n8n: Automatically Save YouTube Playlist Items to Raindrop.io
For teams and professionals who consume a high volume of video content, manually bookmarking YouTube links quickly becomes unmanageable. By combining n8n, the YouTube API, and Raindrop.io, you can implement a robust automation that continuously monitors a playlist and stores every new video as a structured bookmark.
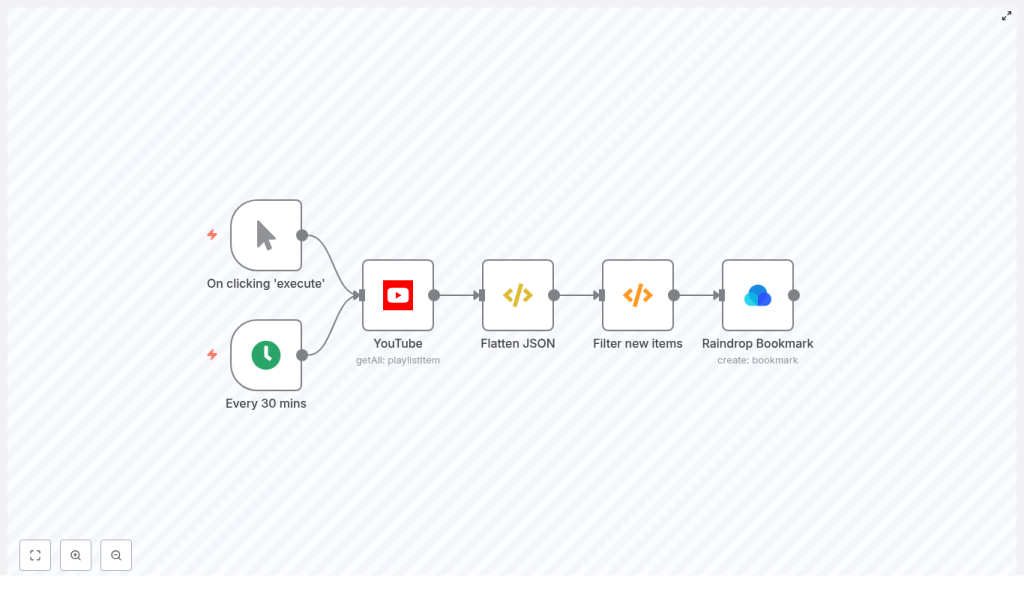
This article walks through an optimized n8n workflow template that:
- Polls a YouTube playlist on a fixed schedule
- Normalizes and filters the API response
- Tracks processed videos using workflow static data
- Creates Raindrop.io bookmarks for newly discovered items
Why automate YouTube to Raindrop.io with n8n?
For automation professionals, the benefits go beyond convenience. A fully automated YouTube-to-Raindrop workflow provides:
- Consistent capture – New videos are bookmarked as soon as they appear in the playlist, without manual intervention.
- Centralized knowledge base – Raindrop.io becomes the single source of truth for your video resources, accessible across devices and platforms.
- Structured enrichment – Tags, titles, and metadata can be standardized or dynamically generated, which improves searchability and downstream processing.
The result is a curated video library that is reliable, searchable, and integrated into your broader automation ecosystem.
Workflow architecture and core components
The workflow is designed around a simple polling pattern with idempotent processing. At a high level it:
- Starts on a schedule or manually for testing
- Fetches all items from a specified YouTube playlist
- Flattens the nested API response to simplify mapping
- Filters out videos that were already processed in previous runs
- Creates Raindrop.io bookmarks only for new videos
Key nodes used in the n8n workflow
- Cron (Every 30 mins) – Triggers the workflow on a recurring schedule. Default interval is 30 minutes, configurable as needed.
- Manual Trigger – Provides an on-demand entry point for initial testing and debugging.
- YouTube (playlistItem.getAll) – Retrieves all items from the specified playlist using the YouTube Data API.
- Flatten JSON (Function Item) – Extracts the
snippetobject from each playlist item to simplify downstream expressions. - Filter new items (Function) – Uses workflow static data to maintain a list of previously processed video IDs and outputs only new entries.
- Raindrop Bookmark (create) – Creates a bookmark in Raindrop.io for each new video, including title, URL, and tags.
Configuration prerequisites
YouTube API access and credentials
Before configuring the nodes, ensure you have valid Google OAuth2 credentials in n8n with permission to read YouTube playlist items.
- Create or reuse a Google Cloud project with YouTube Data API enabled.
- Configure OAuth2 credentials in n8n with the appropriate scopes to access playlist items.
- Confirm that the playlist you want to monitor is either public or owned by the authenticated account.
The YouTube node in this workflow uses the playlistItem.getAll operation, so the credentials must allow read access to that resource.
Raindrop.io credentials
For bookmark creation, configure Raindrop.io credentials in n8n:
- Use an OAuth token or API token that includes permission to create bookmarks.
- Identify the target collection ID in Raindrop.io. You can use
0for the default collection or specify a dedicated collection ID.
Detailed workflow setup in n8n
1. Configure the YouTube node
After adding your Google OAuth2 credentials, configure the YouTube node as follows:
- Resource:
playlistItem - Operation:
getAll - Playlist ID: Replace the placeholder
CHANGE_MEwith your actual playlist ID.
The playlist ID can be extracted from the playlist URL as the value after list=, for example:
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLw-VjHDlEOgs658sP9Q...Use that token (for example PLw-VjHDlEOgs658sP9Q...) as the playlistId in the node configuration.
2. Normalize the YouTube response with a Function Item node
The YouTube API returns a nested JSON structure where most of the useful metadata is contained within the snippet object. To simplify expressions in later nodes, use a Function Item node to replace each item with its snippet:
item = item["snippet"]
return item;After this step, each item passed downstream has the snippet fields at the root level of item.json, which makes it easier to access properties like title, videoOwnerChannelTitle, and resourceId.videoId.
3. Implement idempotency with workflow static data
To ensure that videos are bookmarked only once, the workflow relies on workflow static data. This provides persistent storage across executions within the same workflow and instance.
Use a Function node named for example Filter new items with the following code:
const staticData = getWorkflowStaticData('global');
const newIds = items.map(item => item.json["resourceId"]["videoId"]);
const oldIds = staticData.oldIds; if (!oldIds) { staticData.oldIds = newIds; return items;
}
const actualNewIds = newIds.filter((id) => !oldIds.includes(id));
const actualNew = items.filter((data) => actualNewIds.includes(data.json["resourceId"]["videoId"]));
staticData.oldIds = [...actualNewIds, ...oldIds];
return actualNew;
This logic works as follows:
- First run: If
oldIdsis undefined, the function seeds static data with the current playlist video IDs and returns all items. This prevents repeated bookmarking of existing videos in subsequent runs. - Subsequent runs: The function compares the current playlist video IDs against
oldIdsand returns only those items whose IDs were not previously recorded. It then updatesoldIdsby prepending the newly processed IDs.
4. Create Raindrop.io bookmarks from new items
After filtering, only new videos reach the Raindrop node. Configure the Raindrop Bookmark (create) node as follows:
- link:
=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v={{$json["resourceId"]["videoId"]}} - title:
={{$json["videoOwnerChannelTitle"]}} | {{$json["title"]}} - tags:
youtubeYou can later expand this to dynamic tags based on channel, keywords, or other metadata.
- collectionId: Set to
0for the default collection or the ID of a specific Raindrop collection.
Ensure the Raindrop.io credentials are correctly selected in this node so that bookmark creation is authorized.
5. Define triggers for production and testing
Use two separate triggers for different purposes:
- Cron node:
- Configure to run every 30 minutes by default.
- Adjust the interval based on playlist activity and API quota considerations.
- Manual Trigger node:
- Use for initial validation and troubleshooting.
- Connect it to the same downstream nodes so you can run the entire chain on demand from the n8n editor.
Operational best practices and optimization
Managing static data growth
In high-volume scenarios, the list of processed video IDs in workflow static data can grow significantly. To keep this under control and avoid unnecessary memory usage, replace the final assignment in the filter function with a capped and deduplicated version:
// Keep a unique capped history of processed IDs
const deduped = Array.from(new Set([...actualNewIds, ...oldIds]));
staticData.oldIds = deduped.slice(0, 1000); // keep last 1000 ids
This approach retains only the most recent 1000 unique IDs, which is sufficient for most playlist monitoring use cases while keeping the storage footprint predictable.
Adding content-based filters
In more advanced setups, you might not want to bookmark every video in a playlist. Instead, you can enrich the filter logic to only pass items that match specific criteria, such as keywords in the title or description.
Within the same Function node, extend the filtering logic like this:
const keywords = ['tutorial','deep dive'];
const actualNew = items.filter(data => { const title = (data.json.title || '').toLowerCase(); return actualNewIds.includes(data.json.resourceId.videoId) && keywords.some(k => title.includes(k));
});
This example only returns new videos whose titles contain the specified keywords, which is useful for curating long or mixed-content playlists.
Handling API quotas and rate limits
The workflow uses a polling strategy, so it is important to consider YouTube API quotas:
- Increase the polling interval if the playlist does not change frequently.
- Avoid monitoring very large numbers of playlists with aggressive schedules from the same API key.
- Implement retry strategies or exponential backoff in additional Function or Error Trigger workflows if you expect transient API errors.
On the Raindrop.io side, typical usage for bookmarking new playlist items rarely approaches rate limits, but you should still monitor usage if you scale the pattern across multiple workflows.
Advanced enhancements and integration ideas
Once the core workflow is stable, you can extend it to better fit your information architecture and automation strategy.
- Dynamic tagging:
- Generate tags from the video title, channel name, or playlist name.
- For example, add the channel as a tag to group content by creator.
- Richer bookmark metadata:
- Store the video description or key notes in the Raindrop note field.
- Save the thumbnail URL or other assets as part of the bookmark metadata.
- Notifications and downstream workflows:
- Trigger Slack, email, or mobile push notifications whenever a new bookmark is created.
- Feed new bookmarks into additional n8n workflows for review, tagging, or content analysis.
- Alternative persistence layer:
- If you need cross-workflow or cross-instance history, replace workflow static data with a database node (for example MySQL or PostgreSQL).
- Store video IDs and metadata in a table and query it to determine which items are new.
Testing, validation, and troubleshooting
Initial end-to-end test
Before enabling the Cron trigger in production:
- Use the Manual Trigger node to execute the workflow once.
- Inspect the execution log in n8n to verify:
- The YouTube node returns the expected playlist items.
- The Flatten JSON node exposes the correct snippet fields.
- The Filter new items node outputs the correct subset of videos.
- The Raindrop node successfully creates bookmarks with the expected URL, title, and tags.
- Confirm that the bookmarks appear in the intended Raindrop collection.
Common configuration issues
- Incorrect playlist ID:
- Ensure you are using the playlist ID, not the channel ID.
- Verify that the value after
list=in the URL is used in the YouTube node.
- Insufficient YouTube permissions:
- Recheck the OAuth2 scopes for your Google credential.
- Confirm the authenticated account can access the target playlist.
- Raindrop authentication problems:
- Validate that the token has bookmark creation permission.
- Confirm the specified collection ID exists and is accessible.
Conclusion
This n8n workflow template provides a clean, extensible pattern for synchronizing YouTube playlists with Raindrop.io. By leveraging scheduled polling, workflow static data, and structured metadata mapping, you achieve a reliable, idempotent process that continuously enriches your bookmark repository with new video content.
From there, it is straightforward to add keyword-based filters, manage history size, or integrate notifications and analytics, turning a simple bookmark sync into a powerful content curation pipeline.
Next steps: Import the template into your n8n instance, configure your YouTube playlist ID and credentials for both YouTube and Raindrop.io, then run it manually once for validation. After confirming the behavior, enable the Cron trigger to keep your Raindrop.io collection automatically updated with the latest videos.