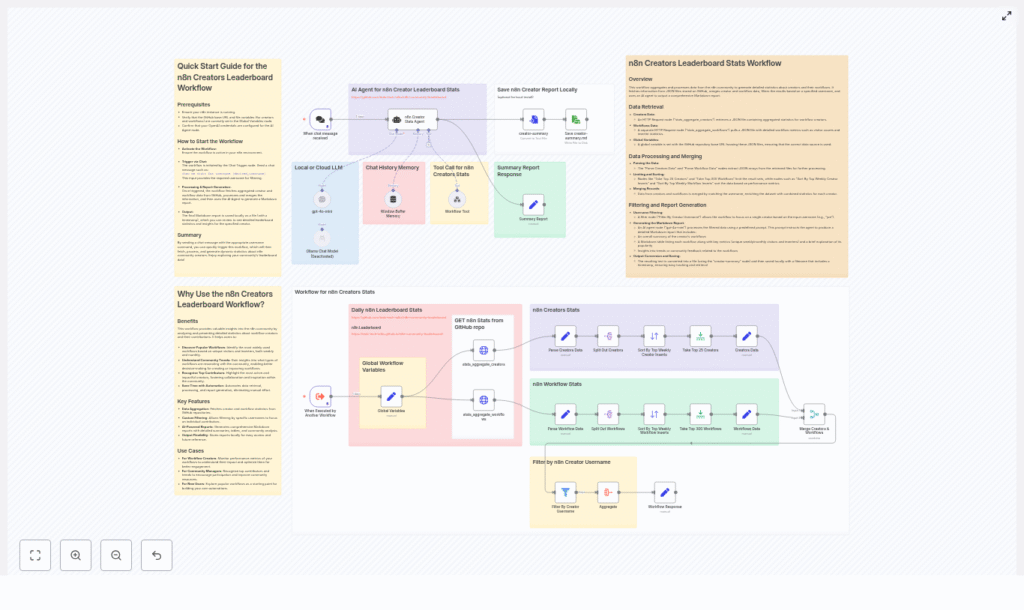
n8n Creators Leaderboard Stats Workflow: Automated Creator Intelligence for n8n Libraries
The n8n Creators Leaderboard Stats Workflow is an automation blueprint for aggregating community performance data and transforming it into AI-generated Markdown reports. It pulls JSON statistics from a GitHub repository, correlates creator and workflow metrics, and produces structured insights that highlight the most impactful contributors and automations. This workflow is particularly suited for community managers, platform operators, and automation professionals who require repeatable, data-driven reporting.
Strategic value for community-led platforms
As marketplaces and workflow libraries scale, the volume of available automations grows faster than manual analysis can keep up. Systematic insight into which creators and workflows drive engagement is critical for:
- Recognizing top contributors and showcasing exemplary workflows to the broader community.
- Monitoring adoption trends using metrics such as unique visitors and inserters across time windows.
- Automating reporting for internal reviews, community updates, newsletters, and dashboards.
By embedding these analytics into an n8n workflow, you obtain a repeatable and auditable process instead of ad hoc, manual data pulls.
Workflow overview and architecture
The workflow implements a linear but extensible pipeline, designed around best practices for data ingestion, transformation, and AI-assisted reporting. At a high level, it performs the following stages:
- Data ingestion – Fetch aggregated JSON metrics from a GitHub repository via HTTP.
- Normalization – Extract and standardize creator and workflow records into consistent arrays.
- Ranking – Sort by key performance indicators and limit to top creators and workflows.
- Enrichment – Merge creator-level and workflow-level data on username.
- Targeted filtering – Optionally narrow results to a specific creator when required.
- AI-driven reporting – Use an LLM to generate a Markdown report with tables and qualitative analysis.
- File output – Persist the Markdown report as a timestamped file to a designated location.
This modular structure makes it straightforward to adapt the workflow to different data sources, metrics, or reporting formats while retaining a clear operational flow.
Key building blocks in n8n
1. Data retrieval layer
The workflow begins with two HTTP Request nodes that access JSON files hosted in a GitHub repository:
- One JSON file contains aggregated creator statistics.
- The other contains workflow-level metrics.
A Global Variables node stores the base GitHub path, which allows you to redirect the workflow to a different repository, branch, or analytics source without modifying multiple nodes. This is a recommended best practice for maintainability and environment-specific configuration.
2. Parsing and preprocessing
Once the JSON documents are retrieved, the workflow uses a combination of Set and SplitOut nodes to:
- Extract the
dataarrays that hold the creators and workflows. - Normalize field names and structures so that subsequent nodes can operate consistently.
To keep the processing scope manageable and focused on the most relevant entries, Sort and Limit nodes are applied. For example:
- Limit to the top 25 creators based on the chosen metric.
- Limit to the top 300 workflows for detailed analysis.
Sorting can be tuned to prioritize particular KPIs such as weekly unique visitors or inserters, depending on your reporting goals.
3. Merging and optional filtering
The workflow then correlates creator and workflow datasets using a Merge node. The merge operation:
- Matches records on the
usernamefield. - Enriches each workflow with its associated creator data, providing a unified view of performance.
A subsequent Filter node can be used to restrict the output to a single creator. This is particularly useful when the workflow is triggered interactively. For example, a chat-based interaction such as show me stats for username joe can be translated into a JSON payload that selects only that creator’s data for the report.
4. AI-powered Markdown report generation
The consolidated dataset is passed to an AI Agent node configured with your preferred LLM (for example, OpenAI). The agent is typically set with a relatively low temperature to favor consistency and accuracy over creativity.
The prompt is structured to instruct the model to produce a comprehensive Markdown report that includes:
- A concise but detailed summary of the creator and their overall impact.
- A Markdown table listing workflows with metrics such as:
- Unique weekly visitors
- Unique monthly visitors
- Unique weekly inserters
- Unique monthly inserters
- Community analysis describing why certain workflows perform well.
- Additional insights such as emerging trends and recommended next steps.
By codifying the report structure in the prompt, you can maintain consistent output across runs and make downstream consumption easier for both humans and systems.
5. Output and file handling
After the AI agent returns the Markdown content, the workflow converts it into a file and writes it to the configured local filesystem. The filename includes a timestamp, which simplifies versioning, auditability, and integration with downstream processes such as newsletters or dashboards.
Deployment and execution: quick start guide
- Prepare the analytics source
Clone the repository that contains the aggregated creator and workflow JSON files, or host your own JSON data in a similar structure. - Configure the GitHub base path
Update the Global Variables node in n8n with the base GitHub URL that points to your JSON files. - Set up LLM credentials
Ensure your OpenAI or other LLM credentials are correctly configured for the AI Agent node. - Activate the workflow
Enable the workflow in your n8n instance. - Trigger the workflow
Use either:- A chat trigger for conversational queries.
- An execute-workflow trigger that receives JSON input, for example:
{"username": "joe"}.
- Review the generated report
Locate the Markdown file in the configured output directory. Confirm the timestamped filename and validate that the content matches your expectations.
Primary use cases and stakeholders
- Community managers
Generate weekly or monthly creator leaderboards, highlight trending workflows, and share insights in community updates or newsletters. - Individual creators
Track which workflows gain traction, refine documentation, and plan content or feature updates based on user behavior. - Platform and product owners
Use aggregated metrics to prioritize improvements, select workflows for featured placement, and inform roadmap decisions.
Customization and extension strategies
The workflow is intentionally designed to be adaptable. Common customization patterns include:
- Alternative analytics sources
Adjust the GitHub base path variable to point to your own metrics repository or analytics pipeline. As long as the JSON structure preserves the expecteddataarrays, minimal changes are required. - Different ranking criteria
Change the Sort node configuration to emphasize different KPIs, such as:- Unique weekly inserters for adoption intensity.
- Monthly visitors for long-term visibility.
- Enhanced AI prompts
Extend the AI agent prompt to add new sections, for example:- Technical deep dives into workflow design.
- Sample usage scenarios or code snippets.
- Interview-style commentary for featured creators.
- Alternative storage backends
Instead of writing to the local filesystem, switch to a cloud-based target such as Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage. This is useful for CI/CD pipelines, multi-node deployments, or centralized reporting.
Troubleshooting and operational considerations
Missing or incomplete JSON data
If the workflow fails to retrieve data or fields appear empty, verify the following:
- The Global Variables base path matches the actual GitHub repository and branch.
- The filenames used in the HTTP Request nodes are correct.
- The JSON documents contain the expected
dataarrays for both creators and workflows.
Suboptimal AI report quality
If the AI-generated Markdown is inconsistent or lacks structure:
- Reduce the temperature setting to encourage more deterministic responses.
- Refine the system prompt and include explicit examples of the desired table format and sections.
- Clarify which metrics must always be present in the output.
File write or permission errors
When the workflow cannot save the Markdown file:
- Confirm that the n8n process has write permissions on the target directory.
- Consider writing to an n8n workspace or a managed storage service if local permissions are constrained.
Security and privacy best practices
The reference implementation reads metrics from public GitHub JSON files. Even in this scenario, you should:
- Avoid embedding sensitive information in public JSON documents.
- If you rely on private metrics, store JSON files in a private repository and configure secure credentials for n8n.
- Review AI-generated reports for any personally identifiable information (PII) and apply anonymization or redaction where necessary.
Adhering to these practices ensures that automation does not inadvertently expose confidential data.
Expected report output
The final Markdown file produced by the workflow typically contains:
- A narrative summary of the creator’s performance and contribution to the ecosystem.
- A structured Markdown table listing each workflow with its key metrics, including weekly and monthly visitors and inserters.
- Community-oriented analysis that explains why certain workflows resonate with users.
- Forward-looking insights such as trends, opportunities for optimization, and recommended next steps for the creator or platform team.
This format is well suited for direct publication in documentation sites, internal reports, or community announcements.
Getting started with the template
To adopt the n8n Creators Leaderboard Stats Workflow in your environment:
- Clone the project that contains the workflow and analytics JSON files.
- Configure the Global Variables node to point to your GitHub metrics source.
- Set up your LLM credentials and validate the AI Agent configuration.
- Activate and trigger the workflow in n8n, then review the generated Markdown output.
Call to action: Visit the GitHub repository at https://github.com/teds-tech-talks/n8n-community-leaderboard to obtain the workflow files, run them locally, and contribute enhancements. For assistance with prompt engineering, output customization, or integration patterns, reach out to the author or join the n8n community chat.
Pro tip: Add a scheduled trigger or cron-based node to generate reports at fixed intervals. You can then pipe the Markdown files into your newsletter workflow or internal analytics dashboard for fully automated community reporting.