How to Verify Phone Numbers in n8n Workflows
Phone number verification is a critical part of many production workflows. Whether you are validating user signups, cleaning CRM records, or preparing contact lists for marketing campaigns, you need a robust way to parse and verify phone numbers before they reach downstream systems.
This guide explains, in a technical and reference-style format, how an n8n workflow template validates phone numbers using a combination of core nodes and an external API integration. The focus is on how data flows between nodes, how expressions are used, and how to extend the workflow safely for real-world automation.
Workflow Overview
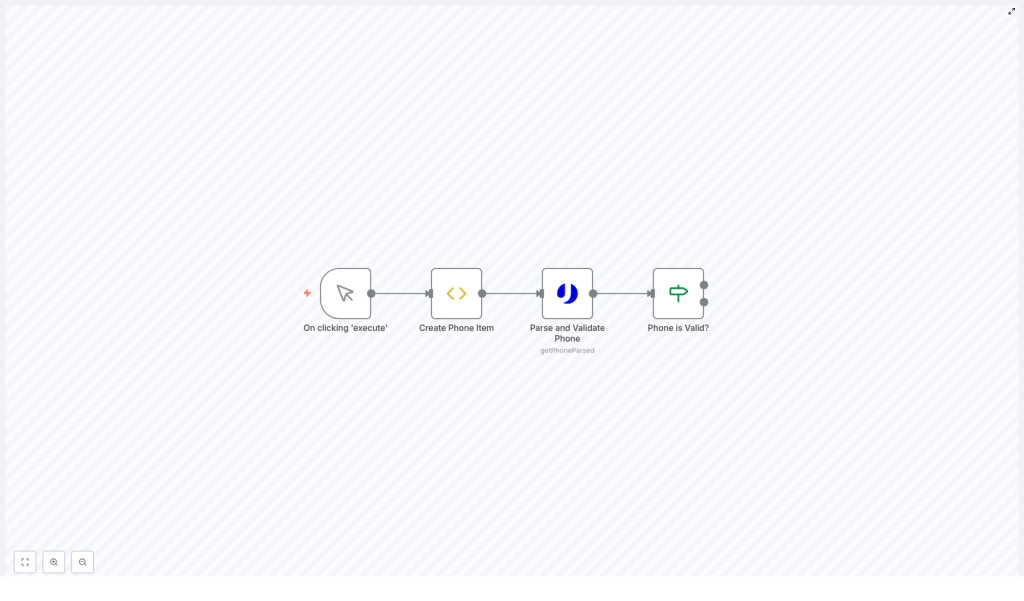
This n8n phone verification workflow performs a simple but complete validation cycle:
- Manual execution of the workflow via a Manual Trigger node.
- Creation of a data item that contains a phone number to verify.
- Parsing and validation of the phone number using the uproc integration and the
getPhoneParsedtool. - Conditional branching based on the validation result using an If node.
The template is intentionally minimal so it can be reused as a building block inside larger n8n automations, or adapted for batch processing, user-facing forms, and external systems.
Workflow Architecture and Data Flow
The workflow consists of four primary nodes executed in sequence:
- Manual Trigger – controls when the workflow starts.
- Create Phone Item (Function or Function Item node) – initializes the payload with a phone number.
- Parse and Validate Phone (uproc node) – calls the
getPhoneParsedtool to analyze and validate the number. - Phone Is Valid? (If node) – evaluates the response and routes items based on validity.
At a high level, the JSON item flows through the workflow as follows:
{ // After "Create Phone Item" "phone": "+34605281220"
}
This phone property is then passed as an input parameter to the getPhoneParsed tool. The response from the uproc integration contains a message object that includes a valid field, along with other metadata such as country code and formatted versions of the number. The If node reads message.valid and compares it to the string "true" to determine the next path.
Node-by-Node Breakdown
1. Manual Trigger Node
Node type: Manual Trigger
The workflow is initiated manually from the n8n editor by clicking Execute Workflow. This trigger is ideal for:
- Interactive testing during development.
- Ad-hoc verification runs.
- Demonstrating or debugging the template without external dependencies.
Because the trigger is manual, this template is safe to modify and experiment with. In production, you can replace this node with other triggers such as Webhook, Cron, or integration-specific triggers to automate verification.
2. Create Phone Item Node
Node type: typically a Function or Function Item node
This node is responsible for creating the data structure that will be passed into the validation step. It sets a single property, phone, on the item:
item.phone = "+34605281220";
return item;
Key characteristics:
- Hardcoded test value: The phone number
+34605281220is used as an example. It is stored on the item asitem.phone. - Simple data model: Only one field is required for the workflow to function, which keeps the template easy to extend.
In a real workflow, you can replace this hardcoded value with:
- Form submissions received via a Webhook node.
- Records fetched from a database (e.g., PostgreSQL, MySQL, or Airtable nodes).
- Data pulled from external services via HTTP Request or native n8n integrations.
When adapting the template, ensure that the property name phone is preserved or adjust downstream expressions accordingly.
3. Parse and Validate Phone Node
Node type: uproc node using the getPhoneParsed tool
This node integrates with the uproc service to parse and validate the phone number according to international and country-specific rules. The phone number is passed dynamically using an n8n expression that references the output of the previous node.
Input Parameter Configuration
The phone number parameter is populated with this expression:
= {{$node["Create Phone Item"].json["phone"]}}
Details of this expression:
$node["Create Phone Item"]selects the previous node by its name..json["phone"]reads thephonefield from the node’s JSON output.- The leading
=tells n8n to interpret the field as an expression rather than a static string.
This ensures that whatever value is set as item.phone in the Create Phone Item node is used as the input to the uproc API.
Validation Output
The getPhoneParsed tool analyzes the phone number and returns a structured response that typically includes:
- Validity status (e.g., a
validfield indicating whether the number is recognized as valid). - Country code associated with the number.
- Formatted versions of the phone number, often in standardized international format.
- Carrier information, when available, such as the provider or network.
In the workflow, the validation result is accessed under the message object of the response JSON. The exact structure is important for the subsequent If node, which reads message.valid.
4. Phone Is Valid? Node
Node type: If node
This node performs a conditional check to determine whether the phone number is valid based on the uproc response.
Condition Configuration
The condition uses an expression that reads the valid field from the previous node’s JSON and converts it to a string:
= {{$node["Parse and Validate Phone"].json["message"]["valid"] + ""}}
Key aspects of this expression:
$node["Parse and Validate Phone"]references the uproc node by name..json["message"]["valid"]accesses thevalidfield inside themessageobject.+ ""coerces the value into a string, which simplifies comparison in the If node configuration.
The If node then compares this string value to "true". If the value equals "true", the item is routed to the true branch. Otherwise, it follows the false branch.
Branch Semantics
- True branch: Executed when the phone number is valid. This is where you typically place downstream processing such as database writes, notifications, or further enrichment.
- False branch: Executed when the number is not valid. You can use this path to log invalid numbers, send alerts, or trigger corrective actions.
This conditional routing is the core decision point of the workflow and can be extended with additional nodes depending on your use case.
Configuration Notes and Practical Considerations
Credentials and Integration Setup
To use the uproc integration in the Parse and Validate Phone node, you must configure valid uproc credentials in n8n. Ensure that:
- The correct credential type is selected in the node configuration.
- API keys or tokens are stored securely in n8n credentials, not hardcoded into expressions.
- The
getPhoneParsedtool is selected as the operation within the uproc node.
If credentials are missing or invalid, the node will fail and the workflow execution will stop at that point. Use n8n’s error view to inspect such failures.
Data Types and Expression Behavior
The workflow relies on string comparison for the validity check. The + "" coercion in the If node expression is important because:
- It normalizes values like
trueorfalse(boolean) into"true"or"false"(string). - It avoids mismatches when the API returns booleans that need to be compared to string literals in the If node configuration.
If you modify the workflow and change the data structure or field types, review the expressions and conditions to ensure they still match the expected format.
Handling Errors and Edge Cases
While the template focuses on the happy path, consider the following edge cases when adapting it:
- Missing or empty phone field: If
item.phoneis empty or undefined, the uproc node may return an error or an invalid result. You can add a preliminary If node to check for a non-empty phone value before calling uproc. - API failures: Network issues or rate limits from uproc can cause node errors. In production, consider using n8n’s Error Workflow feature or wrap the uproc call with retry logic and error handling patterns.
- Unexpected response shape: If the uproc API response changes or if certain fields are missing, the expression
.json["message"]["valid"]may be undefined. You can guard against this by adding checks or default values in a Function node before the If node.
Extending and Customizing the Workflow
The template is intentionally minimal so it can act as a base for more complex automations. Below are common extension patterns you can implement on top of this phone verification workflow.
Persisting Verified Phone Numbers
On the true branch of the Phone Is Valid? node, you can add database or storage nodes to persist verified numbers, for example:
- Insert or update records in a relational database using MySQL, Postgres, or SQLite nodes.
- Sync verified contacts to CRM tools or marketing platforms supported by n8n.
- Write structured logs to a storage service or file system for auditing.
Handling Invalid Numbers
On the false branch, you can implement remediation or notification logic, such as:
- Sending an email or chat message to a support team to review the invalid number.
- Returning validation feedback to the user if the workflow is triggered via a Webhook.
- Flagging or removing invalid records from your contact lists.
Bulk Phone Number Processing
To process multiple phone numbers in one execution:
- Replace the Manual Trigger and Create Phone Item nodes with a node that outputs multiple items, such as a database query or CSV file reader.
- Ensure the node that generates items sets a
phonefield for each item. - Keep the same Parse and Validate Phone and Phone Is Valid? nodes. n8n will iterate over each item automatically.
This pattern lets you validate entire lists of phone numbers using the same logic.
Enriching with Carrier or Region Details
The uproc response can include additional metadata such as carrier and region. After the Parse and Validate Phone node, you can:
- Use a Set or Function node to extract and normalize carrier or region fields.
- Store these attributes in your database or pass them to downstream systems for segmentation.
Summary
This n8n workflow template demonstrates a complete, modular pattern for phone number verification:
- A Manual Trigger node for controlled execution.
- A Create Phone Item node to define the
phonefield. - A Parse and Validate Phone node using the uproc
getPhoneParsedtool. - A Phone Is Valid? If node that branches logic based on
message.valid.
By combining n8n’s expression system, external API integrations, and conditional routing, you can reliably validate phone numbers and integrate the results into your broader automation landscape.
Next Steps
To start using this pattern in your own automations, import the template into your n8n instance, adjust the phone input source, and extend the true and false branches to match your business requirements.