n8n CI/CD Pipeline Auditor Workflow Guide
Follow the story of a DevOps engineer who turns chaotic CI/CD reviews into a smooth, automated process using an n8n workflow that audits pipeline configuration files with OpenAI and delivers polished HTML and email reports.
The problem: one engineer, too many pipelines
When Maya joined her new team as a DevOps engineer, she thought she was ready for anything. She had years of experience, a solid grasp of CI/CD, and a love for automation. What she did not expect was the sheer volume of pipeline files that needed review.
Every week, developers sent her YAML snippets, Jenkinsfiles, and Azure Pipelines configs through email, chat, and even screenshots in tickets. Some were neatly documented, others were mysterious blocks of configuration with no comments at all.
Her reality looked like this:
- No standard way to review pipelines across teams
- Long delays in giving feedback because everything was manual
- Developers confused by cryptic CI/CD configs and missing documentation
- Security and compliance concerns buried inside unreadable files
Each review required her to read through the pipeline, figure out who it was for, what problem it solved, and whether it followed best practices. Then she had to write a clear explanation and send it back in an email. It was important work, but it was also repetitive and slow.
Maya knew there had to be a better way. What she wanted was simple: a standardized, automated CI/CD audit that could turn raw pipeline files into human-readable reports, and send them directly to stakeholders.
The discovery: a CI/CD pipeline auditor template in n8n
One afternoon, while exploring ways to automate her workload, Maya came across an n8n workflow template called CI/CD Pipeline Auditor. The description immediately caught her eye. It promised to:
- Accept pipeline files through a form
- Use an OpenAI model to generate concise audits and documentation
- Email the results as an HTML report
- Return a polished HTML page right in the browser
In other words, exactly what she had been trying to cobble together by hand.
Under the hood, the workflow automated pipeline audits for teams that needed consistent, actionable reviews of YAML, Jenkinsfiles, and Azure Pipelines configurations. It was designed to standardize configuration reviews, save time, and make audits understandable for both engineers and non-technical stakeholders.
For Maya, this was not just a cool template. It was a potential escape from her never-ending backlog of manual CI/CD reviews.
How the workflow actually works: Maya follows the path
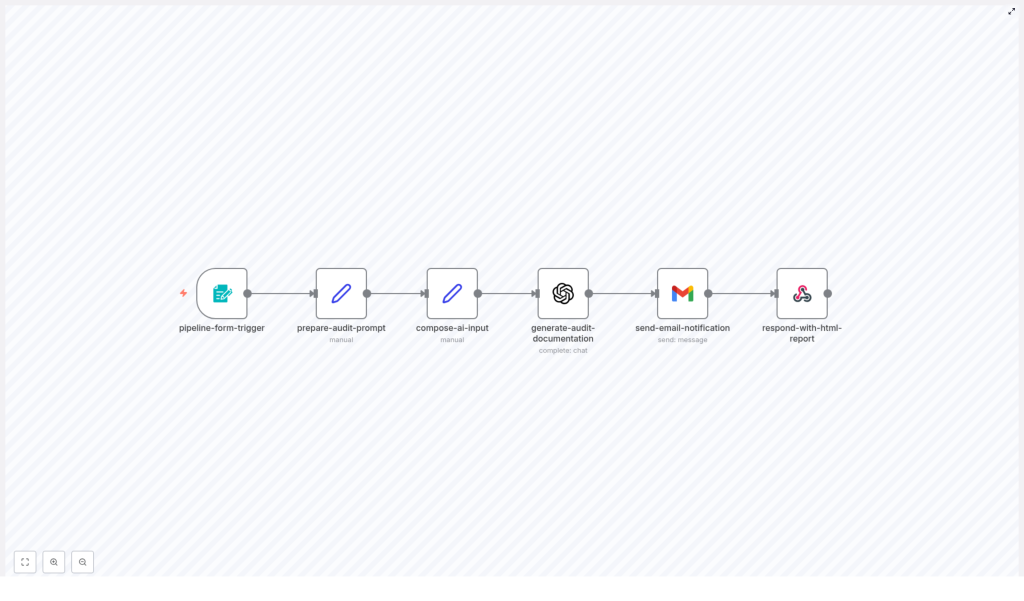
Before she trusted the template with real pipeline files, Maya wanted to understand exactly how it operated. She opened it in n8n and traced the linear flow of nodes from left to right.
The high-level journey of a pipeline file
- Form Trigger collects the pipeline name, pipeline file content, notification email, and pipeline type.
- Set (prepare prompt) builds a detailed prompt with guidelines and examples for OpenAI.
- Set (compose AI input) combines the form data and prompt into a single payload.
- OpenAI (generate audit) produces the audit documentation.
- Gmail (send email) delivers the audit as an HTML email to stakeholders.
- Respond to Webhook returns a polished HTML report directly to the browser or form submitter.
What impressed Maya was how each node had a clear purpose. It was not a messy tangle of logic. It was a straightforward pipeline for auditing pipelines.
Rising action: setting up the auditor in Maya’s environment
To bring the workflow to life, Maya needed a few essentials in place.
Prerequisites she prepared
- An n8n instance with internet access, running in her organization’s environment
- An OpenAI API key added to n8n credentials
- Gmail OAuth2 credentials, ready to use with the email node (or the option to swap to SMTP or SendGrid later)
- Optional but recommended: secure hosting for the webhook so teams outside the internal network could submit pipelines
Installation steps she followed
- Imported the workflow JSON into her n8n instance.
- Opened the Form Trigger node and customized the webhook path and form fields.
- Attached her OpenAI credential to the OpenAI node, set a GPT-4 class model, a moderate temperature (around 0.7), and a generous max tokens limit.
- Configured the Gmail node with OAuth2 details, keeping in mind she could switch to another provider if needed.
- Activated the workflow and prepared a sample pipeline file to test the entire flow.
With the basics wired up, the real test was about to begin.
The turning point: the first automated audit
Maya opened the form exposed by the pipeline-form-trigger node. The form was simple but purposeful, with fields that mapped directly to the workflow logic.
Step 1: submitting a pipeline via the form
The pipeline-form-trigger node provided these fields:
- Pipeline Name as a text input
- Pipeline File as a textarea where she pasted YAML or Jenkinsfile content
- Notification Email for whoever needed the report
- Pipeline Type as a dropdown with options like GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkinsfile, Azure Pipelines, and Other
This single form meant engineers could submit pipeline files for on-demand auditing without needing CLI tools or direct repository access. For Maya, it was the beginning of self-service CI/CD audits.
Step 2: preparing the AI audit prompt
Once the form was submitted, the prepare-audit-prompt Set node took over. Inside it, Maya found a carefully written prompt template for the OpenAI model.
The prompt instructed the model to produce a concise, actionable audit that covered:
- Who the pipeline is for
- The use case and problems it solves
- A clear pipeline overview, including triggers, jobs or stages, environment variables, and images
- Expected outcomes of running the pipeline
- Setup, rollout, and customization tips
- Security and compliance notes
Instead of leaving the model to guess, the node enforced a structured output that Maya could rely on.
Step 3: composing the AI input payload
The next Set node, compose-ai-input, combined the form data and the prompt into a single string payload. It merged:
- The raw pipeline configuration
- The instructions that defined how the audit should look
- Any context from the pipeline type dropdown
This ensured the OpenAI node received everything it needed in one well-structured request.
Step 4: generating the audit with OpenAI
The generate-audit-documentation node was where the magic happened. Using an OpenAI Chat model, configured with GPT-4 class capabilities, it generated the final audit text.
With a moderate temperature and a generous token limit, the model could provide detailed but focused analysis. Maya watched the first run and saw the AI return a full breakdown of her sample pipeline, including explanations and recommendations.
Step 5: emailing the results
Next, the send-email-notification Gmail node took the AI output and wrapped it into an HTML email. It sent the message to the notification address provided in the form, complete with a summary header and formatted sections.
She had already configured OAuth2 credentials in n8n, so the email arrived within seconds. For the first time, a pipeline audit landed in her inbox without her writing a single line of explanation manually.
Step 6: returning a polished HTML report
Finally, the respond-with-html-report node returned a styled HTML page directly to the browser. The template included simple styling, a success badge, and the audit content formatted for readability.
Anyone who submitted a pipeline through the form would see an instant, well-structured report without waiting for a human response.
The result: consistent audits and a calmer DevOps life
Within a week of rolling out the workflow, Maya noticed a shift.
- Configuration reviews became standardized across teams.
- Developers received clear, human-readable audit reports instead of raw YAML feedback.
- Email delivery and HTML output were fully automated, freeing her from repetitive explanations.
- OpenAI’s recommendations were concise and actionable, helping teams improve pipelines faster.
The workflow did not replace her expertise, but it amplified it. She could focus on complex edge cases and architectural decisions instead of re-explaining the same CI/CD basics for every new pipeline.
Going further: how Maya customized the n8n template
Once the core workflow was stable, Maya started extending it to match her organization’s needs. The template was intentionally modular, so customization felt natural.
Ideas she explored
- Adding a code scanner node to run tools like
yamllintorhadolintbefore the audit. - Integrating a secrets scanner, such as GitGuardian, before sending content to OpenAI.
- Persisting audits to a database like MySQL or Postgres for historical tracking.
- Creating tickets in Jira whenever a pipeline needed follow-up work.
- Sending results to Slack or Microsoft Teams channels for faster collaboration.
- Posting audit summaries as comments on GitHub pull requests instead of or in addition to email.
- Introducing role-based access controls and an approval step for production pipeline changes.
Each enhancement built on the same foundation: a simple form, a well-crafted AI prompt, and a clear reporting flow.
Security and compliance: what she put in place
Because the workflow passed pipeline configuration to a third-party model, Maya treated security and compliance as first-class concerns.
She implemented several best practices:
- Masked or removed secrets such as API keys and passwords before sending any content to OpenAI.
- Limited exposure of private repository details by fetching config files server-side whenever possible, instead of asking users to paste sensitive content.
- Used organizational OpenAI access controls and data usage policies to manage how data was handled.
- Logged who requested each audit and defined a retention policy for audit data.
These safeguards allowed her to benefit from automated audits without compromising sensitive information.
Best practices Maya learned while tuning the workflow
Over time, Maya refined the template to make the audits even more reliable and useful.
- She made the OpenAI prompt very explicit about the output structure to ensure consistent formatting.
- She kept the model focused on actionable steps, preferring brevity and clarity over long, unfocused analysis.
- She used the pipeline type dropdown to give the model context, such as whether it was GitHub Actions or a Jenkinsfile.
- She added an initial validation step to catch syntax issues in YAML before sending it to the model.
- She experimented with adding a severity score or checklist style output for quick triage.
These small adjustments turned the workflow from a generic template into a dependable internal tool.
What the AI-generated audit looks like
The prompt in Maya’s workflow asked OpenAI to return a structured audit with clear sections. A typical output followed a pattern like this:
# Who is this pipeline for?
# What problem does this pipeline solve?
# Pipeline Overview
- Triggers
- Jobs/Stages
- Key steps
- Environment variables
# Expected Outcomes
# Setup & Rollout Instructions
# How to customize
# Security & Compliance Considerations
Because the structure was predictable, it was easy to scan, share, and even parse programmatically for further automation.