Ultimate Tesla Tweet Analysis Workflow
Overview
This documentation describes a complete n8n workflow template that continuously monitors Tesla related content on X (formerly Twitter), analyzes both text and images with Google Gemini and Langchain, classifies sentiment and relevance, then logs high value posts into Airtable and notifies a Telegram monitoring group. The workflow is designed for technical users who want a reproducible, configurable pipeline for social media listening and brand monitoring.
The automation uses a combination of scheduled or manual triggers, HTTP based scraping, conditional filtering, AI powered text and image analysis, deduplication, and structured data storage. It is optimized for Tesla specific keywords, but all parameters can be adapted to any brand or topic.
Workflow Architecture
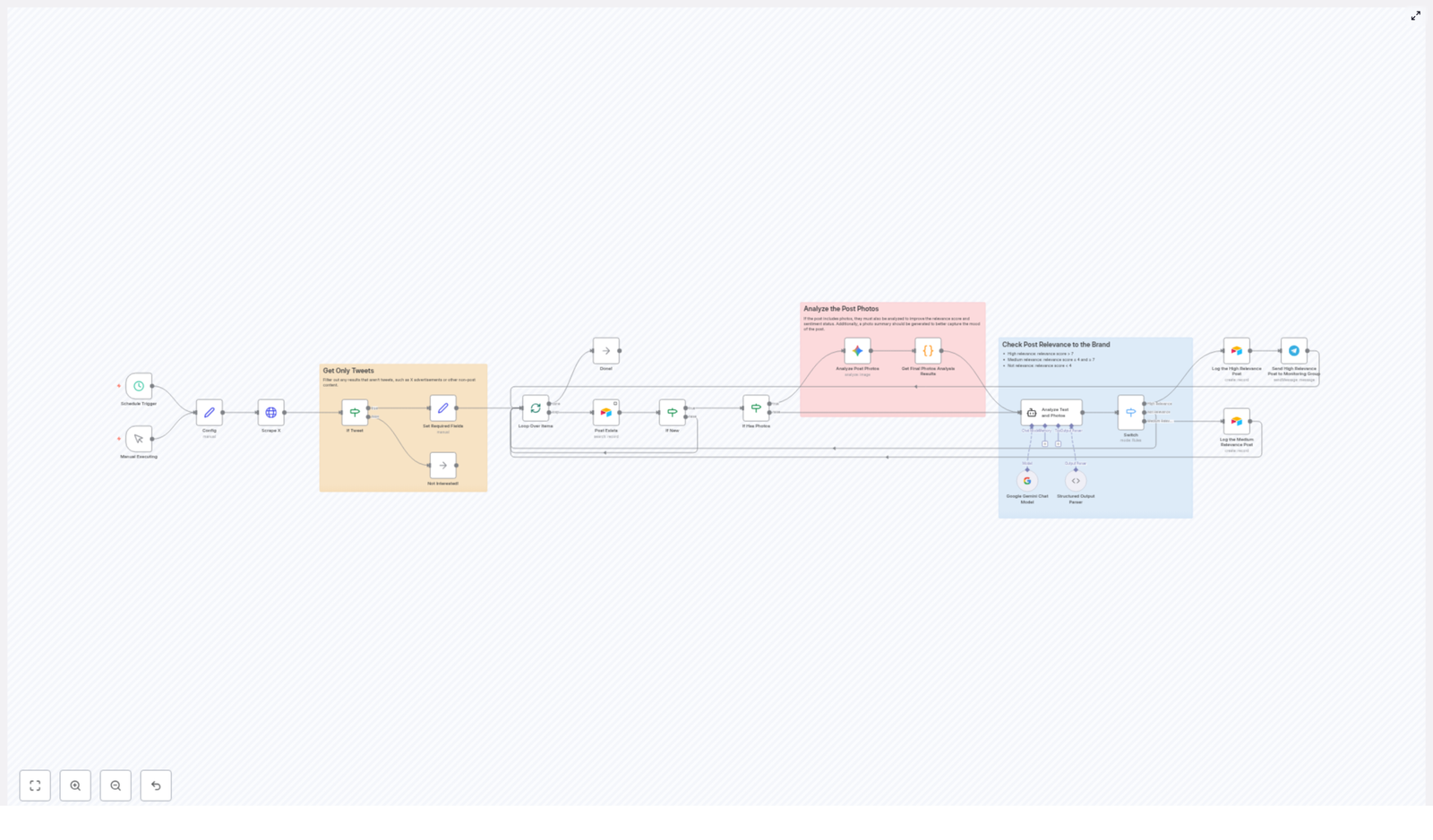
At a high level, the workflow executes the following stages:
- Trigger the workflow on a fixed schedule or manually.
- Configure search parameters and Airtable identifiers.
- Scrape recent Tesla related tweets via an HTTP request to an external API.
- Filter and normalize raw results to keep only relevant tweets.
- Check for duplicates against existing Airtable records.
- Run image analysis with Google Gemini for tweets that contain photos.
- Perform combined text and visual sentiment analysis with a Langchain agent powered by Google Gemini.
- Classify and route tweets by relevance, log to Airtable, and send Telegram alerts for high priority items.
Each stage is implemented as one or more n8n nodes, connected in a linear but conditionally branched flow. Data flows through the workflow as JSON objects that carry tweet metadata, analysis results, and classification scores.
Triggers and Execution Model
Primary Trigger Options
The workflow can start in two ways:
- Cron / Schedule Trigger – Runs automatically every 4 hours to fetch and analyze new Tesla related tweets. This is the default mode for continuous monitoring.
- Manual Trigger – Allows an operator to execute the workflow on demand from the n8n editor, useful for testing, debugging, or ad hoc analysis.
Both triggers feed into the same downstream logic, so the behavior of the workflow remains consistent regardless of how it is started.
Configuration and Parameters
Search and Filtering Parameters
Before scraping, the workflow defines a set of key parameters that control what is retrieved from X and how results are filtered:
- Language – Limits tweets to a specific language code (for example,
enfor English). Only tweets matching this language are processed further. - Search terms – A list of Tesla related keywords and symbols, such as:
Tesla$TSLACybertruckModel YFSD
These terms define the core query for the scraping API.
- Minimum favorites – A threshold for the minimum number of favorites (likes) a tweet must have to be considered. This helps focus on posts with some engagement.
Airtable Configuration
To persist data, the workflow requires Airtable configuration values:
- Base ID – Identifies the Airtable base used for storing tweet records.
- Table ID or table name – Points to the specific table where new entries are created and where duplicates are checked.
These values are usually defined as environment variables or input parameters in n8n, then referenced by the Airtable nodes.
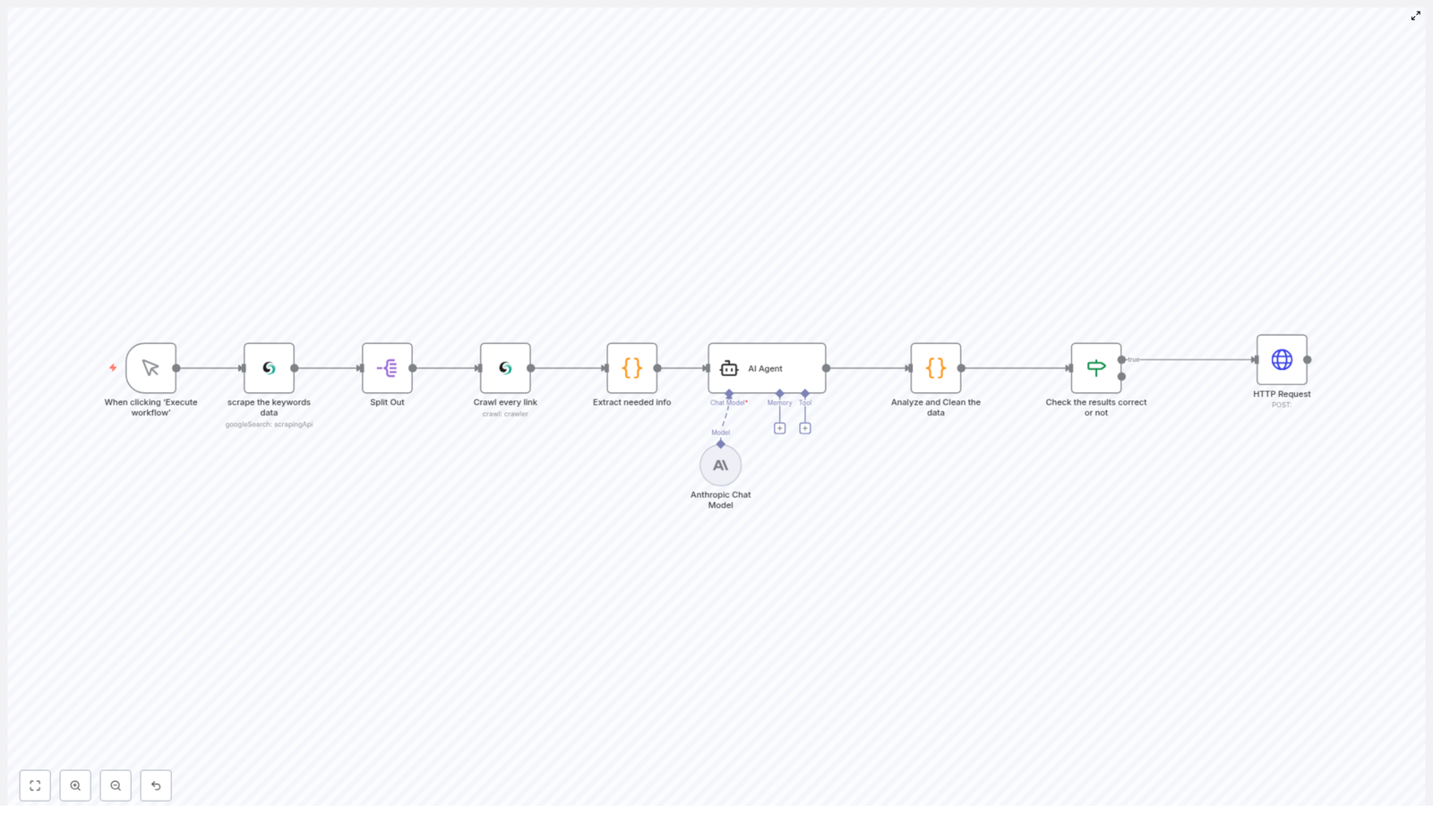
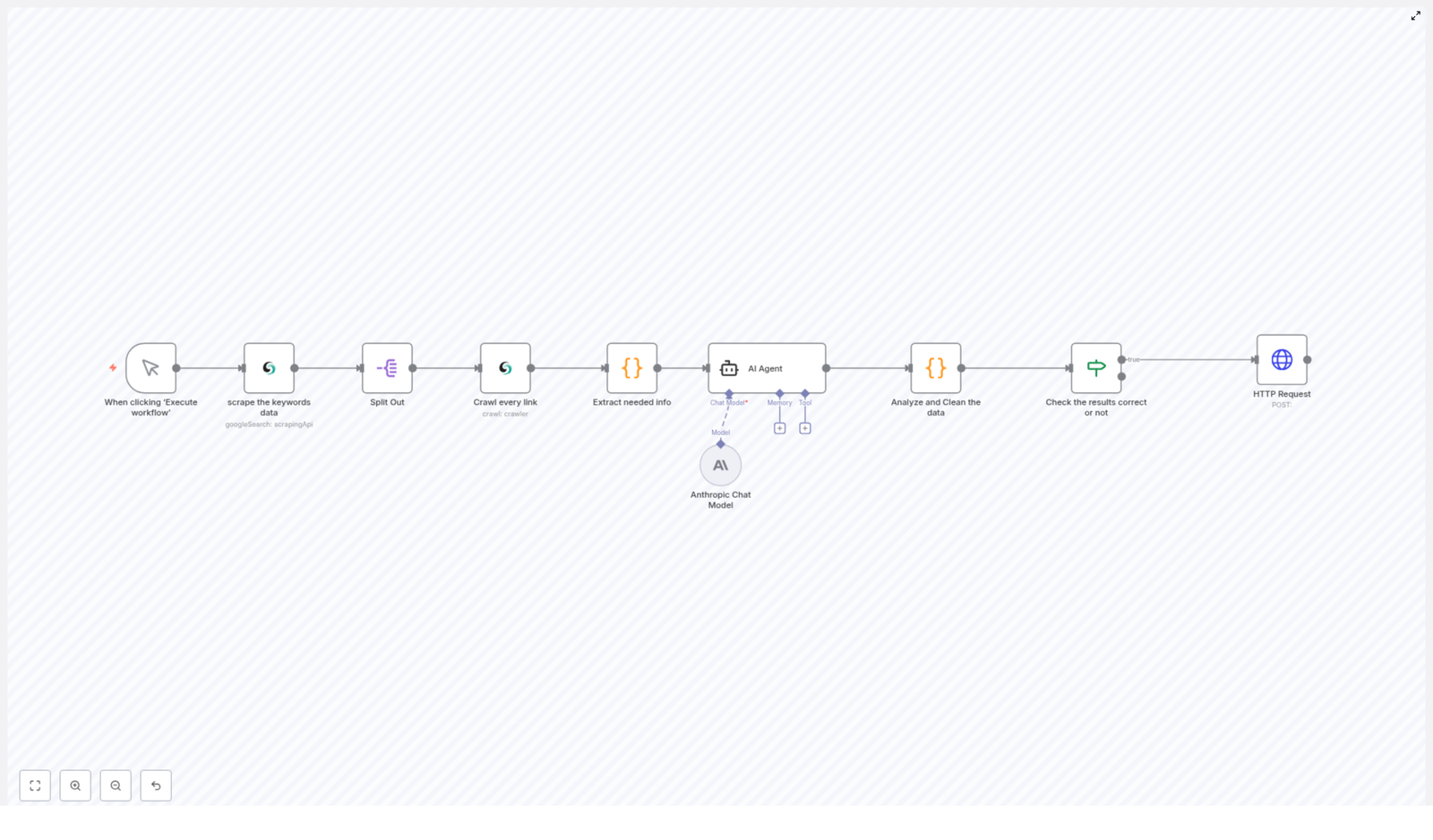
Node-by-Node Breakdown
1. HTTP Request Node – Scraping Tesla Mentions on X
The first processing step is an HTTP Request node that calls an external API endpoint responsible for scraping X. This API:
- Executes a search query using the configured Tesla related keywords.
- Applies language and minimum favorites filters.
- Excludes:
- Retweets
- Replies
- Advertisements and promoted content
- Focuses on original tweets that contain engagement and images where possible.
The node returns a collection of tweet like objects, which may also include some non tweet entities such as ads or cards, depending on the API provider. These are handled in the next stage.
2. Filtering and Normalization Nodes
After the HTTP request, the workflow uses conditional logic nodes (for example, IF or Switch nodes) and data transformation nodes to clean and standardize the results.
Key filtering and processing steps:
- Exclude non-tweet results – Any item that represents an advertisement, card, or non-standard object is filtered out. Only true tweets are passed forward.
- Language validation – Items that do not match the configured language parameter are discarded, even if they passed the initial API filter.
- Card data check – Tweets with card data are excluded. The workflow only continues with tweets that have no card data, which typically represent standard tweet content with or without media.
- Extraction of core fields – For each valid tweet, the workflow extracts and normalizes:
- Tweet ID
- Tweet URL
- Text content
- Language
- Creation timestamp
- Author details (for example, username or display name, depending on available data)
- Media information, including:
- Photos
- Videos
The result is a structured JSON payload per tweet that is ready for downstream analysis and storage.
3. Duplicate Check against Airtable
Before investing compute resources in AI analysis, the workflow performs a deduplication step using Airtable as the source of truth.
Typical behavior of this stage:
- An Airtable node queries the configured base and table for existing records that match the current tweet ID.
- If a matching record is found, the tweet is considered already processed and is not analyzed again.
- If no matching record is found, the tweet continues to the AI analysis stage.
This prevents redundant entries in Airtable and avoids repeated sentiment analysis on the same tweet.
4. Photo Analysis with Google Gemini
For tweets that contain photos, the workflow branches into an image analysis path. If no photos are present, this step is skipped and only text based analysis is performed later.
In the photo branch:
- The workflow inspects the media array and identifies items classified as photos.
- For each photo, a node configured with Google Gemini is invoked to perform image analysis.
- The Gemini model generates:
- Descriptive information about what appears in the image.
- Sentiment related insights where applicable, such as whether the image context seems positive, negative, or neutral toward Tesla or its products.
These per image results are aggregated into a structured object that later feeds into the combined sentiment analysis. If the API fails or a particular image cannot be processed, the workflow can still continue with available text data, depending on how error handling is configured in n8n.
5. Text and Visual Sentiment Analysis with Langchain + Gemini
Next, the workflow combines the tweet text and any image analysis results into a unified context and sends this to a Langchain agent that uses Google Gemini as the underlying model.
The agent receives:
- The original tweet text.
- Summaries or descriptions from the photo analysis stage, if photos exist.
The Langchain agent is responsible for:
- Producing an overall sentiment assessment for the tweet, considering both text and visuals.
- Computing a relevance score that indicates how important or actionable the tweet is for Tesla brand monitoring.
- Generating reasoning that explains why a given sentiment and score were assigned.
- Creating a concise photo summary that captures the essence of the visual content in relation to Tesla.
All of these outputs are attached to the tweet object and used in the classification and routing stage.
6. Classification and Routing
Based on the relevance score returned by the Langchain agent, the workflow classifies each tweet into one of three categories:
- High relevance – score greater than 7.
- Medium relevance – score between 4 and 7 inclusive.
- Low relevance – score lower than 4.
An IF or similar conditional node evaluates the score and routes items into separate branches:
- High relevance branch:
- A new record is created in the configured Airtable table, storing:
- Tweet metadata (ID, URL, text, author, timestamp, media info).
- Sentiment analysis results.
- Relevance score and reasoning.
- Photo summary when available.
- A Telegram node sends a notification to a dedicated monitoring group, allowing the team to react quickly to important posts.
- A new record is created in the configured Airtable table, storing:
- Medium relevance branch:
- Tweets are flagged for weekly review. In practice, this can mean:
- Storing them in Airtable with a different status field.
- Or marking them in a way that makes it easy to filter for periodic manual evaluation.
- Tweets are flagged for weekly review. In practice, this can mean:
- Low relevance branch:
- Tweets are disregarded after analysis and not logged, which keeps Airtable focused on actionable content.
Configuration Notes & Edge Considerations
Credentials and Access
- HTTP Request node – Requires valid credentials or API keys for the X scraping service, configured in n8n credentials.
- Google Gemini – Needs appropriate API access and credentials configured in the Gemini related nodes.
- Airtable – Uses an Airtable API key or personal access token stored as n8n credentials.
- Telegram – Requires a bot token and chat/group ID for sending notifications.
Error Handling
Typical error handling patterns you may want to apply in this workflow include:
- HTTP request failures – Configure the HTTP Request node to retry or fail gracefully if the scraping API is temporarily unavailable.
- AI analysis errors – If Gemini or Langchain calls fail for a specific tweet, you can:
- Skip that tweet and continue processing others.
- Or log the error details in Airtable for later inspection.
- Airtable write conflicts – In rare cases where a tweet is processed twice in a short window, Airtable may already contain a record by the time the write occurs. A pre write duplicate check, as described above, helps mitigate this.
Language and Content Edge Cases
- Tweets that appear multilingual or have missing language metadata might be filtered out if they do not strictly match the configured language code.
- Tweets with card data are intentionally excluded. If you want to include link cards or other rich formats, you would adjust the card data filter logic.
- Tweets with videos but no photos will not go through the photo analysis stage, but their text still goes through sentiment and relevance evaluation.
Advanced Customization Ideas
Although this template is optimized for Tesla brand monitoring, it is straightforward to adapt for other use cases:
- Change keywords and symbols – Replace Tesla specific terms like
Cybertruckor$TSLAwith your own brand names or product lines. - Tune the minimum favorites threshold – Raise it to focus only on viral content, or lower it to capture more early stage conversations.
- Adjust relevance thresholds – Modify the numeric boundaries for high, medium, and low relevance to match your team’s capacity and priorities.
- Extend logging – Add more Airtable fields for internal labels, reviewer assignments, or follow up actions.
- Additional notification channels – Besides Telegram, you can connect Slack, email, or other messaging platforms using additional n8n nodes.
Conclusion
This n8n workflow template delivers a complete, automated pipeline for Tesla tweet analysis. It continuously scrapes X for relevant mentions, filters noise, analyzes both text and images with Google Gemini and Langchain, classifies sentiment and relevance, and logs high priority posts into Airtable while notifying a Telegram group.
For brand monitoring teams, this structure provides real time visibility into social sentiment and visual narratives around Tesla, so they can respond quickly to important conversations and emerging issues.
Interested in deploying this workflow for your own brand monitoring stack? Contact us to get started with a customized social media listening solution built on n8n.