Automate Mailchimp Subscriber Creation from Airtable: A Story of One Marketer’s Turning Point
Introduction: When the Email List Became a Problem
Every Monday morning, Julia, a marketing manager at a growing startup, opened two tabs like clockwork: Airtable and Mailchimp. Airtable held a clean list of new signups from events, lead magnets, and website forms. Mailchimp was where the email campaigns lived. Between them sat a tedious ritual that Julia dreaded.
She would copy names, emails, and interests from Airtable, paste them into Mailchimp, double check for typos, and hope she did not miss anyone. By the time she was done, an hour had passed and her coffee was cold. Worse, there were always small mistakes, outdated lists, and missed subscribers who never received the welcome series they had asked for.
One day, after realizing a batch of high-intent leads never made it into Mailchimp, Julia decided that this was the last time manual list updates would cost her conversions. That is when she discovered an n8n workflow template that could automate Mailchimp subscriber creation directly from Airtable.
Rising Action: Discovering n8n and the Airtable-Mailchimp Template
Julia had heard of n8n as a flexible automation tool, but she had never tried building a workflow herself. The promise of a ready-made template that could:
- Pull users from Airtable
- Send them into a Mailchimp list
- Tag them by interest for segmentation
was exactly what she needed.
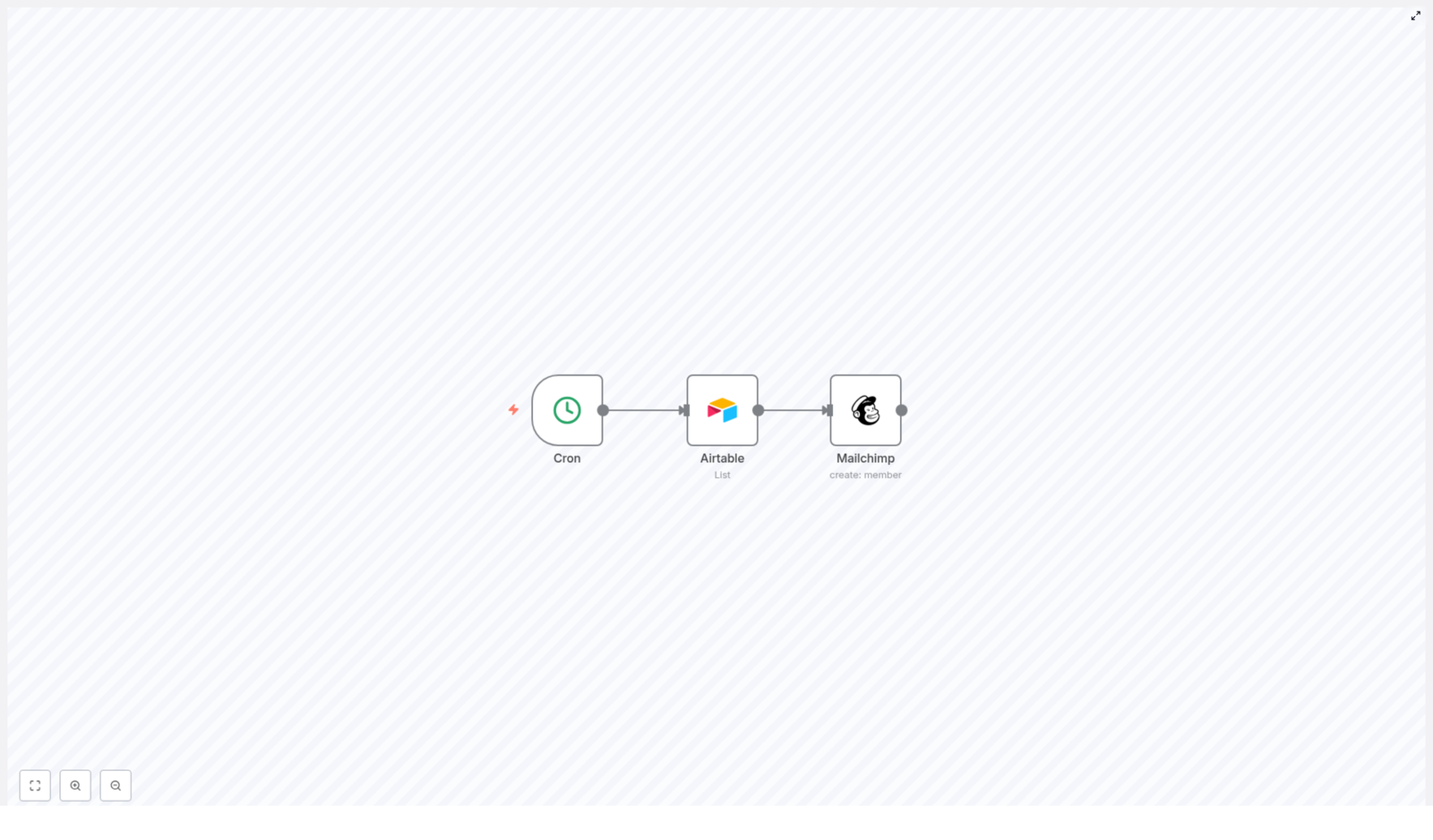
She clicked into the template and realized that under the surface of her problem was a simple automation story with three characters of its own: the Cron node, the Airtable node, and the Mailchimp node. Together, they could replace her repetitive Monday routine with a reliable, hands-off workflow.
The Core of the Workflow: Three Nodes That Changed Everything
The Cron Node – Ending Manual Check-ins
The first piece of the template was the Cron node. Julia quickly understood its role: it would act like a timer that woke the workflow up at specific intervals. Instead of her logging in every Monday to sync data, the Cron node would quietly trigger the automation on a schedule she defined.
She set it to run daily so that new signups from the previous day would automatically sync to Mailchimp. No more waiting a week, no more forgotten updates.
The Airtable Node – Turning a Table into a Source of Truth
Next, Julia looked at the Airtable node. This was where n8n connected to her Airtable base, specifically to the “Users” table that her team had been using for months. The template was already configured to retrieve the core fields she relied on:
- Name – for personalization in email campaigns
- Email – the key identifier for each subscriber
- Interest – the topic or category that each user cared about
She realized this node was doing what she had been doing manually, only faster and with zero chance of miscopying an email address. Each time the Cron node triggered the workflow, the Airtable node would fetch all the relevant records from the Users table, ready to be turned into Mailchimp subscribers.
The Mailchimp Node – Automatically Creating Subscribers
The final step in the template was the Mailchimp node. This was the part Julia cared about most, because it directly impacted her campaigns.
For each Airtable record, the Mailchimp node would:
- Create a new list member in the specified Mailchimp audience
- Use the email and name from Airtable as merge fields, so her dynamic content still worked
- Apply the “Interest” field as a tag, which meant her audience would be automatically segmented based on what users actually cared about
Instead of building segments manually or guessing what people wanted, she could rely on accurate, structured data flowing straight from Airtable into Mailchimp.
The Turning Point: From Manual Chaos to Automated Flow
With the pieces in place, Julia followed the template’s structure and adapted it to her own setup. The steps were surprisingly straightforward once she understood how the nodes worked together.
How Julia Set Up the Automation in n8n
- She confirmed her Airtable base had the required fields: Name, Email, and Interest in a table called “Users”.
- In n8n, she connected her Airtable account and configured the Airtable node to read from that Users table and pull exactly those fields.
- She connected her Mailchimp account, then selected the target Mailchimp list (audience) and set the correct list ID inside the Mailchimp node.
- She adjusted the Cron schedule to run every morning at 8 a.m., right before her daily reports, so new subscribers were always included.
- Finally, she activated the workflow so the automatic syncing could begin.
The first time the workflow ran, she watched as new subscribers appeared in her Mailchimp audience without her lifting a finger. Their names were correctly mapped, their emails were accurate, and each one carried a tag based on their interest, ready for targeted campaigns.
Resolution: What Changed After the Automation Went Live
Within a week, Julia could feel the difference. Instead of spending time copying data, she was creating better campaigns and testing new segments. The Airtable to Mailchimp automation had quietly become a core part of her marketing stack.
Benefits Julia Saw From the n8n Workflow Template
- Time-saving – The workflow automatically added users from Airtable to Mailchimp so she no longer wasted hours on manual data entry.
- Accuracy – With n8n handling the transfer, human errors dropped. No more missing subscribers or mistyped emails.
- Better segmentation – The Interest field became a powerful tag in Mailchimp, letting her send highly relevant content to each segment.
- Scalability – As her database grew, the workflow kept up. She could easily add more fields or adapt the automation for new campaigns without rewriting everything.
Most importantly, her mailing list stayed fresh and up to date. New leads never sat forgotten in Airtable. They were welcomed, nurtured, and segmented from the moment they arrived.
How You Can Follow Julia’s Path
If you are managing signups in Airtable and sending campaigns with Mailchimp, you do not have to keep juggling spreadsheets and manual imports. The same n8n automation template that turned Julia’s Monday headache into a background process can do the same for you.
All it takes is:
- A well structured Airtable base with Name, Email, and Interest fields
- Your Airtable and Mailchimp accounts connected to n8n
- A Cron schedule that matches how often you want your lists to sync
- A few minutes to map fields and activate the workflow
Conclusion: Let Your Tools Do the Repetitive Work
Integrating Airtable with Mailchimp using n8n is more than a technical tweak. It is a shift in how you work. Instead of spending your time moving data from one place to another, you let automation keep your subscriber list accurate, segmented, and ready for action.
That is how Julia went from dreading her weekly list updates to focusing on what really mattered: building campaigns that convert.
Ready to boost your email marketing? Get started with Mailchimp today!