NDA Risk Detector with n8n & Vector Embeddings
This reference guide describes a production-style NDA Risk Detector built in n8n. The workflow automates NDA intake, splits and embeds contract text, stores it in a Redis vector index, and uses an AI agent with tools and memory to identify risky clauses. Results are logged to Google Sheets for auditability and follow-up.
1. Overview
The NDA Risk Detector workflow is designed for legal and product teams that need a repeatable, fast way to surface high-risk clauses in incoming NDAs. Instead of manually scanning each document, the workflow uses vector embeddings and retrieval-augmented generation to:
- Ingest NDA text or file URLs via a webhook endpoint
- Split long contracts into context-preserving chunks
- Generate vector embeddings for each chunk using a selected model
- Index those vectors in a Redis-based vector store
- Query the vector store during evaluation using a Tool layer and short-term Memory
- Run an AI Agent that produces structured risk assessments
- Append results to a Google Sheet for tracking and compliance
By combining embeddings with a vector store, the system can detect semantically similar risk patterns even when the NDA wording is different from your previous templates or examples.
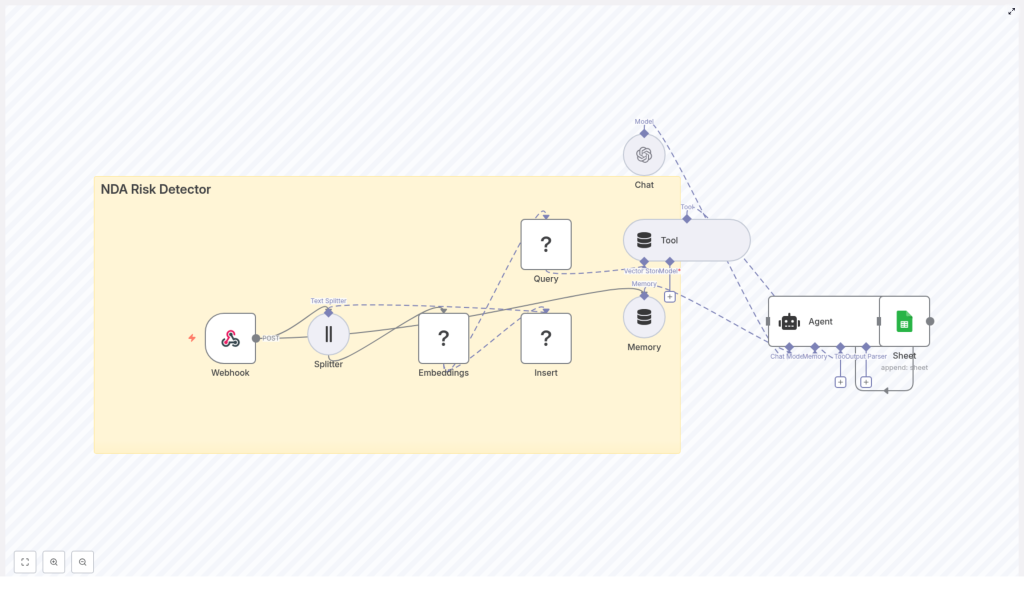
2. Workflow Architecture
At a high level, the n8n workflow implements a data pipeline with two primary paths:
- Ingestion path – For reference NDAs, templates, or precedent clauses that you want to index as context.
- Evaluation path – For newly received NDAs that you want to analyze and score for risk.
Both paths share the core building blocks:
- Webhook node – Entry point for NDA content.
- Text Splitter node – Breaks NDA text into chunks with overlap.
- Embeddings node – Generates vector representations for each chunk.
- Redis Vector Store node – Stores or queries vector embeddings (index name
nda_risk_detectorin the template). - Tool node – Wraps the vector store for Agent usage.
- Memory node – Maintains short-term conversational context.
- Agent / Chat node – Orchestrates the language model, tools, and memory to produce a risk assessment.
- Google Sheets node – Logs results to a spreadsheet for auditing and reporting.
The same architecture can support both batch ingestion of historical NDAs and real-time analysis of new agreements.
3. Node-by-Node Breakdown
3.1 Webhook Node (NDA Intake)
Role: Entry point for external systems to submit NDAs.
- Trigger type: Webhook node configured to accept
POSTrequests. - Payload: The workflow expects either:
- Raw NDA text in the request body, or
- A URL pointing to an NDA file that is processed upstream or by another part of your stack.
- Typical integrations: Form submissions, internal ingestion APIs, or a document upload UI that sends data to the webhook URL.
Configuration notes:
- Ensure the HTTP method is set to
POST. - Define a consistent JSON schema for incoming data (for example,
{ "nda_text": "...", "source_id": "..." }). - Use authentication (e.g. header tokens) if the webhook is exposed externally.
3.2 Text Splitter Node (Document Chunking)
Role: Splits long NDA content into smaller chunks that are suitable for embedding and retrieval.
- Example settings from the template:
chunkSize: 400 characterschunkOverlap: 40 characters
- Purpose:
- Preserves local context within each chunk.
- Prevents exceeding token limits of embedding models.
- Improves retrieval granularity so the agent can reference specific clauses.
Edge cases:
- Very short NDAs may result in a single chunk. The workflow still operates correctly, but retrieval will be less granular.
- Highly formatted or scanned PDFs should be converted to clean text before reaching this node to avoid noisy chunks.
3.3 Embeddings Node (Vector Generation)
Role: Converts each text chunk into a numerical vector representation.
- Template example: Hugging Face Embeddings node.
- Alternatives: OpenAI embeddings or any other supported embeddings provider.
- Inputs: Chunked text from the Text Splitter node.
- Outputs: A vector (array of floats) associated with each text chunk.
Configuration:
- Set up credentials for your chosen provider (Hugging Face or OpenAI).
- Select an embedding model that:
- Supports your primary language(s) of NDAs.
- Provides sufficient semantic resolution for legal text.
- Matches your latency and cost constraints.
Error handling:
- Handle provider-side rate limits by adding delays or batching (see Section 7).
- Log or route failures (e.g. invalid credentials, network issues) to an error-handling branch in your n8n workflow.
3.4 Redis Vector Store Node (Insert & Query)
Role: Serves as the vector database for storing and retrieving clause embeddings.
- Index name (example):
nda_risk_detector. - Modes of operation:
- Insert mode: Used during ingestion to store embeddings and associated chunk metadata.
- Query mode: Used during evaluation runs to retrieve the most relevant chunks.
Insert mode usage:
- Input: Embeddings + original text chunks.
- Recommended for:
- Standard NDA templates.
- Annotated examples of risky clauses.
- Historical NDAs that represent your typical contract language.
Query mode usage:
- Input: Embedding of the clause or query text that the agent or workflow provides.
- Output: Top-N similar chunks with similarity scores and metadata.
- These results are routed to the Tool node so that the Agent can reference them as evidence.
Configuration notes:
- Provide Redis connection details and credentials in n8n.
- Ensure the vector index schema matches the dimensions of your embedding model.
- For sensitive data, use an encrypted Redis instance and restrict network access.
3.5 Tool Node (Vector Store Tooling Layer)
Role: Exposes the Redis vector store as a callable tool for the AI Agent.
- Allows the Agent to issue semantic search queries against the indexed NDA chunks.
- Returns retrieved clauses as structured data that the Agent can incorporate into its reasoning and final answer.
Behavior:
- The Agent decides when to call the Tool based on its prompt and internal logic.
- The Tool returns the most relevant chunks for the Agent to cite as supporting evidence.
3.6 Memory Node (Short-term Context)
Role: Maintains a buffer of previous messages or steps so the Agent can consider earlier parts of the NDA or prior interactions.
- Typically configured as a buffer window memory.
- Stores a limited history to keep token usage manageable.
Use cases:
- Multi-step evaluations where the Agent reviews sections sequentially.
- Follow-up questions or clarifications during a review session.
Configuration considerations:
- If the memory window is too small, the Agent may lose important earlier context.
- If the window is too large, token usage and latency may increase unnecessarily.
3.7 Agent / Chat Node (AI Reasoning Layer)
Role: Central orchestration layer that combines the language model, Tool access, and Memory to produce the NDA risk assessment.
- Supported models: OpenAI or other LLM providers supported by n8n.
- Inputs:
- Prompt instructions for risk analysis.
- Relevant chunks from the Tool node.
- Conversation context from Memory.
- Outputs: Structured risk assessment including:
- Risk categories (for example, termination, indemnity, exclusivity).
- Rationale and supporting references.
- Risk severity scores or qualitative labels.
Configuration notes:
- Attach the Tool node so the Agent can query the vector store when needed.
- Attach the Memory node so the Agent can recall previous steps in the evaluation.
- Configure model credentials (e.g. OpenAI API key) in n8n credentials management.
3.8 Google Sheets Node (Logging & Audit Trail)
Role: Persists evaluation results to a Google Sheet for later review, reporting, and compliance checks.
- Operation: Append mode, adding a new row for each NDA evaluation.
- Typical columns:
- NDA identifier or source link.
- Timestamp of evaluation.
- Summary of risk findings.
- Risk categories and severity scores.
- Optional: IDs or links to relevant chunks.
Configuration notes:
- Set up Google Sheets credentials in n8n.
- Map Agent output fields to specific spreadsheet columns.
- Use a dedicated sheet or tab for NDA risk logs to keep data organized.
4. Step-by-Step Setup Guide
- Configure the Webhook node
Set up a Webhook node in n8n to acceptPOSTrequests containing:- Raw NDA text, or
- A URL reference to the NDA file.
Integrate this endpoint with your existing form, upload UI, or ingestion API.
- Add and tune the Text Splitter node
Connect the Webhook output to a Text Splitter node and configure:chunkSize(for example 400 characters in the template).chunkOverlap(for example 40 characters).
Larger chunks preserve more context but increase token usage and embedding cost. For legal text, 300-600 characters with 20-100 overlap is a common starting range.
- Set up the Embeddings node
Add a Hugging Face Embeddings node or an OpenAI Embeddings node:- Provide the appropriate API key via n8n credentials.
- Select a model compatible with your language and quality requirements.
Connect it to the Text Splitter so each chunk is converted into a vector.
- Index embeddings into Redis
Add a Redis Vector Store node configured with a dedicated index, for example:indexName:nda_risk_detector
In insert mode, send embeddings and their associated text chunks from the Embeddings node into Redis. Use this path to ingest:
- Reference NDAs.
- Templates.
- Precedent clauses and annotated examples.
- Wire the query path for evaluations
For evaluation runs, configure the Redis Vector Store node in query mode:- Provide the query embedding (for example generated from a clause or from the NDA section under review).
- Return the top relevant chunks to the Tool node.
The Tool node will then expose this retrieval capability to the Agent.
- Configure Agent and Memory
Add an Agent (or Chat) node and:- Connect it to your language model provider (e.g. OpenAI credentials).
- Attach the Memory node to maintain a short interaction history.
- Attach the Tool node so the Agent can query the vector store during reasoning.
Craft prompts that instruct the Agent to:
- Identify risky NDA clauses.
- Classify them into categories such as termination, indemnity, and exclusivity.
- Assign risk severity and provide a clear rationale.
- Log results in Google Sheets
Finally, add a Google Sheets node configured to append a new row per evaluation:- Map Agent output fields (risk categories, severity, summary) to sheet columns.
- Include timestamps and NDA identifiers for traceability.
5. Configuration Tips & Best Practices
5.1 Chunking Strategy
- Start with
chunkSizebetween 300 and 600 characters for legal text. - Use
chunkOverlapbetween 20 and 100 characters to avoid splitting important clauses mid-sentence. - Adjust based on:
- Average NDA length.
- Embedding cost constraints.
- Observed retrieval quality.
5.2 Embedding Model Selection
- Higher-quality embeddings usually improve retrieval of nuanced legal language.
- If budget is a concern, run A/B tests across:
- Different embedding models.
- Different chunk sizes.
and compare retrieval precision and recall on a small labeled test set.
5.3 Indexing Strategy in Redis
- Index both:
- Standard, low-risk NDA templates.
- Known risky clauses, ideally annotated with risk categories.
- This combination helps the vector store learn the semantic space of both acceptable and problematic language.
5.4 Prompt Design for the Agent
- Instruct the Agent to:
- Cite specific retrieved chunks as evidence when flagging a risk.
- Produce a concise risk score (for example on a 1-5 scale) per clause or per NDA.
- Explicitly identify which