Live Stream Chat Moderator with n8n & LangChain
Imagine running a live stream where you can stay fully present with your audience, instead of scrambling to delete spam, filter abuse, or track repeat offenders. Moderation does not have to drain your energy or your team’s focus. With the right automation, your chat can practically take care of itself while you concentrate on what matters most: creating, connecting, and growing.
In this guide, you will walk through a complete n8n workflow template that turns scattered tools into a coordinated live stream chat moderator. Using n8n as the orchestrator, LangChain components for text processing, Supabase as a vector store, and Anthropic for conversational intelligence, you will create a system that learns from context, remembers past incidents, and logs every decision to Google Sheets for transparent review.
By the end, you will not just have a production-ready template. You will have a reusable pattern for automation that can free up your time, scale with your community, and become a foundation for even more powerful workflows.
From chaos in chat to calm, focused streaming
Live stream chat can flip from fun to frantic in seconds. Messages flood in, trolls appear, and important questions get buried. Manual moderation struggles to keep up, and even basic scripts fall short when they lack context or memory.
What you really need is a moderator that can:
- React quickly to every message
- Understand context and user history
- Remember past incidents and patterns
- Provide an audit trail of decisions
That is exactly what this n8n template is designed to support. Instead of building a custom backend or stitching together ad-hoc scripts, you can lean on a clear, modular architecture that is easy to extend and maintain.
Adopting an automation mindset
Before we dive into nodes and APIs, it helps to approach this as more than just “setting up a bot.” Think of it as a mindset shift.
With automation-first thinking, you:
- Delegate repetitive, high-volume decisions to a workflow
- Reserve human attention for edge cases and community care
- Turn your moderation process into something you can measure, refine, and scale
n8n, LangChain, Supabase, and Anthropic together give you a toolkit that can grow with your needs. Start with this template, then keep iterating. Each improvement you make compounds, saving more time and creating a safer, more welcoming space for your audience.
Why this n8n architecture works so well
The template uses small, composable services that each do one job well. n8n sits in the middle as the visual workflow orchestrator, connecting every piece into a single, reliable moderation pipeline.
- n8n: visual workflow engine that accepts webhooks, routes data, and coordinates all steps
- Text Splitter & Embeddings: convert chat messages into vectors for semantic search and similarity matching
- Supabase Vector Store: fast, durable storage for embeddings and metadata using a vector database
- Anthropic (or other LLMs): conversational intelligence for classification, reasoning, and moderation decisions
- Google Sheets: simple, accessible audit log for transparency and human review
This architecture keeps each piece replaceable. You can swap providers, adjust parameters, or add new tools without rebuilding from scratch. That flexibility is what makes this template such a strong foundation for long-term growth.
Meet the live stream chat moderator template
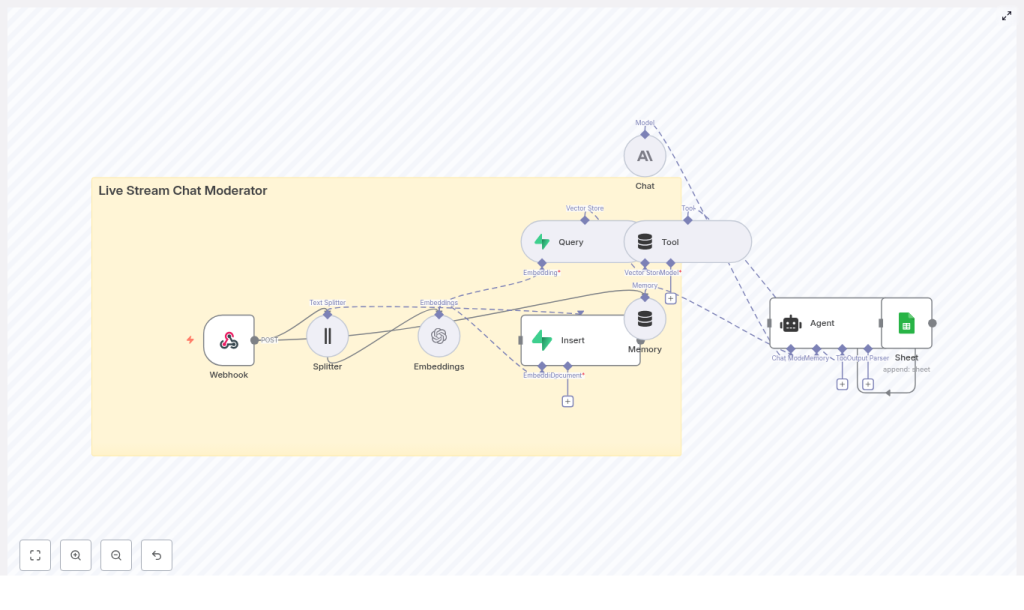
At the heart of this guide is an n8n workflow template that connects your streaming platform to a smart, context-aware moderation agent. Here is how the key nodes fit together:
- Webhook – receives chat events (POST) from your streaming platform or bot
- Splitter – breaks long messages into smaller chunks for embedding and search
- Embeddings – calls OpenAI or another provider to create vector representations
- Insert – stores chunks and embeddings in a Supabase vector store
- Query – looks up similar past messages, rules, or patterns in the vector store
- Tool – exposes the vector store as a tool for the agent to call
- Memory – keeps short-term conversational context for recent chat events
- Chat – Anthropic LLM that analyzes the situation and suggests actions
- Agent – orchestrates tools, memory, and the LLM to produce the final moderation decision
- Sheet – appends the decision and context to a Google Sheet for logging and review
Each node represents a step in your moderation journey, from raw message to thoughtful, explainable action.
How the n8n workflow flows, step by step
1. Receiving chat events at the webhook
Your streaming bot or platform sends chat events into the workflow through the n8n Webhook node. Configure this webhook to accept POST requests, then point your platform or bot to that URL.
The payload should include at least the message text and basic user information. For example:
{ "user_id": "12345", "username": "chat_user", "message": "This is a test message", "channel": "stream-1", "timestamp": "2025-09-04T12:34:56Z"
}
Once this is in place, every new message becomes an opportunity for your automated moderator to learn, respond, and log decisions without manual intervention.
2. Splitting long messages and creating embeddings
Some chat messages are short and simple. Others are long, nuanced, or even multi-line. To handle these effectively, the workflow sends incoming text to the Splitter node.
The Splitter breaks long messages into manageable chunks. This matters because embedding models work best when they receive text within a certain size. Chunking prevents truncation and helps preserve context.
Each chunk then flows into the Embeddings node, which calls OpenAI or your chosen embeddings provider. The result is a vector representation of the text. These vectors are what enable semantic search, pattern detection, and context-aware decisions later in the flow.
3. Storing and querying vectors in Supabase
Next, the workflow uses the Insert node to store both the embeddings and useful metadata in a Supabase vector store. Typical metadata includes:
- message_id
- user_id and username
- channel
- timestamp
- moderation_label (if available)
- a short excerpt of the message
This structure makes it easy to filter and retrieve relevant context later.
When a new message arrives, the Query node searches the vector store for similar messages, known abuse patterns, or policy-related content. This semantic lookup lets the agent recognize repetition, escalation, or subtle variations of harmful behavior that simple keyword filters might miss.
4. Agent reasoning with tools and memory
The real power of this template appears when the Agent node takes over. It acts as a conductor, bringing together:
- The current message
- The Tool node, which gives access to the vector store
- The Memory node, which holds recent chat events
- The Chat node, powered by Anthropic or another LLM
Using LangChain-style orchestration, the agent can reason about what is happening in the chat right now, in light of what has happened before. With that context, it can recommend or generate moderation actions such as:
- Ignore (no action)
- Warn (send a warning message)
- Delete message
- Timeout or ban (for more severe or repeated behavior)
- Flag for human review (and record everything for later inspection)
This is where your automation stops being a simple filter and starts acting like a thoughtful, policy-aware assistant.
5. Logging decisions for human review in Google Sheets
Every decision the agent makes flows into a Sheet node that appends a new row to a Google Sheet. You can include:
- The original message
- User and channel information
- The chosen moderation action
- A rationale or explanation from the LLM
- Nearest neighbor references from the vector store
This simple spreadsheet becomes a powerful audit trail. It supports transparency, appeals, and continuous improvement. As you scan the sheet, you can spot patterns, adjust prompts, refine policies, and gradually shape a safer chat environment with less manual effort.
Getting ready: environment and credentials
To bring this n8n template to life, you will need a few keys and credentials in place. Setting these up once unlocks a reusable automation layer you can apply across many workflows.
- OpenAI or another embeddings provider key for the Embeddings node
- Supabase URL and service key for the vector store connection
- Anthropic API key for the Chat node, or credentials for your preferred LLM
- Google Sheets OAuth credentials for appending logs
- A secure webhook endpoint, ideally protected with a secret token or HMAC signature on incoming POST requests
Once these are configured in n8n, you can reuse them across multiple workflows and templates, not just this live stream moderator.
Designing your vector store for clarity
A well-structured vector store makes your moderation workflow easier to maintain and extend. When setting up your Supabase schema, store both the embedding vector and relevant metadata fields, such as:
- message_id
- user_id and username
- channel
- timestamp
- moderation_label
- a short text excerpt
This setup allows you to:
- Filter by user or channel
- Search for similar incidents over time
- Build higher-level features like reputation scores or dashboards later
Choosing a chunking strategy that fits your needs
Chunking is a small configuration choice that has a big impact on both quality and cost. The template uses a sensible starting point of:
- Chunk size: 400 characters
- Chunk overlap: 40 characters
This balance keeps enough context in each chunk while avoiding unnecessary API calls. If your messages are usually longer or more nuanced, you can increase overlap for richer context. Just remember that larger chunks and more overlap will increase the number of embeddings and storage required.
Moderation policy, safety, and responsibility
Even with a powerful automation stack, your moderation should always align with your platform’s policies and local laws. Technology amplifies your intentions, so it is worth being intentional.
As you roll out this n8n template, consider:
- Using conservative default actions like warnings or flags for review
- Escalating only the clearest or highest-risk cases to timeouts or bans
- Maintaining a clear, documented appeals process
- Reviewing the Google Sheets log regularly to catch misclassifications
Automation is not about removing humans from the loop. It is about freeing humans to focus on empathy, community building, and the cases that truly need judgment and care.
Scaling your automated moderator as your stream grows
As your audience expands, this template can grow with you. You can optimize for performance, cost, and reliability without giving up the core architecture.
- Batch embedding calls when you expect bursts of messages to reduce API overhead
- Use Supabase or another managed vector database with horizontal scaling, such as pgvector on Supabase clusters
- Cache recent queries in memory for ultra-low-latency checks, especially for repeated spam
- Monitor LLM latency and define fallback strategies, such as rules-based moderation when the model is slow or unavailable
With these strategies, your n8n workflow can keep pace with a growing community without forcing you to rebuild from scratch.
Extending the template into a full moderation system
Once the core workflow is running, you can start layering on new capabilities. This is where the template becomes a stepping stone to a richer automation ecosystem.
Popular extensions include:
- Automated user reputation scoring based on historical behavior in the vector store
- Deeper integration with your bot to post warnings, timeouts, or follow-up messages automatically
- A human moderation dashboard that reads from Google Sheets or Supabase for real-time oversight
- Language detection and language-specific moderation policies or assets
Each extension builds on the same foundation: n8n as the orchestrator, vector search for memory, and LLMs for reasoning. As you experiment and iterate, your workflow becomes a unique asset tailored to your community.
Securing your webhook: example signature header
Security is a key part of any production workflow. A common pattern is to sign webhook requests with an HMAC signature and validate it in n8n before processing.
POST /webhook/live_stream_chat_moderator
Headers: X-Hub-Signature: sha256=... # HMAC using your secret
Body: { ... }
# Validate the signature in the first webhook node before processing
By validating this signature in your initial webhook node, you ensure that only trusted sources can trigger your moderation pipeline.
Your next step: turn this template into your automation launchpad
This n8n workflow template is more than a one-off solution. It is a practical, extensible starting point for automated, context-aware live stream moderation that you can keep improving over time.
By combining semantic search via embeddings, a Supabase vector store for memory, and a conversational agent powered by Anthropic or another LLM, you gain a moderator that understands context, learns from history, and escalates intelligently.
From here, you can:
- Import the template into your n8n instance
- Configure your API keys and Supabase project
- Connect your streaming platform or bot to the webhook URL
- Monitor your Google Sheets log and refine your prompts and policies
As you tune and extend this workflow, you will see your manual workload shrink and your capacity to focus on content, strategy, and community growth expand.
Call to action: Try the template today. Deploy it in n8n, run it against a staging or test stream, and use what you learn to refine your automation. Experiment, improve, and make it your own. If you need a deeper walkthrough or want help tailoring it to your platform, export the workflow or reach out for a guided customization.