Summarize Customer Emails with n8n & Weaviate
Efficient handling of customer communication is critical for modern support and operations teams. Manual review of long email threads does not scale, and it is easy to lose context across interactions. This guide explains how to implement a production-ready n8n workflow template that automatically summarizes customer emails using a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pattern with Weaviate, Cohere embeddings, and an Anthropic chat model, while logging outcomes to Google Sheets and surfacing failures in Slack.
The result is an end-to-end automation that ingests inbound emails, transforms them into vector embeddings, stores and retrieves context from Weaviate, and generates concise, actionable summaries that your team can trust.
Solution architecture and design rationale
This workflow is built around a modular architecture that separates ingestion, vectorization, retrieval, generation, and monitoring. Each component is chosen to support scalability, observability, and maintainability:
- n8n – central orchestration layer with webhook triggers, error handling, and node-based logic.
- Text splitting – prepares long emails for embedding and retrieval by chunking them into manageable segments.
- Cohere embeddings – converts text chunks into high-quality vector representations.
- Weaviate – vector database used for semantic storage and retrieval of email content.
- Anthropic / Chat model – RAG agent that uses retrieved context and short-term memory to produce summaries.
- Google Sheets & Slack – lightweight observability stack for logging, review, and alerting.
This combination enables a robust RAG workflow: incoming emails are embedded and stored once, then efficiently retrieved and summarized on demand with consistent context and clear operational visibility.
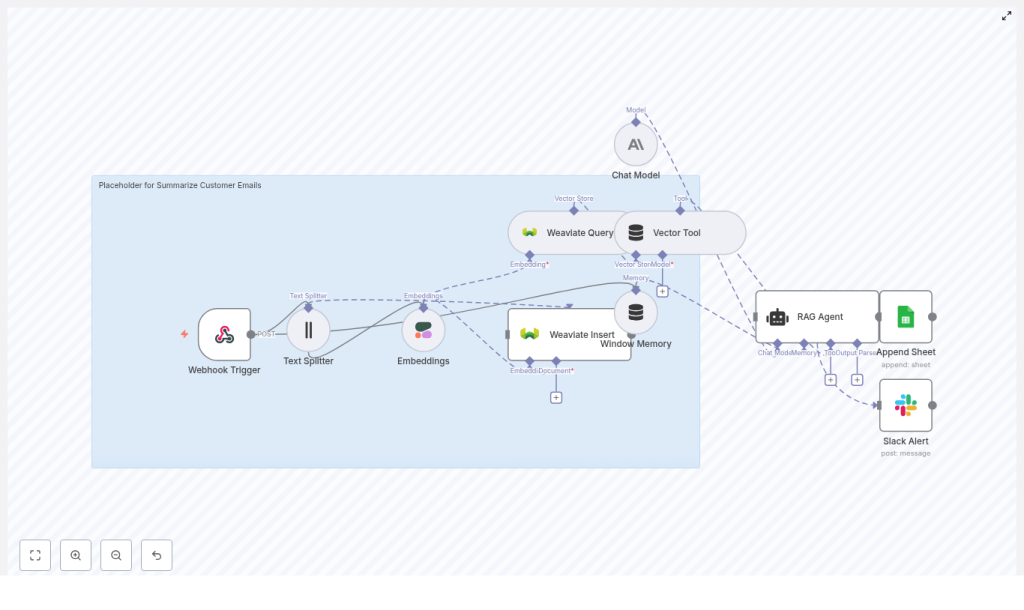
End-to-end workflow overview in n8n
On the n8n canvas, the template is organized into distinct stages that form a complete pipeline:
- Webhook Trigger – receives inbound customer emails via HTTP POST.
- Text Splitter – segments the email body into overlapping chunks.
- Embeddings (Cohere) – generates vector embeddings for each chunk.
- Weaviate Insert – writes embedded chunks and metadata into a Weaviate index (
summarize_customer_emails). - Weaviate Query + Vector Tool – retrieves relevant chunks for the current summarization task.
- Window Memory – maintains short-term context across related messages.
- Chat Model + RAG Agent – composes the final summary and suggested response.
- Append Sheet (Google Sheets) – records summary results and status.
- Slack Alert (onError) – notifies a Slack channel when any downstream step fails.
The following sections walk through each stage in more depth, including configuration guidance and operational best practices.
Ingestion and preprocessing
Webhook Trigger configuration
The workflow starts with an n8n Webhook Trigger node configured to accept HTTP POST requests. This endpoint is intended to receive raw email payloads from your email provider or an intermediate mail-to-webhook service.
Key considerations:
- Configure your email system to forward incoming messages to the n8n webhook URL.
- Validate requests using HMAC signatures, API keys, or IP allowlists to protect the endpoint from abuse.
- Normalize the email payload so that the workflow can reliably access fields such as subject, body, sender, and message ID.
Text splitting for long emails
Customer emails, especially threads, can easily exceed typical model context limits. The Text Splitter node breaks the email body into overlapping chunks so that each piece can be embedded and retrieved efficiently.
Recommended template settings:
chunkSize: 400 characterschunkOverlap: 40 characters
This configuration provides a balance between coherence within each chunk and retrieval precision. For models with larger context windows, you can increase chunkSize. For domains where crucial information often crosses chunk boundaries, consider increasing chunkOverlap to preserve continuity.
Vectorization and storage with Cohere and Weaviate
Embedding generation with Cohere
After splitting, each text chunk is passed to an Embeddings node configured with Cohere. The template uses embed-english-v3.0 or the latest recommended Cohere embedding model.
Implementation notes:
- Attach your Cohere API credentials in n8n and store them securely in the credentials vault.
- Monitor embedding usage because this step often becomes the main cost driver at scale.
- Consider batching chunks where possible to reduce network overhead and improve throughput.
Persisting context in Weaviate
The Weaviate Insert node writes embedding vectors and associated metadata into a Weaviate index. In this template the index name is set to summarize_customer_emails to isolate this use case.
Alongside the vector, store metadata fields that will later enable targeted retrieval and filtering, such as:
- Original email ID or message ID
- Customer identifier or email (hashed if sensitive)
- Timestamp of receipt
- Optional labels, sentiment, or priority tags
Well-designed metadata is critical for advanced retrieval strategies, for example filtering by customer, date range, or ticket priority.
Retrieval and RAG orchestration
Querying Weaviate and exposing a vector tool
When a summary is requested, the workflow uses a Weaviate Query node to retrieve the most relevant chunks for the current email or thread. The Vector Tool node then exposes this vector store to the RAG agent so that the agent can call back into Weaviate as needed during generation.
Best practices:
- Use the same embedding model for both indexing and querying to maintain vector space consistency.
- Tune the number of retrieved results (for example, top 5 hits) to control prompt size and cost.
- Leverage metadata filters to restrict retrieval to the relevant customer or conversation.
Window Memory for conversational continuity
The Window Memory node helps preserve short-term context across multiple related emails, such as follow-ups in the same thread. Instead of re-fetching and re-summarizing the entire history on each request, window memory maintains a compact representation of recent context.
This improves:
- Coherence across multi-message summaries.
- Continuity of action items and decisions over time.
- Latency, since not all prior messages need to be reprocessed.
Summary generation with Anthropic and RAG
Configuring the Chat Model and RAG agent
The core of the workflow is the Chat Model + RAG Agent stage, which uses an Anthropic chat model. The agent combines three elements:
- System instructions that define the assistant behavior.
- Retrieved context from Weaviate via the Vector Tool.
- Short-term context from the Window Memory node.
Guidelines for configuration:
- Use a concise system message, for example: You are an assistant for Summarize Customer Emails.
- Set temperature and safety parameters to favor stable, factual output over creativity.
- Ensure the prompt explicitly instructs the model to rely only on retrieved context to minimize hallucinations.
Prompt structure and output format
To make summaries operationally useful, structure the output into clear sections. A typical pattern is:
- Subject summary – a short description of the customer issue or request.
- Action items – a numbered list of tasks or follow-ups required.
- Suggested response – draft reply text that an agent can quickly review and send.
Example system and user prompt for the RAG agent:
<system>You are an assistant for Summarize Customer Emails. Produce a brief summary, list action items, and draft a suggested reply. Use the retrieved context only. Keep the summary under 120 words.</system>
<user>Email body: {original_email}
Retrieved context: {weaviate_hits}
</user>
Additional recommendations:
- Constrain the subject summary length, for example 50 to 150 words, to keep outputs scannable.
- Ask the model to enumerate action items explicitly with bullet points or numbering.
- Include retrieved context as an append-only section in the prompt so the model grounds its output in actual email content.
Logging, monitoring, and alerting
Google Sheets logging for auditability
The Append Sheet node writes each summarization result to Google Sheets. This provides a simple but effective audit trail that non-technical stakeholders can inspect.
Typical columns include:
- Email ID or conversation ID
- Generated summary text
- Status (success, failure, needs review)
- Timestamp of processing
- Optional notes or reviewer comments
This log supports manual quality checks, helps identify problematic cases, and can be used to iterate on prompt design and retrieval parameters.
Slack alerts using the onError path
Reliability is handled via n8n’s onError path. If any node in the workflow fails, an error branch sends a Slack Alert message to a designated channel.
Include in the alert:
- Error message and stack or diagnostic details.
- The affected email ID or key metadata for quick lookup.
- A link to the relevant Google Sheet row if available.
This pattern ensures that failures are visible in real time and can be triaged before they impact downstream workflows or customer SLAs.
Security and privacy controls
Since this workflow processes customer email content, robust security and privacy practices are essential:
- Hash or redact personally identifiable information (PII) before storing content in Weaviate, especially for long-term retention.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) and network restrictions for both n8n and Weaviate instances.
- Store all API keys and credentials in the n8n credentials vault and rotate them regularly.
- Limit access to Google Sheets logs or anonymize fields where appropriate to reduce exposure.
These measures help maintain compliance with internal policies and external regulations while still enabling advanced automation.
Scaling, performance, and cost optimization
As email volume increases, you will want to optimize the workflow for both performance and cost:
- Batch embeddings – group multiple chunks into a single Cohere request to improve throughput and reduce per-request overhead.
- Incremental ingestion – only embed and store new or changed segments instead of reprocessing entire threads.
- Vector store maintenance – periodically prune stale vectors from Weaviate and rebalance indices to keep retrieval fast.
- Context window tuning – adjust the number of retrieved hits and chunk sizes to manage token consumption in the chat model.
Monitoring embedding counts, vector store growth, and LLM token usage will help you keep the solution cost effective without sacrificing quality.
Quality control and continuous improvement
To ensure the summaries remain accurate and actionable over time, implement systematic quality checks:
- Sampling and human review – regularly review a percentage of auto-generated summaries to validate clarity and correctness.
- Error tracking – use the Google Sheets status column and Slack onError alerts to monitor failure patterns.
- Latency metrics – track response times for embedding creation and Weaviate queries to detect performance regressions.
Techniques to improve summarization accuracy
- Increase
chunkOverlapfor emails where critical context spans multiple chunks. - Enrich Weaviate metadata with structured fields such as labels, sentiment, or priority to improve retrieval precision.
- Experiment with alternative or domain-specific embedding models if your content is highly specialized.
Iterating on these parameters will typically yield significant gains in summary quality without major architectural changes.
Putting it into practice
This n8n template provides a strong foundation for automated customer email summarization using a RAG-based architecture. It strikes a practical balance between accuracy, cost, and operational simplicity, while remaining flexible enough to extend.
Once the core workflow is stable, you can layer on additional capabilities such as sentiment analysis, automated ticket creation, priority-based routing, or integration with CRM and help desk platforms.
Next steps:
- Import the n8n template into your environment.
- Configure credentials for Cohere, Weaviate, Anthropic, Google Sheets, and Slack.
- Set up email forwarding to the n8n webhook.
- Manually review the first 100 summaries, adjust chunking, retrieval parameters, and prompts, then roll out more broadly.
If you require a tailored implementation or deeper integration with your existing tooling, consider engaging your internal platform team or contacting specialists for a guided deployment.