Scrape LinkedIn Jobs to Google Sheets with n8n + Bright Data
Building a reliable stream of hiring signals from LinkedIn is highly valuable for recruiting, sales, and market intelligence. This guide explains how to implement a production-ready LinkedIn job scraping workflow using Bright Data’s Dataset API, orchestrated with n8n, and persisted in Google Sheets.
The result is a repeatable automation that collects fresh job postings, cleans and normalizes the data, then appends structured records to a Google Sheet for downstream analysis or outreach.
Why automate LinkedIn job scraping with n8n and Bright Data?
LinkedIn job posts are a strong indicator of hiring intent, organizational growth, and budget availability. Manually monitoring these signals is not scalable. Automating the process offers several advantages:
- Timeliness – capture new roles within hours of posting, not days.
- Consistency – maintain an always-on pipeline instead of ad hoc searches.
- Data quality – apply repeatable cleaning and normalization logic.
- Extensibility – easily route the same data into CRMs, Slack, or other systems.
By combining Bright Data’s dataset snapshots with n8n’s workflow engine and Google Sheets as a lightweight data store, you get a robust yet accessible solution for LinkedIn job scraping.
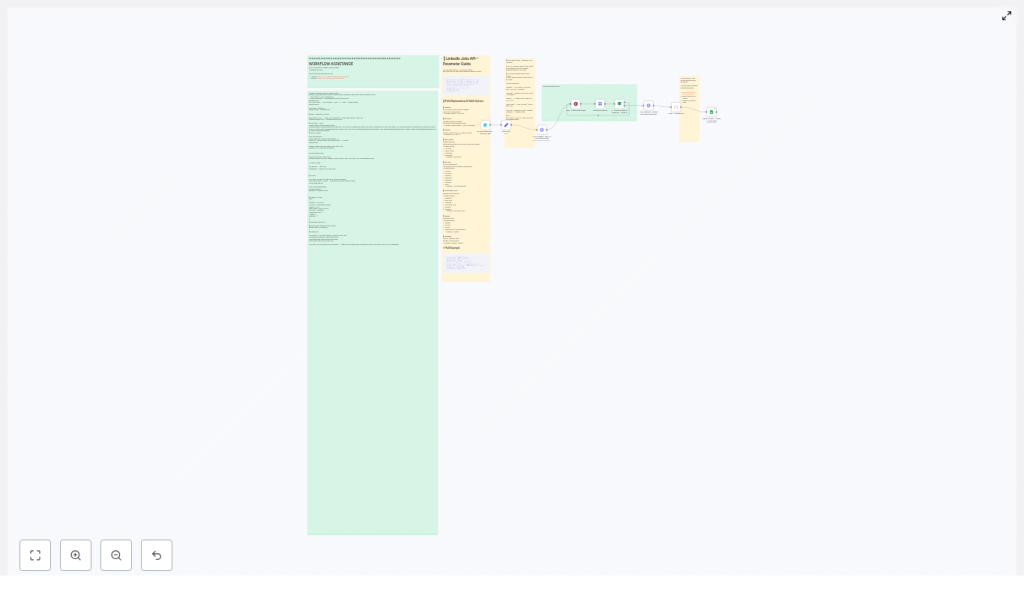
Architecture overview
The workflow centers on a simple pattern: accept user-defined search parameters, request a dataset snapshot from Bright Data, wait for processing to complete, then fetch and transform the results before writing them to Google Sheets.
High-level workflow steps
- A user submits search criteria in n8n (location, keyword, country).
- n8n triggers a Bright Data dataset snapshot via HTTP POST.
- The workflow periodically polls Bright Data for snapshot progress.
- Once ready, n8n retrieves the snapshot data in JSON format.
- Custom JavaScript in a Code node cleans and flattens the job records.
- Normalized rows are appended to a Google Sheet, one job per row.
This pattern is easy to adapt: you can change filters, extend the transformation logic, or plug the cleaned data into additional systems.
Prerequisites and credentials
Before assembling the workflow, ensure the following components and credentials are available:
- Bright Data API key for authorization against the Dataset API.
- n8n instance (cloud or self-hosted) with access to:
- HTTP Request node
- Wait node
- If node
- Code node
- Google Sheets node
- Google account connected to n8n using OAuth2 for Google Sheets access.
Bright Data authorization header
All Bright Data API calls must include a Bearer token in the Authorization header:
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY
Configuring the Bright Data Dataset API
The workflow uses Bright Data’s Dataset API to request and retrieve LinkedIn job data. You will primarily interact with three endpoints:
- Trigger:
https://api.brightdata.com/datasets/v3/trigger - Progress:
https://api.brightdata.com/datasets/v3/progress/{{snapshot_id}} - Snapshot:
https://api.brightdata.com/datasets/v3/snapshot/{{snapshot_id}}?format=json
Example POST body for discover dataset
The Bright Data trigger endpoint accepts a JSON array of query objects. You can adjust filters such as time range, job type, and remote options to refine your dataset.
[ { "location": "New York", "keyword": "Marketing Manager", "country": "US", "time_range": "Past 24 hours", "job_type": "Part-time", "experience_level": "", "remote": "", "company": "" }
]
Leaving some fields blank broadens the search, which is useful for exploratory prospecting. For more targeted streams, define specific keywords, locations, or time windows.
Detailed n8n workflow design
The following section walks through each node and its role in the automation, from capturing inputs to persisting cleaned records.
1. Form Trigger – capture user search parameters
Start with a trigger mechanism in n8n that collects the search criteria. This is often implemented using a form or a webhook that accepts parameters such as:
- Job Location (e.g. “New York”)
- Keyword (e.g. “Marketing Manager”)
- Country (2-letter code, e.g. “US”)
These values are then injected into the JSON payload that n8n sends to Bright Data’s trigger endpoint.
2. HTTP Request – trigger a dataset snapshot
Next, configure an HTTP Request node to initiate the snapshot generation:
- Method: POST
- URL:
https://api.brightdata.com/datasets/v3/trigger - Headers: include the Authorization header with your Bearer token.
- Body: JSON array with the search parameters as shown above.
The response from this call contains a snapshot_id. Store this value in the workflow context, since it will be used for progress polling and final data retrieval.
3. Wait and poll – monitor snapshot progress
Bright Data may take some time to prepare the dataset. To handle this gracefully, implement a polling loop using the Wait and HTTP Request nodes.
- Use a Wait node to pause execution for a defined interval, typically 1 to 3 minutes.
- After the pause, use an HTTP Request node to call:
https://api.brightdata.com/datasets/v3/progress/{{snapshot_id}} - Inspect the returned status field using an If node.
Continue polling while status == "running". Once the status differs from running, the snapshot is ready to be fetched.
4. HTTP Request – fetch the completed snapshot
When the snapshot is complete, use another HTTP Request node to download the data in JSON format:
- Method: GET
- URL:
https://api.brightdata.com/datasets/v3/snapshot/{{snapshot_id}}?format=json - Headers: include the same Authorization header.
The response contains an array of job posting objects. These will be passed to a Code node for transformation and normalization.
5. Code node – clean and flatten job data
Raw job records often contain nested objects and HTML-formatted descriptions. A small JavaScript routine inside an n8n Code node can standardize these fields and prepare them for tabular storage.
Typical transformations include:
- Stripping HTML tags from job descriptions.
- Flattening nested objects such as
job_posterandbase_salary. - Normalizing whitespace and removing HTML entities.
Example Code node logic:
// Helper function to strip HTML tags
function stripHtml(html) { return html .replace(/<[^>]+>/g, '') .replace(/ /g, ' ') .replace(/&[a-z]+;/g, '') .replace(/\s+/g, ' ') .trim();
}
return items.map(item => { const data = item.json; if (data.job_poster) { data.job_poster_name = data.job_poster.name || ''; data.job_poster_title = data.job_poster.title || ''; data.job_poster_url = data.job_poster.url || ''; delete data.job_poster; } if (data.base_salary) { data.salary_min = data.base_salary.min_amount || ''; data.salary_max = data.base_salary.max_amount || ''; data.salary_currency = data.base_salary.currency || ''; data.salary_period = data.base_salary.payment_period || ''; delete data.base_salary; } if (data.job_description_formatted) { data.job_description_plain = stripHtml(data.job_description_formatted); } return { json: data };
});
This approach keeps the workflow transparent and easy to extend. You can add additional mappings or normalization rules as needed.
6. Google Sheets node – append normalized rows
Finally, connect the cleaned data to Google Sheets:
- Select the appropriate Google Sheets account via OAuth2.
- Choose the target spreadsheet and worksheet.
- Use the Append operation so each job posting is added as a new row.
Map the flattened fields to your sheet columns. Typical mappings include:
job_titlecompany_namejob_locationsalary_min,salary_max,salary_currency,salary_periodapply_linkjob_description_plainjob_poster_nametimestampor ingestion time
With this setup, Google Sheets becomes a simple but effective UI for browsing, filtering, and annotating job leads.
Google Sheets template structure
To accelerate deployment, prepare a Google Sheet that already contains the most relevant columns, plus room for additional attributes from Bright Data.
Recommended columns include:
job_titlecompany_namejob_locationjob_description_plainsalary_minsalary_maxapply_linkjob_poster_nametimestamp
You can always extend the schema with additional columns if Bright Data exposes more fields that are useful for your specific use case.
Best practices for a robust LinkedIn job scraping pipeline
To operate this workflow reliably and at scale, consider the following operational and design best practices.
Search and filtering strategy
- Use shorter
time_rangevalues such as “Past 24 hours” or “Past Week” to focus on fresh openings and reduce noise. - Leave optional filters blank when you want to explore broader markets or identify emerging employers in a segment.
- Gradually tighten filters (job_type, experience_level, remote) once you understand the volume and quality of results.
Rate limiting and polling behavior
- Respect Bright Data rate limits by spacing out snapshot triggers and progress checks.
- Adjust the Wait node interval if you encounter throttling or want to optimize API usage.
- Consider adding basic backoff logic if you operate at higher volumes.
Advanced workflow logic in n8n
- Introduce scoring or prioritization logic to flag high-intent roles (for example seniority, company size, or location).
- Branch the workflow to send targeted alerts to Slack, email, or a CRM when certain conditions are met.
- Use additional n8n nodes to deduplicate entries or track which postings have already been processed.
Troubleshooting and security considerations
As with any production automation, monitoring and secure handling of credentials are critical.
- 401 / 403 errors: verify that the Bright Data API key is valid and that the Authorization header uses the correct Bearer token format.
- Empty or sparse results: broaden the keyword or time_range, and relax filters such as job_type or experience_level.
- Rate limit responses: increase the Wait polling interval or implement exponential backoff in your workflow design.
- Data privacy: avoid storing sensitive PII in plain text, restrict access to the Google Sheet, and rotate API keys on a regular schedule.
Key use cases for automated LinkedIn job scraping
Once the workflow is in place, it can support multiple teams and objectives:
- Job seekers: monitor newly posted roles in your target geography or function and track application status directly in a sheet.
- Sales teams: identify organizations that are actively hiring as a proxy for growth, new initiatives, or fresh budget allocation.
- Recruiters and agencies: centralize new job postings, then enrich and segment them for tailored outreach to candidates.
Next steps and implementation resources
To deploy this workflow end-to-end:
- Prepare or copy a Google Sheets template with the relevant columns.
- Configure your Bright Data API key and connect it to n8n via the HTTP Request nodes.
- Connect your Google account to n8n using OAuth2 and configure the Google Sheets node.
- Import or recreate the n8n workflow, then customize filters, scoring, and routing logic as required.
If you would like access to the exact n8n workflow JSON, the template sheet, or support with customizing filters and prioritization logic, get in touch:
Email: Yaron@nofluff.online
For a visual walkthrough and additional implementation tips, refer to the creator’s YouTube channel and LinkedIn content, which provide detailed demonstrations of the workflow in action.
Start your automated job stream now – connect Bright Data and n8n, push results into Google Sheets, and react faster to real-time hiring signals.