Efficient Webpage Content Fetching & Processing Workflow
Overview and Use Case
Reliable webpage content extraction is fundamental for web scraping, data enrichment, content analysis, and AI-driven automation. This n8n workflow template provides a robust pattern for fetching HTML pages, validating inputs, handling errors in a controlled way, and returning either full or simplified content in a clean Markdown format.
The workflow is designed for automation professionals who need to convert natural language requests into structured HTTP calls, process the resulting HTML, and keep resource usage predictable by enforcing content length limits.
High-Level Architecture
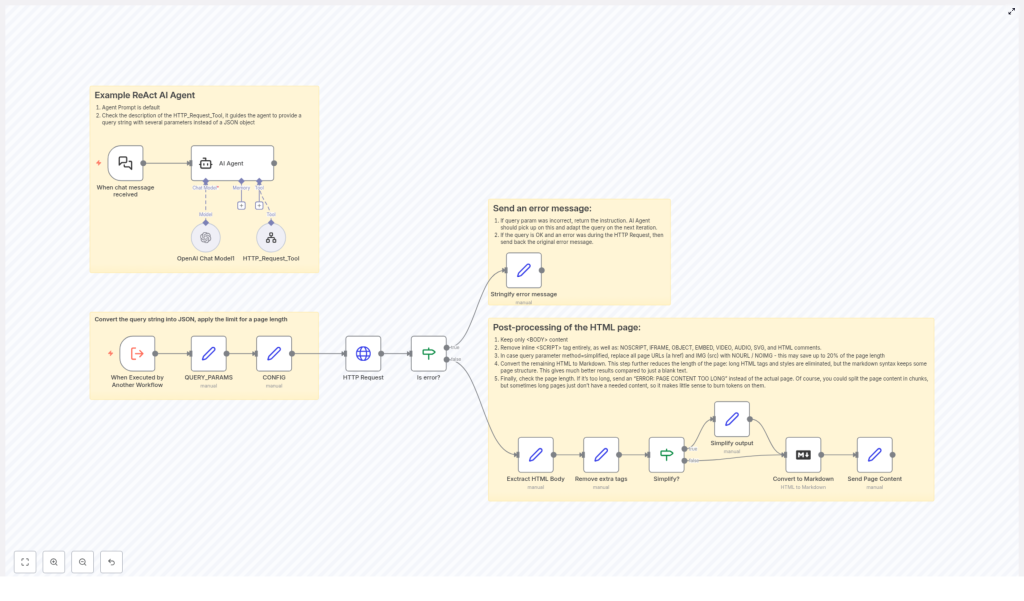
At a high level, the workflow performs four main functions:
- Interpret natural language instructions and translate them into query parameters.
- Fetch webpage content via an HTTP request, with controlled configuration.
- Validate responses, manage errors, and constrain output size.
- Post-process HTML into a structured, optionally simplified Markdown representation.
These capabilities are implemented using a combination of the ReAct AI Agent, OpenAI Chat Model, HTTP Request node, and a series of transformation and validation steps in n8n.
Core Workflow Components
ReAct AI Agent as the Orchestration Layer
The ReAct AI Agent is the central orchestrator of this workflow. It receives natural language input and determines how to act on it by coordinating multiple tools:
- OpenAI Chat Model is used for language understanding, interpretation of user intent, and generation of structured instructions.
- HTTP_Request_Tool is invoked by the agent to perform the actual retrieval of live webpage content based on the interpreted query parameters.
This ReAct pattern allows the workflow to bridge free-form user queries with deterministic automation steps, which is especially valuable when building intelligent scraping or content processing pipelines.
Query Parsing and Configuration Management
Once the workflow is triggered, it converts the incoming query string into a structured JSON representation to make downstream processing predictable and reusable.
- QUERY_PARAMS: The raw query string is parsed into a JSON object. Each query parameter becomes a key-value pair, which can then be referenced by subsequent nodes.
- CONFIG: A configuration object sets operational constraints, most notably a maximum page length. By default, this is configured to
70000characters, which acts as a hard limit for the amount of content returned.
This approach ensures that the workflow can be adapted or parameterized without changing the core logic. Adjusting the maximum length or adding new query parameters becomes a configuration task instead of a redesign.
Fetching Webpage Content
HTTP Request Node Behavior
The HTTP Request node is responsible for performing the actual page fetch. It takes the URL derived from the parsed query parameters and encodes it safely before sending the request.
Key characteristics:
- The URL is encoded to avoid issues with special characters in query strings.
- The node is configured to handle unauthorized certificates safely, which is useful when dealing with a variety of websites and SSL configurations.
- The raw HTML response is passed along for subsequent checks and transformations.
Error Detection and Reporting
To ensure that downstream processing only runs on valid responses, the workflow introduces a structured error handling layer.
- Is error? node checks whether the HTTP request resulted in an error, for example due to network issues or invalid URLs.
- If an error is detected, a dedicated step called Stringify error message converts the error details into a clear, human-readable message that is returned to the caller.
- If no error is found, the workflow proceeds to HTML extraction and transformation.
This pattern improves observability and makes it easier to integrate the workflow into larger systems, since failures are explicit and formatted rather than ambiguous or silent.
HTML Content Processing Pipeline
After a successful HTTP response, the workflow applies a series of transformations to clean, simplify, and reformat the HTML into a more useful representation.
Step 1: Extract the HTML Body
The first post-processing step isolates the content inside the <body> tag. This focuses processing on the main page content and excludes headers, metadata, and other non-essential elements that typically live outside the body.
Step 2: Remove Non-Essential Tags
The workflow then strips out elements that are not relevant to content analysis or that can interfere with downstream processing:
<script>tags<noscript>tags<iframe>tags- Other inline or embedded elements that add noise or potential security concerns
By removing these tags, the workflow reduces clutter, minimizes the chance of executing or parsing unnecessary code, and prepares a cleaner HTML structure for further transformation.
Step 3: Optional Simplification of Links and Images
Depending on the query method and configuration, the workflow can simplify the page content by replacing certain elements with placeholders. This is particularly useful when the consumer is only interested in textual content or when output size needs to be minimized.
- Links are replaced with the placeholder
NOURL. - Images are replaced with the placeholder
NOIMG.
This optional simplification step provides a flexible mechanism to offer both full and reduced versions of the content without maintaining separate workflows.
Step 4: Convert HTML to Markdown
Once the HTML has been cleaned and optionally simplified, it is converted into Markdown. Markdown offers a leaner, more structured representation that retains headings, lists, and basic formatting while remaining easy to parse, store, or feed into language models.
This conversion significantly improves compatibility with downstream tools and analytical workflows that prefer text-based formats over raw HTML.
Step 5: Enforce Maximum Length and Return Content
The final step checks the length of the generated Markdown content against the configured maximum page length defined in CONFIG (default 70000 characters).
- If the content length is within the limit, the Markdown is returned as the final output.
- If it exceeds the limit, the workflow returns a clear status message instead:
ERROR: PAGE CONTENT TOO LONG.
This safeguard prevents excessive payloads, protects downstream systems from overload, and enforces predictable resource usage across multiple executions.
Key Benefits and Automation Best Practices
- Controlled resource consumption: The explicit page length check ensures that large or unexpectedly complex pages do not overwhelm the system or downstream consumers.
- Flexible output modes: Support for both full and simplified content (via
NOURLandNOIMGplaceholders) allows the same workflow to serve different use cases, from detailed analysis to lightweight preview. - Robust error handling: Centralized error detection and stringified error messages make it easy to integrate this workflow into larger automation pipelines and monitoring setups.
- Clean, safe content: Systematic removal of scripts, iframes, and other non-essential elements improves security and reduces noise, which is critical for AI and analytics workloads.
- Config-driven behavior: Using configuration nodes like
QUERY_PARAMSandCONFIGpromotes maintainability and makes it simple to adjust limits or parameters without refactoring the workflow.
Practical Applications
This n8n template is particularly suited for:
- Web scraping pipelines that need pre-cleaned content for downstream parsing or NLP.
- AI agents that must fetch and summarize web pages while staying within token or size limits.
- Content monitoring systems that periodically fetch and process pages for changes or compliance checks.
- Knowledge extraction workflows that convert web content into Markdown for storage in knowledge bases or vector databases.
Getting Started
To leverage this workflow in your own environment:
- Import the template into your n8n instance.
- Review and adjust
CONFIG, especially the maximum page length, to align with your system limits and use case. - Customize the query handling in
QUERY_PARAMSif you need additional parameters or different URL-building logic. - Integrate the ReAct AI Agent with your preferred OpenAI Chat Model configuration and credentials.
- Connect the workflow to upstream triggers or downstream systems such as databases, queues, or other automation services.
Conclusion
This workflow template provides a structured, production-ready pattern for transforming natural language instructions into reliable web content extraction. By combining the ReAct AI Agent, HTTP Request handling, thorough HTML clean-up, and Markdown conversion, it delivers a controlled, transparent, and scalable solution for automation professionals who work extensively with web data.
Adopting this pattern can significantly improve the efficiency, reliability, and maintainability of your web scraping and content processing automations.