POC: Build a Pizza Order Chatbot with n8n and LangChain
Imagine handing off your repetitive order questions to a friendly digital assistant so you can focus on the work that really moves your business forward. In this guide, you will walk through a proof-of-concept (POC) n8n workflow that does exactly that: a conversational pizza ordering chatbot powered by n8n and LangChain.
By the end, you will not just have a working chatbot that can answer menu questions, take orders, and check order status. You will also have a reusable pattern for building more automated, focused workflows in your own world, whether you run a small shop or are experimenting inside a larger product team.
The starting point: too many simple questions, not enough time
Every growing business eventually hits the same wall. Customers keep asking:
- “What is on the menu?”
- “Can I order a pizza with this topping?”
- “What is the status of my order?”
Each request is simple, but together they pull you or your team away from deeper work. You know automation could help, yet traditional solutions often feel heavy, opaque, and hard to iterate on.
This is where n8n and LangChain can change your trajectory. With a visual workflow and an AI agent, you can build a transparent, auditable conversational assistant that you can tweak, extend, and grow over time.
Shifting your mindset: from manual handling to smart delegation
Before diving into the template, it helps to shift how you think about automation. Instead of trying to build a “perfect” chatbot from day one, treat this pizza bot as a safe playground:
- Start small – handle simple menu inquiries and orders first.
- Keep everything visible – use n8n’s visual nodes to see exactly what happens at each step.
- Iterate quickly – refine prompts, endpoints, and logic as you test with real conversations.
This POC is not just about pizza. It is a pattern for how you can gradually automate more of your customer interactions without losing control or clarity.
What this n8n + LangChain POC actually does
The workflow connects ChatGPT, short-term memory, and simple HTTP endpoints so an AI agent can:
- Respond to menu questions using a “Get Products” endpoint
- Accept new orders and send them to an “Order Product” endpoint
- Check the status of existing orders via a “Get Order” endpoint
Everything is orchestrated by an AI agent node in n8n that uses LangChain components. The logic stays visible in the n8n UI, while OpenAI handles natural language understanding.
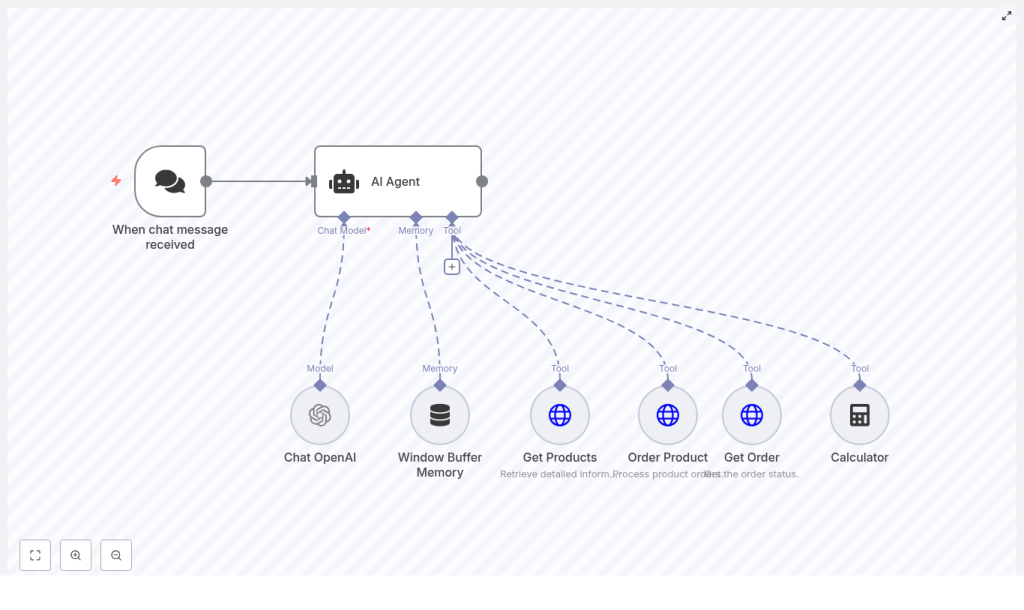
High-level architecture of the workflow
Here are the main building blocks you will see in the template:
- When chat message received – chat trigger that starts the workflow when a user sends a message.
- AI Agent – a LangChain agent, guided by a system prompt (“Pizzaro the pizza bot”), that decides which tools to use.
- Chat OpenAI – the language model that interprets user intent and generates responses.
- Window Buffer Memory – short-term memory so the bot can keep recent context in a multi-turn conversation.
- Get Products – HTTP GET tool that returns available menu items as JSON.
- Order Product – HTTP POST tool that creates a new order.
- Get Order – HTTP GET tool that retrieves the status of an existing order.
- Calculator – optional helper tool for totals, quantities, or simple math.
These pieces are intentionally simple. The power comes from how they combine into a clear, testable workflow that you can expand later.
Core design principles that keep this POC practical
1. Let the AI agent handle intent
The AI agent is the “brain” of the workflow. It receives the user’s message and decides which tool to call, for example:
- Menu lookup
- Order creation
- Order status check
A strong system prompt guides this behavior. In this POC, the prompt includes instructions like:
If a customer asks about the menu, provide the available products.
If placing an order, confirm details and call the order tool.
If asking about order status, use the order status tool.This approach keeps your logic flexible. You can refine the instructions over time without rewriting code.
2. Keep state small, simple, and accessible
Instead of building a full database for a POC, the workflow uses Window Buffer Memory. This gives your chatbot short-term memory of recent messages, so it can:
- Remember a user’s name during the conversation
- Handle clarifying questions
- Support multi-turn ordering flows
Because the memory window is limited, it stays efficient and easy to manage while still feeling conversational.
3. Use HTTP tools as a bridge to your systems
The integration layer is intentionally straightforward:
- Get Products – returns catalog JSON
- Order Product – accepts an order payload
- Get Order – returns order details by id or user info
In production, these endpoints might connect to microservices, a database, or a Google Sheet. In a POC, they can point to n8n webhooks, mock APIs, or simple serverless functions. This keeps your experimentation light while still mirroring a real-world architecture.
Your journey: from blank canvas to working chatbot
Let’s walk through the setup step by step. Think of this as your first automation chapter. You can follow it exactly, then adapt it to your own use case once it is running.
Step 1 – Create the chat trigger
Start by adding the “When chat message received” node. This is the entry point of your conversational workflow.
Configure:
- An initial greeting message
- Public webhook access if you want easy external testing
Example greeting used in the template:
Hellooo! 👋 My name is Pizzaro 🍕. I'm here to help with your pizza order. How can I assist you?
📣 INFO: If you’d like to order a pizza, please include your name + pizza type + quantity. Thank you!This sets the tone and gives users a clear way to interact from the first message.
Step 2 – Add and configure the AI Agent
Next, connect the chat trigger node to an AI Agent node.
In the AI Agent configuration:
- Attach a Chat OpenAI node as the language model.
- Attach a Window Buffer Memory node for short-term memory.
- Define a system prompt that sets expectations for Pizzaro’s behavior.
Example system prompt:
Your name is Pizzaro, and you are an assistant for handling customer pizza orders.
1. If a customer asks about the menu, provide information on the available products.
2. If a customer is placing an order, confirm the order details, inform them that the order is being processed, and thank them.
3. If a customer inquires about their order status, provide the order date, pizza type, and quantity.This prompt is your main control surface. As you test and improve the chatbot, you can refine these instructions to guide the agent toward more accurate and helpful behavior.
Step 3 – Add the integration tools as agent tools
Now you will connect the AI agent to the real work: your endpoints and utilities. Attach the following tools as agent tools:
- Get Products (GET) – returns catalog JSON when users ask questions like “What is on the menu?”
- Order Product (POST) – accepts an order payload after the agent has confirmed details with the user.
- Get Order (GET) – retrieves order details based on an order id or other identifying info.
- Calculator – optional, but useful for totals, discounts, or quantity calculations.
With these tools wired in, the agent can move from “chatting” to “taking action” in your systems.
Step 4 – Design structured responses and payloads
For the agent to work reliably, your HTTP tools should return and accept structured JSON. This makes it easier for the model to extract and reuse fields in its responses.
Example payloads:
GET /webhook/get-products
Response: { "products": [{"id": 1, "name": "Margherita", "price": 9.99}, ...] }
POST /webhook/order-product
Request: { "name": "Alice", "productId": 1, "quantity": 2 }
Response: { "orderId": "ORD-1001", "status": "processing", "date": "2025-09-01" }With this structure, the AI agent can easily confirm details back to the user, such as:
- Order date
- Pizza type
- Quantity
- Order id and status
This is where your chatbot starts to feel like a real assistant, not just a demo.
Testing your new automated assistant
Once everything is connected, it is time to see your work in action. Trigger the chat webhook and try a few realistic scenarios:
- Ask for the menu
Send: “Show me the menu”
Expected: The agent callsGet Productsand lists available pizzas. - Place an order
Send: “My name is Sam. I want 2 Margheritas.”
Expected: The agent parses the details, confirms them, callsOrder Product, and returns a confirmation with order id and status. - Check order status
Send: “What is the status of my order ORD-1001?”
Expected: The agent callsGet Orderand replies with the order date, pizza type, and quantity.
Each successful test is a small but meaningful step in reclaiming your time and proving that automation can support your work, not complicate it.
Tips to improve accuracy and reliability
As you experiment and iterate, a few practices will help your n8n chatbot perform more consistently:
- Refine the system prompt – be explicit about when the agent should call each tool and how it should respond.
- Keep JSON consistent – use stable field names and shapes in your HTTP responses so the model can reliably extract data.
- Validate user input – check names, quantities, and product ids. If something is missing or unclear, instruct the agent to ask follow-up questions.
- Limit memory scope – keep the Window Buffer Memory focused on recent, relevant turns to reduce confusion or drift.
Think of this as continuous tuning. Small adjustments here can significantly boost the quality of the experience for your users.
Security and production considerations
When you are ready to move beyond a POC and into a more production-like setup, keep these safeguards in mind:
- Protect webhooks with authentication (HMAC, tokens) and avoid exposing unnecessary endpoints publicly.
- Sanitize and validate all user inputs before sending them to back-end services.
- Log transactions and maintain an order audit trail in persistent storage.
- Apply rate limiting for both OpenAI and your own APIs to control costs and prevent abuse.
These steps help you scale your automation with confidence instead of worry.
Growing beyond pizza: how to extend this POC
This workflow is intentionally modular. Once you are comfortable with the basics, you can extend it to support richer customer journeys. Some common next steps include:
- Payment integration – connect Stripe or another payment provider after order confirmation.
- Delivery tracking – integrate courier or delivery APIs and surface tracking info through the
Get Ordertool. - Personalization – store customer preferences in a database and let the bot remember favorite orders.
- Analytics and reporting – build dashboards for order volume, popular items, and peak times.
Every improvement you make here can be reused in other workflows: support bots, internal tools, booking assistants, and more.
What this template unlocks for you
This n8n + LangChain POC is more than a pizza demo. It is a practical, visual example of how to:
- Connect AI to real business endpoints with clear, auditable logic
- Prototype conversational experiences without heavy engineering
- Iterate quickly in a low-risk environment, then scale what works
Once you have this template running, you have a foundation you can return to whenever you want to automate the next repetitive interaction in your business.
Ready to take the next step?
You do not have to start from scratch. You can import the ready-made workflow, plug in your credentials, and begin experimenting within minutes.
To get started:
- Import the provided workflow into n8n.
- Configure your OpenAI credentials in the Chat OpenAI node.
- Point the HTTP tools to mock endpoints, n8n webhooks, or your real catalog and order services.
If you need a starter template for webhooks or want to use something simple like a Google Sheet as your backend, you can adapt the endpoints without changing the overall pattern.
Call to action: Import the template, run a few test conversations, and notice how it feels to let an automated assistant handle the basics. Then, adjust the system prompt and tools to match your own business. Each tweak moves you closer to a more focused, automated workflow that gives you back time and clarity.