker, hybrid and filtered searches are very helpful, for example:
- Filter by
destination_country = "Germany" - Filter by
nationality = "India"when policies differ by origin - Filter by
effective_dateto avoid outdated rules
Step 5 – Query Weaviate When a Question Arrives
When the webhook receives a new query, you need to search Weaviate for relevant policy chunks.
- Take the traveler question and context from the webhook payload.
- Generate an embedding for that question using the same Cohere model used for document embeddings.
- Use a Weaviate Query node to perform a semantic search against the
visa_requirement_checkerindex.
- Node: Weaviate Query
- indexName:
visa_requirement_checker
Combine the query embedding with metadata filters. For example, you might filter on:
destination_country = "Germany"traveler_nationality = "India"effective_date <= today
The query returns the top matching chunks, which you pass to the agent as a tool or context input. These chunks act as evidence for the final answer.
Step 6 – Add Memory and a Chat Model
Many visa conversations are multi-step. The traveler might ask follow-up questions like:
- “What about business travel instead of tourism?”
- “Does this apply to multiple entries?”
To handle this, you attach a memory component to your chat model so it can reference previous turns.
- Node: Chat (LLM)
- Model: Anthropic or another chat LLM
The chat model receives:
- The traveler question and attributes from the webhook
- The retrieved policy chunks from Weaviate
- The conversation history from the memory buffer
Its job is to generate a clear, policy-backed response. You can instruct the model to cite specific documents or chunks when needed, and to be explicit about uncertainty.
Step 7 – Orchestrate with an Agent and Log to Google Sheets
The Agent node coordinates tool calls (such as Weaviate search) and parses the final response into a structured format.
After the agent produces an answer, you log the interaction:
- Node: Google Sheets
- operation: append
- documentId:
SHEET_ID - sheetName:
Log
Typical fields to log include:
- Timestamp
- Nationality, destination, passport type, travel reason, stay duration
- Original question text
- Model verdict (visa required or visa-free)
- Short explanation
- Confidence score
- References or URLs used
This creates an audit trail that can be reviewed for quality, compliance, and analytics.
Sample Response Format for the Agent
To make downstream processing easier, design the agent to return a structured JSON object. For example:
- Verdict (visa required or visa-free)
- Short explanation
- Relevant citations with titles, excerpts, and URLs
- Confidence score
- Recommended next steps
{ "verdict": "Visa required", "explanation": "Holders of Indian passports require a Schengen visa for stays over 90 days.", "citations": [ {"title": "German Embassy Policy", "url": "https://...", "excerpt": "Visitors from India require..."} ], "confidence": 0.89, "next_steps": "Apply at the nearest German embassy or consulate."
}
You can then log this JSON directly to Google Sheets or transform it into another format for your frontend.
Key Configuration Summary
Here is a quick reference of important node settings so you can map them into your own n8n instance:
- Webhook node:
method = POST,path = visa_requirement_checker - Text Splitter node:
chunkSize = 400,chunkOverlap = 40 - Embeddings node:
model = cohere, with Cohere API credentials - Weaviate Insert/Query nodes:
indexName = visa_requirement_checker - Chat node:
model = Anthropicor another chat LLM - Google Sheets node:
operation = append,documentId = SHEET_ID,sheetName = Log
Best Practices for Accurate Visa Automation
Use Rich Metadata
Metadata is one of your strongest tools for improving accuracy. For each vector, include fields such as:
- Destination country
- Relevant nationality or traveler category
- Document type (policy, FAQ, legal text)
- Effective date and expiry date if applicable
- Language and jurisdiction
Rich metadata helps prevent “cross-country policy leakage”, where rules for one country are mistakenly applied to another.
Choose Chunk Size Carefully
Chunk size affects both performance and quality:
- Around 400 characters with 40 character overlap is a good starting point.
- Smaller chunks can give more targeted retrieval but may lose context.
- Larger chunks can preserve context but increase embedding cost and may mix unrelated rules.
Experiment with chunk sizes and evaluate retrieval relevance on real visa queries.
Combine Semantic and Exact Filters
Hybrid search is powerful for visa rules because you often know some exact attributes in advance. Combine:
- Semantic similarity on the question text
- Filters like
nationality,destination_country,passport_type, andeffective_date
This reduces the chance of retrieving unrelated but semantically similar text.
Promote Safety and Truthfulness
Visa decisions can have serious consequences. Encourage safe behavior by:
- Including references or citations with each answer
- Providing a confidence score when possible
- Advising users to confirm critical decisions with an official consulate or embassy, especially when the model is uncertain
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Low Relevance or Incorrect Results
If the answers do not match the expected visa rules, check the following:
- Embedding model consistency: Ensure you use the same Cohere embedding model for both insertion and query. Mixing models usually degrades performance.
- Metadata filters: Add or tighten filters such as country, nationality, and date ranges to narrow down the candidate set.
- Chunking strategy: Try different chunk sizes or overlaps. Very small or very large chunks can cause irrelevant retrieval.
Rate Limits and Cost Management
Embedding and chat model calls often dominate cost. To keep this under control:
- Cache embeddings for frequently asked questions or common country combinations.
- Batch vector inserts instead of sending each chunk individually.
- Use caching with a time-to-live (TTL) for popular answers to reduce repeated LLM calls.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Visa data can be sensitive, especially when it includes personal identifiers. Follow these guidelines:
- Store only non-sensitive information in vector stores and logs.
- Avoid embedding or logging passport numbers,