Build a RAG Agent with Memory using n8n, Supabase & Postgres
Ever had a user ask, “Wait, what did I say earlier?” and your chatbot just stares back like it has the memory of a goldfish? Or spent way too much time copy-pasting docs into prompts like some kind of highly paid human OCR?
This is exactly the kind of repetitive pain this n8n workflow template is here to fix. With it, you can build a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) agent that:
- Remembers past conversations using Postgres chat memory
- Finds the right information using a Supabase vector store
- Ingests binary files from Google Drive and turns them into searchable embeddings
In other words, you get a chat agent that is not only smart, but also remembers what you told it and actually reads your documents. Let’s walk through what this template does, how the pieces fit together, and how to get it running without losing your weekend.
What this n8n RAG template actually does
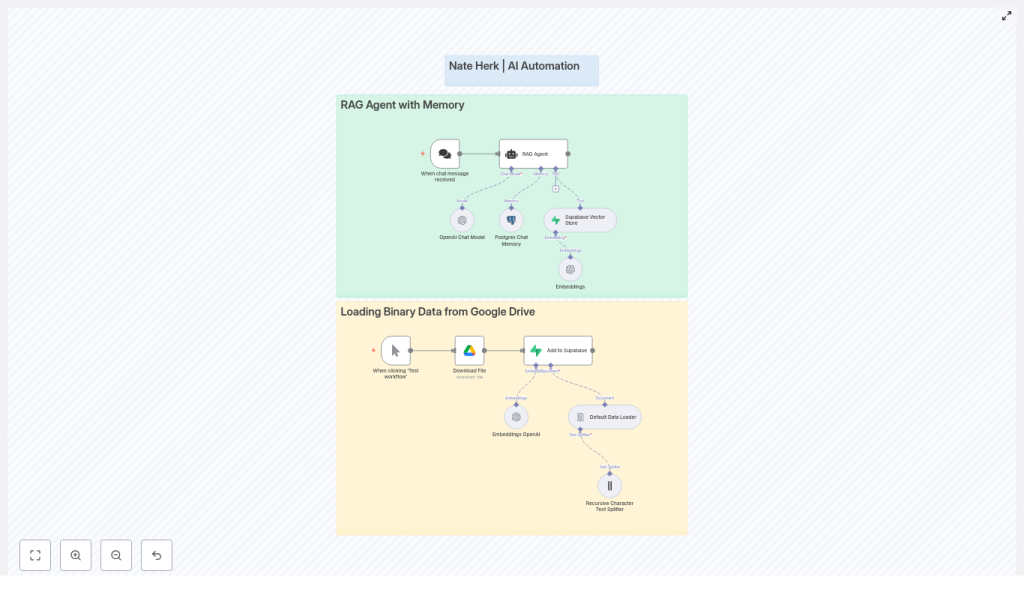
The workflow is split into two main superpowers, each represented as its own section in n8n:
1. RAG Agent with Memory (the conversational brain)
This part of the workflow is what users interact with. It:
- Receives incoming chat messages
- Uses an OpenAI chat model (like
gpt-4o-minior another supported model) to generate answers - Saves and loads chat history from Postgres so the agent remembers previous turns
- Queries a Supabase vector store to pull in relevant document snippets at response time
The result is a context-aware RAG agent that can answer questions using your own knowledge base instead of hallucinating its way through life.
2. Loading Binary Data from Google Drive (the document pipeline)
This is the behind-the-scenes ingestion flow. It:
- Downloads files from Google Drive
- Splits them into manageable text chunks using a Default Data Loader and a Recursive Character Text Splitter
- Generates embeddings for each chunk using OpenAI Embeddings
- Stores those embeddings in Supabase so they can be retrieved later by the RAG agent
You can think of this as your “feed the brain” pipeline. Every time you run it, your agent gets a little smarter about your documents.
Meet the key workflow components
Let’s quickly introduce the main nodes so you know who is doing what inside the n8n workflow.
When chat message received
This trigger node is the front door. Whenever a user sends a chat message, this node fires and hands the message to the RAG agent. It is the starting point for every conversation.
RAG Agent
The RAG Agent node is the coordinator. It:
- Calls the OpenAI chat model to generate responses
- Loads and saves chat history using Postgres chat memory
- Uses the Supabase vector store as a tool to fetch relevant documents based on the user’s query
It is the node that ties together language model, memory, and retrieval so your agent can respond with context.
OpenAI Chat Model
This node runs the conversational LLM. It uses:
- The user’s latest message
- Relevant document snippets from Supabase
- Previous conversation turns from Postgres memory
to generate a coherent reply that feels like one continuous conversation rather than a series of disconnected one-liners.
Postgres Chat Memory
This node is responsible for remembering what was said. It persistently stores:
- Conversation ids
- Roles (user, assistant, system)
- Message text
- Timestamps
Future messages in the same session can reference this stored history, which improves personalization and keeps the agent from asking “Can you repeat that?” every 30 seconds.
Supabase Vector Store
This is where your document embeddings live. The vector store:
- Stores embedding vectors along with metadata such as filename, chunk id, text snippet, and timestamp
- Supports nearest-neighbor search for fast retrieval of relevant passages
Whenever the RAG agent needs context, it queries Supabase for the most relevant chunks to ground its answer.
Embeddings OpenAI
This node takes plain text or extracted content and turns it into vector embeddings. Those vectors are then written into Supabase so the RAG agent can find them later during retrieval.
Loading binary data flow (Google Drive to Supabase)
This part of the workflow is all about ingestion. It:
- Downloads a file from Google Drive using your OAuth2 credentials
- Uses a Default Data Loader to extract text
- Applies a Recursive Character Text Splitter to break the text into usable chunks
- Generates embeddings via OpenAI Embeddings
- Inserts those embeddings into your Supabase vector table
Once this is done, your documents are fully searchable by the RAG agent.
How the end-to-end RAG flow works
Here is how everything comes together when the system is running.
- The user sends a message. The When chat message received node triggers and forwards the message to the RAG Agent.
- The RAG Agent:
- Asks Postgres chat memory for recent conversation history
- Queries the Supabase vector store to find the most relevant document passages
- The OpenAI Chat Model:
- Combines the user’s message, retrieved documents, and chat memory
- Generates a context-aware response
The RAG Agent can then update Postgres memory with the latest user message and assistant reply.
- Separately, when you want to add new documents to your knowledge base, you:
- Click Test workflow on the ingestion part of the flow
- Download a file from Google Drive
- Split the text into chunks
- Compute embeddings
- Insert those vectors into Supabase
Once both the chat and ingestion flows are configured, you have a full loop: ingest docs, embed them, store them, then query them during conversations.
Before you start: setup and prerequisites
You do not need a PhD in MLOps to use this template, but you do need a few things ready:
- n8n instance (cloud or self-hosted)
- Supabase project with the vector extension enabled or a configured vector table
- Postgres instance for chat memory
(this can be the same Postgres that backs Supabase if you prefer) - OpenAI API key for both chat and embeddings
- Google Drive OAuth2 credentials to download binary files
On the database side, make sure your schemas are ready:
- Supabase vector table Needs columns for:
- Embedding vector
- Metadata like filename
- Chunk id
- Text snippet
- Timestamp
- Postgres chat memory Should support:
- Conversation id
- Role
- Message text
- Timestamps
Quick configuration checklist
Once your infrastructure is ready, follow this simplified setup guide inside n8n.
- Import the template into n8n.
Use the provided workflow template so you start with all nodes wired together. - Configure your credentials.
Fill in the credentials for each relevant node:- OpenAI API key in:
- OpenAI Chat Model node
- OpenAI Embeddings node
- Supabase credentials in:
- Supabase Vector Store node
- Add to Supabase or equivalent insert nodes
- Postgres credentials for the Postgres Chat Memory node
- Google Drive OAuth2 credentials for the file download node
- OpenAI API key in:
- Tune the RAG Agent behavior.
Review the RAG Agent’s:- System prompt
- Retrieval configuration (for example number of documents to fetch)
- Memory window size
- Tool permissions (so it can actually call the vector store)
- Test binary ingestion.
Use the Test workflow trigger on the ingestion flow:- Download a sample file from Google Drive
- Confirm that text is split into chunks
- Check that embeddings are generated and successfully stored in Supabase
- Simulate chat queries.
Try multi-turn conversations, for example:- Ask a question about a document you uploaded
- Follow up with “And what about the second section?”
- Verify that the agent remembers earlier messages and uses the correct document context
Troubleshooting: when your RAG agent acts weird
If something feels off, here are common issues and how to fix them without rage-quitting.
- Irrelevant or low-quality retrievals
Try:- Increasing the number of nearest neighbors returned from the vector store
- Adjusting your text splitter settings so chunks are more semantically coherent
- Embedding insertion errors in Supabase
Double-check:- Embedding dimensionality matches the vector column definition
- The Supabase vector column type is correctly configured for your embedding model
- API rate limit issues
If OpenAI or Supabase start complaining:- Monitor usage and rate limits
- Add retry or backoff logic in n8n
- Introduce rate-limiting if you expect high traffic
- Slow or overloaded chat memory
For Postgres performance:- Ensure the memory table is indexed on conversation id and timestamps
- Optimize queries if you plan to support many concurrent sessions
Security and privacy: keep your data (and keys) safe
RAG agents are great, but you still need to treat data carefully:
- Store API keys in secure places like environment variables or n8n credentials, not in random notes or screenshots
- Use least-privilege roles for Supabase and Postgres so each service only has access to what it needs
- If you handle sensitive user data:
- Define data retention policies
- Consider redacting sensitive fields before storage
- Use encryption at rest for stored messages and document contents where appropriate
Best practices for a solid production RAG setup
Once everything is working, a few tweaks can make your life easier in the long run.
- Use a text splitter tuned to your content.
Legal contracts, support tickets, PDFs, and technical docs all benefit from different chunking strategies. Better chunks usually mean better retrieval. - Refresh embeddings when documents change.
If your docs are updated regularly, schedule re-ingestion so the vector store does not serve outdated information. - Design memory retention rules.
Keep long-term facts and important history, but truncate or archive casual chatter to control storage and keep retrieval focused on what matters. - Log behavior safely.
With appropriate privacy safeguards, log:- What was retrieved
- What the model responded with
This helps you debug, improve prompts, and refine retrieval strategies.
Next steps: where to go after the first version
Once your n8n RAG agent with Supabase and Postgres is up and running, you can start leveling it up:
- Add role-based access and multi-tenant routing.
Serve multiple teams or customers from the same infrastructure while keeping data separated. - Introduce a feedback loop.
Let users rate responses and use that feedback to:- Re-rank retrieved documents
- Improve prompts and retrieval settings over time
- Connect more tools to the RAG Agent.
Extend it with:- Search APIs
- Database queries
- Function calls or other utilities
so your agent can handle richer, task-oriented workflows instead of just Q&A.
Wrapping up
This n8n template gives you a practical starting point for building a RAG agent that is both conversational and grounded in your actual data. By combining:
- OpenAI chat models
- Postgres-based chat memory
- Supabase vector search
- Google Drive ingestion for binary files
you get a robust, production-ready workflow that turns repetitive manual tasks into automated magic.
Ready to try it? Import the workflow into your n8n instance, plug in your credentials, and hit Test workflow to start loading documents from Google Drive. Once the embeddings are in Supabase, your RAG agent is ready to chat with real context.
If you want help customizing the template for your use case, you can always reach out to the n8n community or check the documentation linked inside the workflow.
Call to action: Try the template now and subscribe to our newsletter for more tips on building production-grade RAG systems and automation patterns that save you from repetitive work.
Keywords: n8n RAG agent, Supabase vector store, Postgres chat memory, OpenAI embeddings, Google Drive ingestion, LangChain integration.