Overview
This documentation-style guide describes a production-ready n8n image captioning workflow template that integrates OpenAI embeddings, a Weaviate vector database, a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) agent, and downstream integrations for Google Sheets logging and Slack error alerts. The workflow is designed for teams that need scalable, context-aware, and searchable image captions, for example to improve alt text accessibility, auto-tag large image libraries, or enrich metadata for internal search.
The template focuses on text-centric processing. Images are typically pre-processed outside of n8n (for example via OCR or a vision model), and the resulting textual description is sent into the workflow, where it is chunked, embedded, indexed in Weaviate, and then used as context for caption generation via a RAG pattern.
High-level Architecture
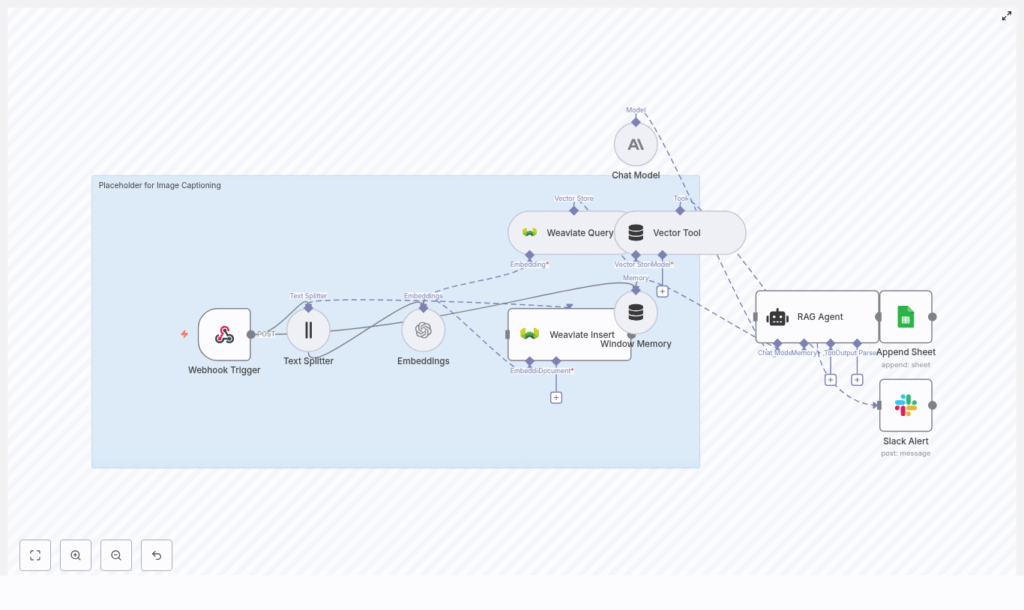
The workflow is organized into several logical stages, each implemented with one or more n8n nodes:
- Ingress: Webhook Trigger node that receives image-related payloads (ID, URL, OCR text, metadata).
- Pre-processing: Text Splitter node that chunks long text into smaller segments.
- Vectorization: Embeddings node (OpenAI
text-embedding-3-small) that converts text chunks into dense vectors. - Persistence & Retrieval: Weaviate Insert and Weaviate Query nodes that store and retrieve embeddings for semantic search.
- RAG Context: Window Memory node plus a Vector Tool that provide short-term conversation history and external vector context to the RAG agent.
- Caption Generation: Chat Model node (Anthropic) combined with a RAG Agent that synthesizes final captions.
- Logging: Google Sheets Append node that records generated captions and status for audit and review.
- Monitoring: Slack node that sends error alerts to a specified channel.
This pattern combines long-term vector storage with retrieval-augmented generation, which allows captions to be both context-aware and scalable across large image collections.
Use Cases & Rationale
The workflow is suitable for:
- Enriching or generating alt text for accessibility.
- Creating concise and extended captions for social media or content management systems.
- Auto-tagging and metadata enrichment for digital asset management.
- Building a searchable corpus of image descriptions using vector search.
By indexing OCR text or other descriptive content in Weaviate, you can later perform semantic queries to retrieve related images, then use the RAG agent to generate or refine captions with awareness of similar content and prior context.
Data Flow Summary
- Client sends a POST request with image identifiers and text (for example, OCR output) to the Webhook Trigger.
- The text is split into overlapping chunks by the Text Splitter node.
- Each chunk is embedded via the OpenAI Embeddings node.
- Resulting vectors and associated metadata are inserted into Weaviate using the Weaviate Insert node.
- When generating or refining a caption, the workflow queries Weaviate for similar chunks via the Weaviate Query node.
- The Vector Tool exposes the retrieved chunks to the RAG agent, while Window Memory provides short-term conversational context.
- The Chat Model (Anthropic) and RAG Agent synthesize a concise alt-text caption and a longer descriptive caption.
- Results are appended to a Google Sheet for logging, and any errors trigger a Slack alert.
Node-by-Node Breakdown
1. Webhook Trigger
Node type: Webhook
Purpose: Entry point for image-related data.
Configure the Webhook node to accept POST requests at a path such as /image-captioning. The incoming JSON payload can include an image identifier, optional URL, OCR text, and metadata. A typical payload structure is:
{ "image_id": "img_12345", "image_url": "https://.../image.jpg", "ocr_text": "A woman walking a dog in a park on a sunny day", "metadata": { "source": "app-upload", "user_id": "u_789" }
}
Recommended pattern:
- Perform heavy compute tasks (OCR, vision models) outside n8n (for example in a separate service or batch job).
- Post only the resulting text and metadata to this webhook to keep the workflow responsive and resource-light.
Security considerations:
- Protect the endpoint using HMAC signatures, API keys, or an IP allowlist.
- Validate payload structure and required fields (for example,
image_idandocr_textor equivalent text field) before further processing.
2. Text Splitter
Node type: Text Splitter (CharacterTextSplitter)
Purpose: Break long text into smaller, overlapping chunks for more stable embeddings.
Configure the Text Splitter with parameters similar to:
chunkSize = 400chunkOverlap = 40
This configuration keeps each chunk small enough for efficient embedding while preserving local context via overlap. It is particularly useful when OCR output or metadata descriptions are long, or when you want to index multiple descriptive sections per image.
Edge cases:
- If the incoming text is shorter than
chunkSize, the node will output a single chunk. - Empty or whitespace-only text will result in no meaningful chunks, which will later cause empty embeddings; handle this case explicitly if needed.
3. Embeddings (OpenAI)
Node type: OpenAI Embeddings
Purpose: Convert each text chunk into a numeric vector representation.
In the template, the Embeddings node is configured to use the OpenAI model:
model = text-embedding-3-small
Configuration notes:
- Store OpenAI API credentials securely using n8n Credentials and reference them in this node.
- Ensure that the embedding dimensionality expected by Weaviate matches the chosen model (for example, schema vector dimension must be consistent with
text-embedding-3-small). - Handle API errors gracefully, for example by using n8n error workflows or by routing failed items to a Slack alert.
Common issues:
- If the input text is empty or non-informative (for example, placeholders), embeddings may be unhelpful or empty. Validate input upstream.
- Rate limits from OpenAI can cause transient failures. Consider adding retries or backoff logic via n8n error handling.
4. Weaviate Insert
Node type: Weaviate Insert
Purpose: Persist embeddings and associated metadata into a Weaviate index for later semantic retrieval.
Configure a Weaviate class (index) such as image_captioning with fields like:
image_id(string)chunk_text(text)metadata(object/map)embedding(vector) – typically handled as the object vector in Weaviate
The Weaviate Insert node should map the embedding output and metadata from the previous nodes into this schema.
Best practices:
- Use batch insertion where available to reduce API overhead and improve throughput.
- Include provenance in
metadata, such asuser_id,source, and timestamps, so you can filter or re-rank results later.
Error handling:
- If inserts fail, verify that:
- The class schema exists and is correctly configured.
- The vector dimensionality matches the OpenAI embedding model.
- Authentication and endpoint configuration for Weaviate are correct.
5. Weaviate Query & Vector Tool
Node types: Weaviate Query, Vector Tool
Purpose: Retrieve semantically similar chunks and expose them as a tool to the RAG agent.
For caption generation, the workflow queries Weaviate to fetch the most relevant chunks based on a query vector or query text. Typical parameters include:
indexName = image_captioningtop_k = 5(number of similar chunks to retrieve)
The retrieved results are passed into a Vector Tool, which the RAG agent can invoke to obtain external context during generation.
Filtering and precision:
- If you see too many unrelated or overly similar results, add metadata-based filters (for example, filter by
image_id,source, or time ranges) to narrow the search space. - Adjust
top_kto balance recall vs. noise. Higher values give more context but can introduce irrelevant chunks.
6. Window Memory
Node type: Window Memory
Purpose: Maintain short-term conversational context for the RAG agent across multiple turns.
The Window Memory node stores a limited window of recent exchanges, which is especially useful in session-based flows where a user iteratively refines captions or requests variations. This context is provided alongside the retrieved vector data to the RAG agent.
Usage notes:
- Tune the memory window size based on your typical conversation length and token budget.
- For single-shot caption generation, memory impact will be minimal but still safe to keep for future extensibility.
7. Chat Model & RAG Agent
Node types: Chat Model (Anthropic), RAG Agent
Purpose: Use a large language model with retrieval-augmented context to generate final captions.
The template uses Anthropic as the chat model backend. The RAG agent is configured with a system message similar to:
“You are an assistant for Image Captioning”
The agent receives three main inputs:
- Window Memory (short-term conversational context).
- Vector Tool results (retrieved chunks from Weaviate).
- The current user instruction or prompt.
Using these, it composes:
- A short, alt-text-style caption.
- A longer descriptive caption suitable for metadata or search enrichment.
Prompt template example:
System: You are an assistant for Image Captioning. Use the retrieved context and memory to produce a single concise descriptive caption.
User: Given the following context chunks:
{retrieved_chunks}
Produce (1) a short caption suitable for alt text (max 125 chars) and
(2) a longer descriptive caption for metadata (2-3 sentences).
Quality tuning:
- If captions are too generic, strengthen the system message or include more explicit formatting and content instructions.
- If important details are missing, increase
top_kin Weaviate Query or adjust chunking parameters to preserve more context.
8. Google Sheets Append
Node type: Google Sheets (Append Sheet)
Purpose: Persist caption results and status for auditing, QA, or manual review.
Configure the Append Sheet node to target a specific SHEET_ID and sheet name (for example, Log). Typical columns include:
image_idcaption(or separate columns for short and long captions)status(for example,success,failed)timestamp
Notes:
- Ensure Google credentials are set via n8n Credentials and that the service account or user has write access to the target sheet.
- Use this log as a source for manual review, A/B testing of prompts, or backfilling improved captions later.
9. Slack Alert for Errors
Node type: Slack
Purpose: Notify operations or development teams when the workflow encounters errors.
Configure the Slack node to send messages to an alerts channel, for example #alerts. Use the node error message placeholder to include details, such as:
{$json.error.message}
This helps you quickly detect and respond to issues like API rate limits, Weaviate outages, or schema mismatches.
Configuration & Credentials
Core Credentials
- OpenAI: API key configured in n8n Credentials, used by the Embeddings node.
- Anthropic: API key configured for the Chat Model node.
- Weaviate: Endpoint, API key or authentication token configured for Insert and Query nodes.
- Google Sheets: OAuth or service account credentials for the Append Sheet node.
- Slack: OAuth token or webhook URL for sending alerts.
Webhook & Security
- Use HTTPS for the webhook URL.
- Validate signatures or API keys on incoming requests.
- Sanitize text inputs to avoid injection into prompts or logs.
Practical Tips & Best Practices
- Offload heavy compute: Run OCR and vision models outside n8n and send only text payloads to the webhook to keep the workflow lightweight.
- Optimize chunking: Tune
chunkSizeandchunkOverlapbased on typical text length. Larger chunks capture more context but can dilute vector specificity. - Metadata usage: Store provenance (user, source, timestamps) in Weaviate metadata to enable targeted queries and analytics.
- Monitoring Weaviate: Track health, latency, and storage usage. Plan capacity for expected vector counts and query load.
- Rate limiting: Respect OpenAI and Anthropic rate limits. Implement retry or exponential backoff strategies using n8n error workflows or node-level settings.
- Accessibility focus: When captions are used as alt text, favor clear, factual descriptions over creative language.
Troubleshooting Guide
- Empty or missing embeddings:
- Confirm that
ocr_textor equivalent input text is not empty. - Check that the Text Splitter is producing at least one chunk.
- Confirm that
- Poor caption quality:
- Increase
top_kin the Weaviate Query node to provide more context. - Refine the RAG agent system prompt with clearer instructions and examples.
- Increase
- Weaviate insert failures:
- Verify that the class schema fields and vector dimension match the embedding model.
- Check authentication, endpoint configuration, and any network restrictions.
- Slow performance:
- Batch inserts into Weaviate where possible.
- Use asynchronous processing so the webhook can acknowledge requests quickly and offload work to background jobs.
- Too many similar or irrelevant results: