Build an NDA Risk Detector with n8n & LangChain
Imagine never having to manually scan every NDA line by line again. With a smart NDA risk detector built on n8n and LangChain, you can quickly spot risky clauses, log them for audit, and keep your legal team focused on the tricky edge cases instead of the boring repetitive work.
In this guide, we will walk through a production-ready n8n workflow template that ties together:
- n8n for orchestration and automation
- LangChain components for document handling
- Hugging Face embeddings for semantic understanding
- Redis as a vector store for fast search
- OpenAI for clause analysis and suggestions
- Google Sheets for logging and auditing
We will keep all the technical bits accurate, but explain them in a more conversational way so you can actually picture how this fits into your day-to-day work.
When does an NDA risk detector make sense?
If you are dealing with NDAs on a regular basis, you probably know this pattern:
- Sales or partnerships send over yet another NDA.
- Legal gets pulled in to check if anything looks off.
- Everyone waits while someone reads dense legal text.
It is not that every NDA is dangerous, it is that you cannot afford to miss the few that are. That is where automation helps. An NDA risk detector built with n8n and LangChain is especially useful if you:
- Receive a high volume of NDAs from partners, vendors, or customers.
- Have limited legal bandwidth and need a fast triage step.
- Want a structured record of what was flagged, when, and why.
This workflow will:
- Highlight potentially risky clauses, such as:
- Overly broad definitions of confidential information
- Indefinite confidentiality terms
- Restrictive IP or assignment clauses
- Pull out the exact text of the clause and its context so a human can review it quickly.
- Log every analysis into Google Sheets for audit trails and trend analysis.
It will not replace legal review, but it will get you from “no idea what is in this NDA” to “here are the clauses we should actually care about” in seconds.
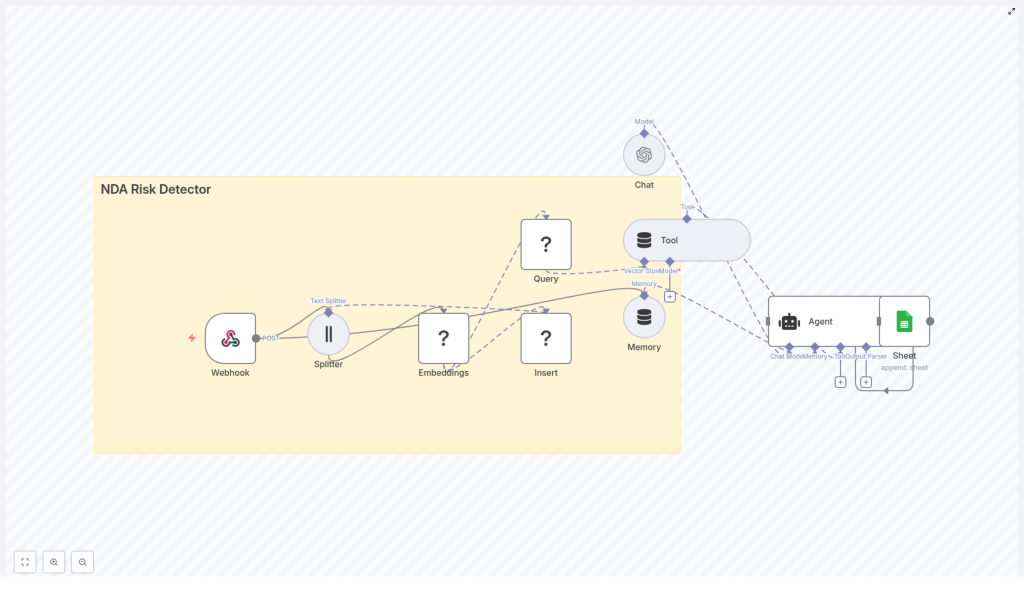
High-level view of the n8n NDA workflow
Before we dive into each step, here is what the template does end to end:
- Webhook (n8n) – receives the NDA text via POST.
- Text Splitter – breaks the document into overlapping chunks.
- Embeddings (Hugging Face) – turns each chunk into a semantic vector.
- Insert (Redis Vector Store) – stores those vectors in a Redis index called nda_risk_detector.
- Query & Tool – semantically searches the Redis index for similar risky clauses.
- Memory (buffer) – gives the agent short-term memory of recent context.
- Chat (OpenAI) + Agent – analyzes the retrieved chunks, scores the risk, and suggests remediation.
- Google Sheets – appends a row with all the findings for each NDA.
Think of it as: “capture NDA input, break it down, understand it semantically, compare it with risky patterns, ask an LLM for a judgment, then log everything.”
Step-by-step: how the NDA workflow runs in n8n
1. Capture the NDA with a Webhook
Everything starts with the Webhook node in n8n. It accepts a POST request that contains either:
- The raw NDA text, or
- A link to the document that you fetch and convert to text upstream
This makes it easy to plug into whatever you already use. You can send NDAs from:
- Web forms
- Email parsers
- CRM or contract tools
- Other automations in your stack
The Webhook centralizes all NDA intake in one consistent entry point.
2. Split the NDA into workable chunks
Long legal documents are hard to process as one piece. The Text Splitter node solves this by breaking the NDA into overlapping segments, using character-based chunking with:
- chunkSize = 400
- chunkOverlap = 40
Why does this matter? Chunking:
- Keeps each piece short enough for embedding models and LLM context limits.
- Preserves continuity between clauses with a small overlap so you do not lose context mid-sentence.
The result is a list of text chunks that still feel like coherent clauses, not random fragments.
3. Turn chunks into embeddings with Hugging Face
Next, each chunk goes into the Embeddings node, which uses a Hugging Face model in this template.
Embeddings turn text into numeric vectors that capture meaning. Instead of comparing strings literally, you can now search based on semantic similarity, such as “this clause feels like that other risky clause we saw before.”
These vectors are what we will store and search later in Redis.
4. Store vectors in a Redis vector index
The Insert node writes each embedding to a Redis vector store, under the index name nda_risk_detector.
Redis is a great fit here because it is:
- Fast enough for real-time or near real-time semantic search.
- Cost-effective and battle-tested in production environments.
Along with the vector itself, you should store helpful metadata such as:
- Source document ID or name
- Chunk position or index
- The original text of the chunk
This metadata makes it easier to trace findings back to the exact place in the NDA later.
5. Retrieve the most relevant chunks via semantic search
When you analyze a new NDA or a specific clause, the Query node performs a semantic search against the nda_risk_detector Redis index.
It returns the top chunks that are most similar to your input. That means you can:
- Compare new clauses against previously flagged risky ones.
- Leverage your growing corpus of examples to improve detection over time.
The Query node feeds these retrieved chunks into the downstream Agent as context, so the language model is not starting from scratch every time. It already sees patterns that look similar to known risks.
6. Analyze risk using an Agent with memory
This is where the intelligence comes together. The workflow wires up:
- The Redis Tool and similarity search results
- A Memory buffer that stores recent context
- An Agent node that uses an OpenAI Chat model
The Agent receives:
- The retrieved chunks from Redis
- Any relevant recent interactions from the Memory buffer
- The NDA text or clause that you want to evaluate (passed in via
$jsonin this workflow)
Based on a carefully designed prompt, the Agent should:
- Classify the risk level for each clause as High, Medium, or Low.
- Extract the exact risky clause text and its location if available.
- Explain in plain language why the clause is risky.
- Propose concise remediation language your legal team could use in negotiations.
This turns raw text into structured, actionable insights that your team can actually use.
7. Log every NDA analysis into Google Sheets
Finally, the workflow hands the Agent’s output to a Google Sheets node, which appends a new row for each analyzed NDA.
A typical row might include:
- Timestamp
- Document ID or name
- Risk level
- Extracted clause or clause excerpt
- Suggested remediation
- Optional reviewer notes
Over time, this gives you:
- An audit trail for compliance and internal review
- Data you can analyze to see which risks show up most often
- A simple way for non-technical stakeholders to monitor the system
Designing an effective prompt for the Agent
The quality of your NDA risk detector depends heavily on the prompt you give the Agent. Here is an example prompt used in this workflow that you can adapt:
You are a legal-tech assistant. Given the NDA clause(s) below and any context, do the following:
1) Classify each clause as High / Medium / Low risk (HIGH = likely blocks signing without legal review).
2) Extract the exact clause text.
3) Provide a one-sentence explanation of the risk.
4) Suggest remediation language (concise).
Return JSON with fields: risk_level, clause_text, explanation, suggestion.
Context: {{retrieved_chunks}}
Clause to evaluate: {{clause_or_full_text}}
A few practical tips:
- Keep the instructions deterministic. Spell out exactly what you want in numbered steps.
- Ask for JSON output so n8n can parse and route the results programmatically.
- Customize the risk definitions and suggestions to match your company’s policies and jurisdictions.
Over time, you can refine the wording based on real outputs and edge cases your legal team encounters.
Improving accuracy with scoring and thresholds
To make the detector robust, you can combine two things:
- Semantic similarity scores from your Redis vector search
- Risk classifications from the LLM
Here are some best practices:
- Use a similarity threshold, for example a cosine similarity of 0.7, to decide which chunks you even send to the Agent.
- Automatically flag high similarity hits as likely risky, and route medium or low similarity hits for human review.
- Maintain a labeled dataset of clauses and their risk levels so you can:
- Tune your thresholds over time
- Iterate on prompt wording
- Potentially train supervised models later
This hybrid approach lets you balance automation with control, instead of blindly trusting any single model output.
Privacy, security, and compliance considerations
NDAs often contain very sensitive business information, so it is important to treat this workflow like any other production system handling confidential data. Some practical steps:
- Encrypt data at rest in Redis and in Google Sheets wherever your stack allows it.
- Lock down access to API keys, Redis instances, and Sheets. Use short-lived credentials and environment variables in n8n.
- Keep humans in the loop for high-risk or highly sensitive clauses. The model should assist, not replace, legal judgment.
Make sure your approach aligns with your organization’s security, privacy, and regulatory requirements.
Tuning the workflow for production use
Once the basic pipeline is running, you can start tuning it for your specific NDA patterns and traffic.
- Experiment with embedding models Try different Hugging Face models. Higher quality embeddings generally improve recall and precision, although they may cost more in compute.
- Adjust chunking parameters If your NDAs tend to have long or short clauses, tweak
chunkSizeandchunkOverlapto better match your documents. - Control LLM costs Cache frequent queries where possible and apply rate limits in n8n to keep OpenAI usage under control.
- Scale your storage Google Sheets is perfect for early-stage logging and lightweight analytics. As volume grows, consider moving to a database or data warehouse for more advanced reporting.
What does the output actually look like?
Here is a simple example of how a row in your Google Sheet might look after the workflow finishes:
- Timestamp: 2025-01-01 12:00 UTC
- Document: Partner NDA v3
- Risk level: High
- Clause excerpt: “Confidential information includes all information, whether oral or written…”
- Suggestion: Narrow the definition to exclude general knowledge and add a 3-year confidentiality period.
From here, a legal reviewer can quickly decide whether to accept, negotiate, or reject the clause, without having to re-read the entire NDA from scratch.
Ideas for next steps and enhancements
Once you are happy with the core detector, you can keep building on top of it. Some ideas:
- Add a dashboard Create a front-end view where legal, sales, or operations teams can see and triage flagged NDAs in one place.
- Integrate with contract tools Connect the workflow to your existing systems such as DocuSign, CLM tools, or CRM, so NDAs flow in and out automatically.
- Train a supervised classifier Use your labeled clauses and Sheet data to train a more specialized model that can boost precision and reduce noise.
Wrapping up
This n8n + LangChain workflow gives you a practical, production-ready way to automate NDA review. By combining:
- Semantic search via Hugging Face embeddings and Redis
- LLM-based analysis with an OpenAI-powered Agent
- Structured logging into Google Sheets
you get a fast triage layer that highlights risky clauses, suggests remediation language, and keeps a clean audit trail, all without slowing down deal velocity.
Want to put this into practice? You can use the template as a starting point and customize it for your legal standards, risk appetite, and tech stack.
If you would like help turning this into a detailed n8n setup guide, tailoring prompts to your jurisdiction, or sketching a deployment architecture, feel free to reach out or start your free trial of n8n and begin experimenting.
Call to action: What is your biggest NDA headache right now? Drop it in the comments, and I will suggest concrete prompt templates and threshold settings you can try in this workflow.