How to Verify Phone Numbers Using an n8n Workflow Template
Why Phone Number Validation Matters
Accurate phone numbers are essential for user verification, transactional messaging, and reliable customer communication. Invalid or poorly formatted numbers can lead to failed SMS deliveries, security issues, and unnecessary operational cost. For teams that manage large volumes of contact data, manual checks are not sustainable.
n8n, an extensible open-source workflow automation platform, enables you to automate phone validation at scale. By combining native nodes with external APIs, you can centralize data quality checks in a repeatable, auditable workflow.
Use Case Overview
This workflow template demonstrates how to validate a phone number in n8n using the getPhoneParsed tool from uproc. The logic is intentionally simple so it can be embedded into larger automations such as user onboarding, CRM enrichment, or lead qualification pipelines.
The workflow executes the following core steps:
- Trigger the validation process on demand or from another event
- Provide a phone number as input
- Send the number to uproc’s
getPhoneParsedtool for parsing and validation - Evaluate the result and branch the flow based on whether the number is valid
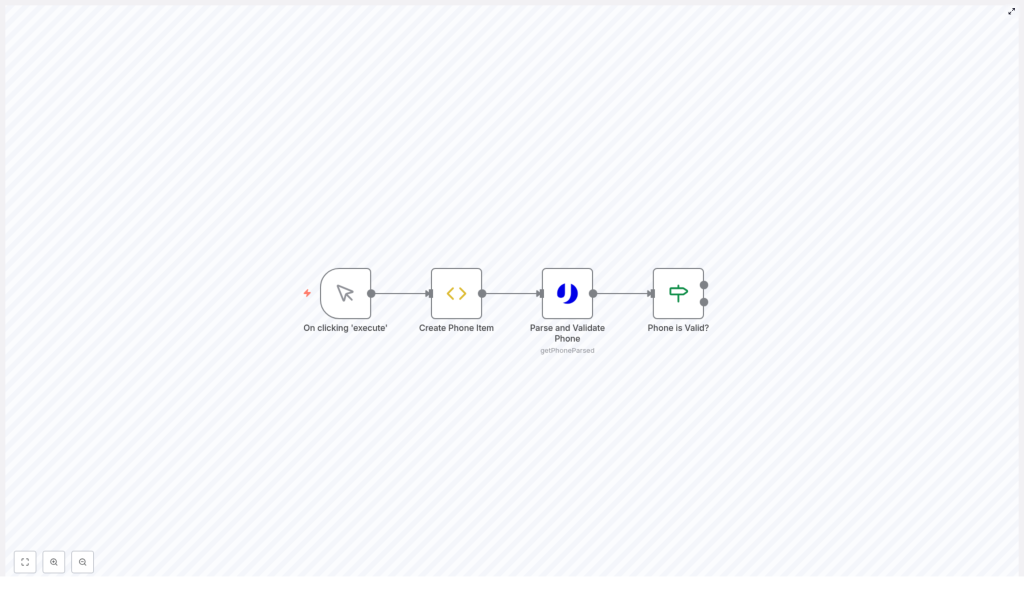
Workflow Architecture
The template is composed of four primary nodes connected in sequence:
- Manual Trigger – Starts the workflow execution
- Create Phone Item – Prepares the phone number to validate
- Parse and Validate Phone – Calls uproc’s
getPhoneParsedendpoint - Phone is Valid? – Uses conditional logic to branch based on the validation result
Although minimal, this structure follows automation best practices: a clear trigger, a deterministic input, a dedicated validation step, and explicit branching logic.
Node-by-Node Breakdown
1. Triggering the Workflow
Node type: Manual Trigger
The workflow starts with a Manual Trigger node. This is ideal for testing, debugging, and demonstration purposes because it lets you execute the workflow directly from the n8n editor.
In production scenarios, automation professionals typically replace this node with more suitable triggers, for example:
- Webhook Trigger to validate numbers from external applications or web forms
- Cron Trigger to run scheduled bulk validations
- App-specific Triggers (such as CRM or database events) for real-time data quality checks
The rest of the workflow remains compatible with these alternative triggers, which makes the template easy to adapt and reuse.
2. Preparing the Phone Number Input
Node type: functionItem (Create Phone Item)
This node creates the data structure that will be passed to the validation service. It sets a phone property on the current item. In the template, the phone number is hardcoded for demonstration:
item.phone = "+34605281220";
return item;
For real-world usage, you would typically replace this hardcoded value with dynamic input, for example:
- Values coming from a previous node such as a Webhook, database query, or form submission
- Numbers read from a CSV or spreadsheet in batch processing workflows
Maintaining a consistent field name, such as item.phone, helps standardize downstream logic and simplifies workflow maintenance.
3. Parsing and Validating the Phone Number
Node type: uproc (Parse and Validate Phone)
The core validation step is handled by the uproc node, which integrates with the getPhoneParsed tool. This node sends the phone number to uproc, which then:
- Parses the phone number
- Checks its structure and format
- Determines whether the number is valid
- Returns a response that includes a
validflag and other metadata
To use this node, you must configure valid uproc API credentials in n8n. These credentials ensure secure communication with the uproc service and are managed centrally in n8n’s credential store.
From an automation best practice perspective, keep credentials separate from workflow logic and avoid hardcoding secrets directly in nodes. This approach improves security and simplifies environment-specific configuration.
4. Conditional Logic: Is the Phone Valid?
Node type: if (Phone is Valid?)
The final node evaluates the response from uproc. It checks whether the field message.valid is equal to true. Based on this condition, the workflow branches into two paths:
- True branch for valid phone numbers
- False branch for invalid phone numbers
This conditional structure allows you to implement differentiated handling, such as:
- Accepting valid numbers and storing them in a CRM or marketing platform
- Flagging or rejecting invalid entries and notifying users or administrators
- Triggering remediation workflows, such as asking users to update their contact information
Explicit branching like this keeps the workflow transparent and easier to troubleshoot.
Implementing the Template in Your n8n Instance
To start using this phone validation workflow template, follow these steps:
- Import the workflow JSON into your n8n instance using the Import from file or clipboard option.
- Configure uproc credentials in the n8n Credentials section and link them to the uproc node that uses the
getPhoneParsedtool. - Adjust the input phone number in the
Create Phone Itemnode:- For testing, you may keep or change the hardcoded number.
- For production, map this field from the data source that provides user phone numbers.
- Execute the workflow manually using the Manual Trigger to verify that your credentials, input, and logic are working as expected.
- Extend the valid and invalid branches with your own business logic, such as database updates, notifications, or error handling.
Best Practices for Phone Validation Workflows in n8n
- Centralize validation in a reusable sub-workflow or template so multiple processes can share the same logic.
- Log validation outcomes for observability and auditing. Consider writing results to a log store, monitoring system, or data warehouse.
- Handle edge cases gracefully, including network errors, API timeouts, or unexpected response formats from uproc.
- Normalize phone formats after validation, for example by storing numbers in a consistent international format for downstream systems.
- Secure API credentials using n8n’s credential management rather than embedding secrets in node parameters.
Advantages of Using n8n for Automated Phone Validation
- Full automation – Replace manual checks with a repeatable workflow that validates every number as it enters your systems.
- Rich integration capabilities – Combine the uproc
getPhoneParsedtool with other APIs and services to build complete data quality pipelines. - Scalable design – Extend the template to support bulk validation jobs or integrate it into high-throughput event-driven architectures.
- Flexible customization – Tailor conditional logic, error handling, and downstream actions to align with your specific business rules and compliance requirements.
Conclusion
This n8n workflow template provides a concise and effective pattern for programmatic phone number verification using the uproc getPhoneParsed tool. By understanding the role of each node and how they interact, you can confidently embed phone validation into your existing automation landscape, improve contact data quality, and reduce operational friction.
Next Steps
If you are ready to enhance the reliability of your contact data, integrate this template into your n8n setup and adapt it to your own triggers and systems.
Import the workflow, connect your uproc account, and start validating phone numbers automatically.