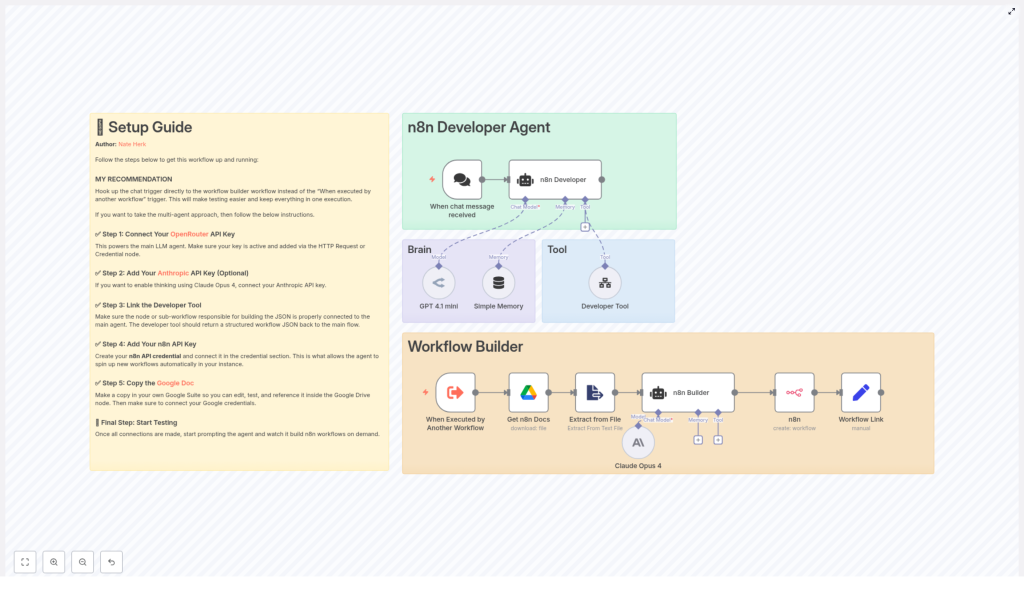
n8n Developer Agent: Build Workflows with LLMs
The n8n Developer Agent template connects low-code workflow automation with large language models (LLMs) so you can generate complete, importable n8n workflow JSON from plain language requests. This guide walks you through what the Developer Agent is, how it works inside n8n, how to set it up, and how to use it safely in real projects.
Learning goals
By the end of this tutorial-style article, you will be able to:
- Explain what the n8n Developer Agent does and how it uses LLMs
- Understand each component in the template, from chat trigger to n8n API
- Configure the template step by step in your own n8n instance
- Write effective prompts that produce useful workflow JSON
- Test, validate, and safely deploy LLM-generated workflows
Concept overview: What is the n8n Developer Agent?
The n8n Developer Agent is a multi-agent workflow pattern that turns natural language instructions into complete n8n workflow JSON that you can import directly into your instance. Instead of manually adding nodes, wiring connections, and configuring settings, you describe the workflow in plain language and let the LLM handle the technical details.
At a high level, the template combines:
- A chat trigger that collects your request exactly as you typed it
- An LLM-powered developer tool that outputs pure workflow JSON
- Memory to keep short-term context across back-and-forth conversations
- Supporting integrations such as Google Drive and the n8n API to provide documentation and to create workflows programmatically
Key benefits of using the Developer Agent
- Rapid prototyping – Turn a simple text request into a working n8n workflow JSON in minutes.
- Less manual configuration – The LLM creates nodes, connections, and settings for you.
- Repeatable structure – The JSON is formatted for direct import into n8n, which makes it easy to reuse and adapt.
How the Developer Agent works inside n8n
To understand the template, it helps to walk through the data flow: from your chat message, through the LLM, to a finished workflow in your n8n instance.
1. Chat trigger – capturing user intent
The workflow starts with a chat trigger node. This node receives your natural language description of the workflow you want. For example:
“Create a workflow that reads new Google Drive files and posts them to Slack.”
The important detail is that the chat trigger passes your message to the agent without changing the wording. The LLM developer tool receives your exact instruction, which reduces the chance of misinterpretation.
2. LLM agents and the developer tool
After the chat trigger, the template routes your prompt to the main LLM agent. This agent is configured with a developer tool, powered by an LLM such as OpenRouter or Anthropic, that has one specific job:
Produce a valid JSON object that represents a complete n8n workflow.
The JSON output is expected to include:
nodesarrayconnectionsobject- workflow settings and metadata
- sticky notes documenting credentials or configuration steps
The agent uses a strict system message so the LLM knows it must return JSON only, with no extra explanations or commentary. This is critical for reliable import into n8n.
3. Supporting nodes and context
Around the main agent, the template includes several supporting nodes that help the LLM generate better workflows and apply them automatically:
- Google Drive node – Downloads a reference documentation file that provides internal guidelines or examples for the LLM.
- Extract-from-File node – Parses content from the downloaded documentation so it can be used as context in the prompt.
- n8n API node – Uses the generated JSON to create new workflows programmatically in your n8n instance.
- Memory buffer node – Stores short-term conversational context, which is useful if you refine the workflow over several messages.
These pieces work together so that a single natural language request can move through the system and come out as a ready-to-import workflow, or even a workflow that is already created in your instance.
Step-by-step setup guide
In this section, you will configure the template in your own n8n environment. Follow the steps in order for a smooth setup.
Step 1 – Connect your main LLM provider (OpenRouter or similar)
The core of the Developer Agent is its connection to an LLM. Most commonly, this is done through OpenRouter or another compatible provider.
- Obtain an API key from your chosen LLM provider.
- In n8n, create a credential for that provider. This is typically done using:
- An HTTP Request credential configured with your API key, or
- A dedicated LLM credential type if available in your n8n version.
- Link this credential to the nodes that call the LLM so the agent can generate workflow JSON.
Step 2 – (Optional) Add Claude / Anthropic as a secondary model
You can optionally use Claude (Anthropic) as a second model for more complex reasoning or comparison.
- Get your Anthropic API key.
- Create an Anthropic credential in n8n.
- Configure the workflow so that Claude is used for:
- Intermediate “thinking” steps, or
- Drafting and comparing potential workflow outputs before finalizing the JSON.
This is optional, but it can improve the quality of generated workflows in complex scenarios.
Step 3 – Configure the Developer Tool
The Developer Tool node (or sub-workflow, depending on your template version) is the component that turns your prompt into JSON.
Make sure it is set up to:
- Receive the unmodified user prompt directly from the chat trigger or agent
- Use a strict system message that instructs the LLM to:
- Return only valid JSON
- Include all required n8n workflow fields
- Add sticky notes for any manual configuration or credentials
- Return a response that is immediately usable as n8n workflow JSON
Step 4 – Add your n8n API credential
To let the template create workflows automatically in your instance, you need an n8n API credential.
- In n8n, create an API key or token with permissions to create workflows.
- Create an n8n API credential and store the key there.
- In the template, connect this credential to the n8n API node that performs a
POSTrequest with the generated JSON.
When configured correctly, the workflow can send the JSON to your n8n instance and receive a link to the newly created workflow in return.
Step 5 – Provide reference documentation via Google Drive
The template includes a Google Drive node that downloads an internal documentation file. This document gives the LLM more context about your preferred patterns, naming conventions, or internal rules.
- Copy the provided documentation file into your own Google Drive.
- In n8n, set up a Google OAuth2 credential that grants read access to that file.
- Update the Google Drive node in the template to:
- Use your OAuth2 credential
- Point to the correct file or folder ID
The content of this file is then parsed by an Extract-from-File node and used to give the LLM richer context when generating workflows.
Using the Developer Agent effectively
Designing strong prompts
The quality of the generated workflow depends heavily on the prompt you provide. Good prompts are specific and structured.
Include the following in your request:
- Clear goal – What business outcome or automation do you want? Example: “Monitor a Google Drive folder and post the names of new files to Slack.”
- Required integrations – Mention tools like Slack, Google Drive, Gmail, GitHub, databases, or APIs.
- Constraints and behavior – Error handling, retry logic, scheduling, or filtering rules.
The developer tool is configured to output JSON only. If your prompt is vague or contradictory, the LLM is more likely to miss nodes or produce incomplete workflows.
Validating and testing generated workflows
Treat LLM-generated workflows as prototypes that still need validation. Follow this checklist:
- Test in a safe environment – Use a staging or development n8n instance before production.
- Inspect the JSON structure – Confirm that the
nodesarray andconnectionsobject are present and consistent. - Set credentials manually – The JSON should refer to credential names, not raw keys. Add or map credentials inside n8n as needed.
- Use sticky notes as a checklist – The template includes sticky notes that highlight remaining manual steps, such as connecting specific OAuth credentials.
- Run a dry run – Trigger the workflow with test data and verify each node behaves as expected.
Security and credential best practices
When working with LLM-generated automation, keep security in mind:
- Never hard-code API keys in the generated JSON. Use n8n credential references instead.
- Document required credentials with sticky notes or node descriptions, not by embedding secrets.
- Apply least-privilege access to all service accounts and API tokens used by the workflow.
- Review permission scopes for integrations like Google Drive, Slack, or GitHub.
Common use cases for the n8n Developer Agent
Once the template is set up, you can use it as a kind of “workflow generator” for many scenarios.
- Integration scaffolding Generate starter workflows that connect services such as Gmail, Google Drive, and Slack. You can then refine the generated workflow manually.
- Rapid onboarding for business users Give non-technical teammates a chat interface where they can request automations without writing any JSON or touching the editor.
- Prototyping data pipelines Let the LLM create ETL-like workflows, for example: parse files from Google Drive, transform the data, and send it into a database or external API.
- Batch automation templates Produce multiple variations of a similar workflow by changing only a few parameters in the prompt, such as the source folder, target channel, or filter conditions.
Troubleshooting guide
Issue: LLM output is not valid JSON
If the response from the developer tool is not clean JSON, check the following:
- System prompt configuration Make sure the system message for the developer tool clearly requires:
- JSON only, with no explanations
- No markdown formatting or backticks
- Unmodified user prompt Confirm that the chat trigger passes your message directly without adding extra text that might confuse the model.
- Post-processing step If needed, add a simple parsing or “output cleaning” step to extract the JSON block if the model still adds surrounding text.
Issue: Workflow imports fail in n8n
If n8n rejects the JSON during import or when using the n8n API:
- Check node types Make sure each node type exists in your version of n8n. Newer node types might not be available in older instances.
- Verify required fields Confirm that node IDs, parameters, and the
connectionsstructure are present and consistent. - Review API logs If you are importing via the n8n API node, inspect the response and logs to see which element is causing the failure.
- Use the n8n import UI Try importing the JSON manually through the n8n interface to get more detailed error messages.
Real-world governance and review
LLM-driven workflow generation can significantly accelerate development, but it should be integrated into a broader governance process.
- Human review step Have an engineer or power user review each generated workflow before it is promoted to production.
- Comprehensive testing Test edge cases, error paths, and integration failures, not just the happy path.
- Role-based access control Limit who can run, edit, or deploy generated workflows, especially those that touch sensitive data.
Walkthrough example: from prompt to workflow
To tie everything together, here is a simple example you can try once your template is configured:
- Open the chat interface connected to the Developer Agent template.
- Enter the prompt: “Create a workflow that watches a Google Drive folder and posts new file names to Slack.”
- The chat trigger passes your prompt to the LLM developer tool.
- The LLM generates workflow JSON with: