n8n + LINE Messaging API: Reply & Push Technical Guide
Learn how to integrate the LINE Messaging API with n8n to automatically reply to incoming messages using replyToken and to push outbound messages to specific users. This guide walks through a ready-to-use n8n workflow template, explains the difference between Reply and Push APIs, and covers configuration, testing, and security considerations.
1. Technical Overview
This workflow template connects LINE Messaging API events to n8n so you can:
- Reply with
replyTokenwhen LINE sends amessageevent to your webhook. - Push messages to a known LINE user ID (UID) on demand from n8n.
The implementation uses only standard n8n nodes and the official LINE HTTP endpoints, so it can be deployed on any n8n instance (self-hosted or cloud) without custom code.
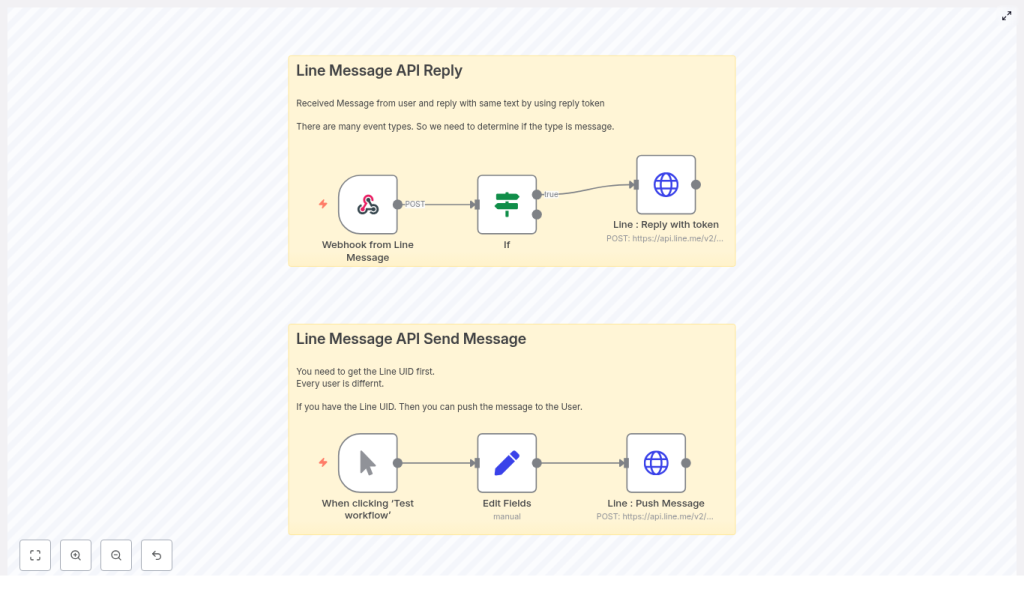
2. Workflow Architecture
The template is composed of two logical flows that share the same LINE channel credentials:
2.1 Inbound flow – Reply using replyToken
- Webhook from Line Message (Webhook node) Receives HTTP POST requests from LINE Messaging API.
- If (event type check) Filters incoming events so only
messageevents are processed. - Line: Reply with token (HTTP Request node) Calls
/v2/bot/message/replywith thereplyTokenfrom the webhook payload.
2.2 Outbound flow – Push message to a known UID
- Manual Trigger Starts the workflow manually from within the n8n editor for testing.
- Edit Fields (Set node) Injects a
line_uidfield into the item for use in the push request. - Line: Push Message (HTTP Request node) Calls
/v2/bot/message/pushwith the specifiedline_uid.
Both flows rely on the same Channel Access Token for authentication against the LINE Messaging API.
3. Prerequisites & LINE Channel Setup
3.1 Create a Messaging API channel
In the LINE Developers Console, create a new Messaging API channel. From the channel settings, obtain:
- Channel Access Token A long-lived token used as a Bearer token in the
Authorizationheader for all HTTP calls to LINE. - Channel Secret A secret used to validate the
X-Line-Signatureheader on incoming webhook requests.
3.2 Configure webhook URL in LINE console
Once your n8n Webhook node is configured (see below), set the webhook URL in the LINE Developers Console to:
{YOUR_N8N_PUBLIC_URL}/{WEBHOOK_PATH}For local development, use ngrok or a similar tunneling tool to expose your local n8n instance. The public ngrok URL should be used as {YOUR_N8N_PUBLIC_URL}.
4. Node-by-Node Breakdown
4.1 Webhook from Line Message (Webhook node)
This node is the entry point for all LINE events.
- HTTP Method:
POST - Path: e.g.
638c118e-1c98-4491-b6ff-14e2e75380b6(You can use any unique path; just ensure it matches what is configured in the LINE console.)
LINE sends a JSON structure that includes an events array. The workflow assumes at least one event is present and accesses the first element via:
$json.body.events[0]4.1.1 Typical event payload structure
Although the full payload is not reproduced here, the workflow accesses the following keys:
body.events[0].type– event type, for example"message"body.events[0].replyToken– token used for the Reply APIbody.events[0].message.text– text content of the incoming messagebody.events[0].source.userId– LINE UID of the sender
4.2 If node – Filter event type
The If node ensures that only message events are passed to the Reply API logic. This avoids running reply logic for follow, unfollow, join, postback, or other event types.
The condition is configured as:
Condition: {{$json.body.events[0].type}} == "message"Items that match the condition go to the true branch and are processed by the Reply HTTP Request node. Items that do not match can be ignored or routed elsewhere, depending on how you extend the workflow.
4.3 Line: Reply with token (HTTP Request node)
This node calls the LINE Reply API to send an immediate response to the user who triggered the event.
4.3.1 HTTP configuration
Method: POST
URL: https://api.line.me/v2/bot/message/reply
Headers: Authorization: Bearer {CHANNEL_ACCESS_TOKEN}
Content-Type: application/json4.3.2 JSON body in the workflow
The template uses n8n expressions to map the incoming replyToken and message text into the reply:
{ "replyToken": "{{ $('Webhook from Line Message').item.json.body.events[0].replyToken }}", "messages": [ { "type": "text", "text": "收到您的訊息 : {{ $('Webhook from Line Message').item.json.body.events[0].message.text }}" } ]
}Key points:
replyTokenis short-lived It can only be used once and must be used quickly after the event is received. If it expires or is used twice, the API will return an error.- Message format The
messagesarray follows LINE’s standard message object schema. Here it sends a singletextmessage that echoes the user input.
4.4 Manual Trigger node
The Manual Trigger node is used purely for testing the Push API flow from the n8n editor. It does not receive data from LINE directly. When you click “Test workflow”, this node emits a single empty item that is then enriched by the Set node.
4.5 Edit Fields (Set node)
The Set node is used to add a field containing the target user’s LINE UID:
- Field name:
line_uid - Value: a sample UID or an expression, for example:
Uxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
In production, you would typically populate line_uid from a database, Google Sheets, or from previously stored webhook data.
4.6 Line: Push Message (HTTP Request node)
This node sends proactive messages to users using the LINE Push API.
4.6.1 HTTP configuration
Method: POST
URL: https://api.line.me/v2/bot/message/push
Headers: Authorization: Bearer {CHANNEL_ACCESS_TOKEN}
Content-Type: application/json4.6.2 JSON body in the workflow
{ "to": "{{ $json.line_uid }}", "messages": [ { "type": "text", "text": "推播測試" } ]
}Important details:
tofield Must contain a valid LINE UID that is associated with your channel. The template reads it from$json.line_uid, which is set in the previous node.- Message content Currently a static text message (
"推播測試"). You can replace this with expressions or variables from earlier nodes.
4.6.3 Obtaining the LINE UID
To get a user’s UID, you can:
- Extract it from webhook events:
$json.body.events[0].source.userId - Use LINE Login flows where applicable to retrieve user identifiers.
Always handle UIDs as personal data. Obtain consent before storing them and avoid exposing them in logs or public endpoints.
5. Configuration & Credentials in n8n
5.1 Storing the Channel Access Token
For security, do not hard-code the Channel Access Token in node parameters. Instead:
- Create an HTTP Request credential or use environment variables in n8n.
- Reference the token via n8n’s credential system in the HTTP Request nodes.
5.2 Webhook URL and path alignment
Ensure that:
- The Webhook node path (for example
638c118e-1c98-4491-b6ff-14e2e75380b6) matches the path appended to your n8n public URL. - The resulting full URL is exactly the same as the one configured in the LINE Developers Console.
5.3 replyToken vs Push API usage
- Reply API Used for immediate, event-driven responses. Requires
replyTokenfrom the current event and must be called within a short time window. - Push API Used for proactive messages that are not directly tied to a specific incoming event. Requires the user’s UID and appropriate channel permissions.
6. Security & Best Practices
- Verify incoming webhooks Use the
X-Line-Signatureheader and your Channel Secret to validate that requests actually come from LINE. Implement this verification in a Code node or external reverse proxy if needed. - Protect credentials Store the Channel Access Token and Channel Secret in n8n credentials or environment variables. Avoid committing them to version control or exposing them in logs.
- Handle UIDs as sensitive data Treat LINE UIDs as personal identifiers. Do not expose them publicly and ensure any persistence complies with your privacy policy and user consent.
- Respect messaging policies Use the Reply API for direct responses to user actions. Use the Push API only when you have explicit permission to send users proactive notifications.
7. Testing & Troubleshooting
7.1 Webhook not firing
If the Webhook node does not receive events:
- Confirm the webhook URL in the LINE Developers Console exactly matches your n8n Webhook URL and path.
- If running n8n locally, ensure ngrok (or similar) is active and that you updated the LINE console with the current public URL.
- Check that the webhook is enabled in the LINE channel settings.
7.2 Reply not delivered
If the Reply API call fails or messages do not appear in LINE:
- Verify that you are using the exact
replyTokenfrom the current event payload. - Inspect the HTTP Request node’s response body in n8n for error codes such as expired token, invalid access token, or rate limiting.
- Ensure the Reply HTTP Request node is only executed once per incoming event.
7.3 Push API errors
If the Push API returns an error:
- Confirm that the
tofield contains a valid and correct LINE UID. - Check that your channel is allowed to send push messages and is not restricted by account or plan limitations.
- Review the error message returned by LINE in the HTTP Request node’s response for more detail.
8. Reference: JSON Bodies Used in the Template
8.1 Reply node JSON body
{ "replyToken": "{{ $('Webhook from Line Message').item.json.body.events[0].replyToken }}", "messages": [ { "type": "text", "text": "收到您的訊息 : {{ $('Webhook from Line Message').item.json.body.events[0].message.text }}" } ]
}8.2 Push node JSON body
{ "to": "{{ $json.line_uid }}", "messages": [ { "type": "text", "text": "推播測試" } ]
}9. Common Use Cases for This Template
- Auto-reply confirmations Send instant acknowledgements such as “order received” or “appointment booked” whenever a user messages your LINE bot.
- Customer support triage Automatically reply with basic information or routing questions before handing off to a human agent.
- Event-driven notifications Trigger push messages to known users when external events occur, such as system alerts or CRM updates.
- Keyword-based chatbots Use n8n logic and external APIs to respond differently based on message content, while still using the Reply and Push APIs.
10. Advanced Customization Ideas
Once the base template is working, you can extend it in several directions:
- Richer event handling Enhance the
Ifnode or add additional logic to distinguish between text, images, stickers, and other message types. - Persistence layer Connect a database or Google Sheets node to store user UIDs, preferences, and interaction history.
- Advanced message formats Integrate LINE Rich Messages or Flex Messages to provide more sophisticated UI elements in replies and push messages.
For deeper API details and rate limits, refer to the official LINE Messaging API documentation. You can also explore n8n community examples for additional LINE integration patterns.