Using OpenAI Models in n8n Workflows: Examples & Best Practices
Overview
OpenAI models such as ChatGPT, Whisper-1, and DALLE-2 can be integrated directly into n8n workflows to automate a wide range of language and media tasks. Typical use cases include:
- Speech-to-text transcription
- Summarization and translation
- Programmatic multi-turn conversations
- Prompt-driven image generation
- SVG and HTML code generation
- Quick email reply suggestions
This reference-style guide describes a sample n8n workflow template that combines these capabilities using OpenAI models. It focuses on technical configuration, node behavior, and data flow so you can adapt the pattern to your own automations.
API Approach: Legacy Davinci vs Modern ChatGPT / Whisper
Previous n8n workflows often relied on the Davinci-003 model using the OpenAI Text Completion and Edit operations. While functional, this legacy approach is:
- Significantly more expensive per token compared to ChatGPT models
- Less aligned with current OpenAI feature development
The recommended approach is to migrate to the ChatGPT and Whisper APIs:
- ChatGPT for conversational and instruction-following tasks such as summarization, translation, and content generation
- Whisper-1 for audio transcription
For details on these APIs and pricing, see the official OpenAI post:
Introducing ChatGPT and Whisper APIs.
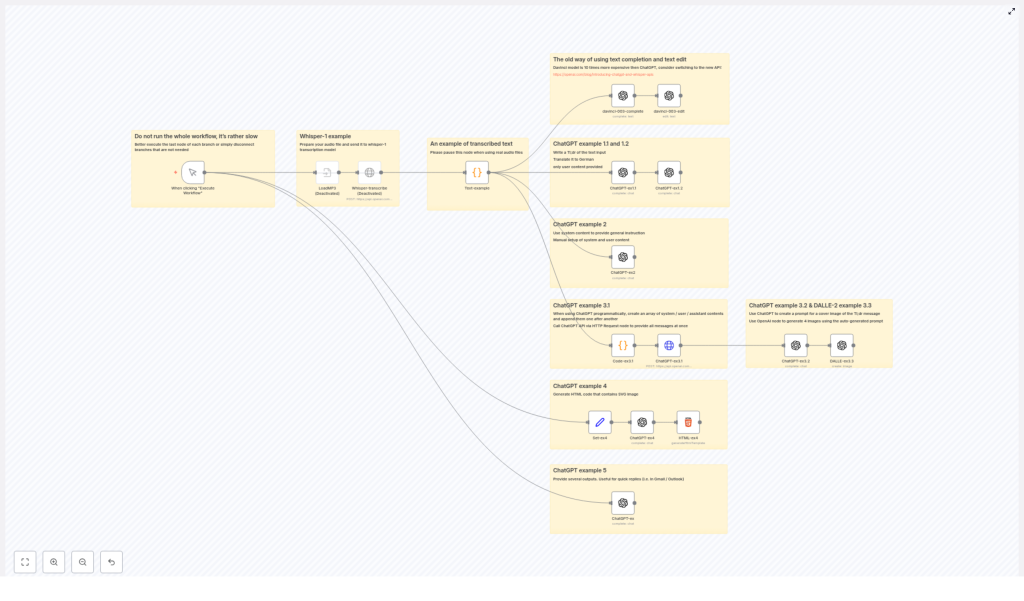
Workflow Architecture
The template is structured as a collection of related examples, each focusing on a specific OpenAI capability. The nodes are designed so you can enable or disable sections independently during testing.
High-Level Components
- Whisper-1 Transcription – Accepts audio input and produces text output.
- Static Text Example – Provides a fixed transcript for testing downstream text-processing nodes.
- Summarization and Translation – Uses ChatGPT to generate a tl;dr and a German translation.
- Programmatic Multi-turn Chat – Builds a message array with roles and sends it to ChatGPT via HTTP.
- Prompt-to-Image Pipeline – Uses ChatGPT to craft a DALLE-2 prompt, then generates comic-style images.
- SVG / HTML Code Generation – Produces SVG-based HTML snippets using ChatGPT.
- Quick Reply Generator – Creates short email reply suggestions from user input.
Data typically flows from an input node (audio or text) into one or more ChatGPT or Whisper calls, then optionally into downstream processing nodes such as image generation or code rendering.
Node-by-Node Breakdown
1. Whisper-1 Transcription Node
This section of the workflow demonstrates how to connect audio input to OpenAI’s Whisper-1 model.
Purpose
- Convert uploaded audio files into text for downstream processing.
Typical Configuration
- Node type: OpenAI (or HTTP Request, depending on your n8n version and preference)
- Model: whisper-1
- Operation: Transcription
- Input: Binary audio file from a previous node (for example, webhook, file upload, or storage)
Data Flow
- An upstream node provides an audio file as binary data.
- The Whisper-1 node sends the file to the OpenAI transcription endpoint.
- Whisper-1 returns the transcript as text in the JSON output.
- The transcript becomes the input for other nodes such as summarization, translation, or prompt generation.
Notes and Edge Cases
- Large audio files may significantly increase execution time. During testing, you can disable this node and use the static text example instead.
- Ensure the correct binary property name is configured in the node if your file is not in the default property.
2. Static Text Example Node
To avoid repeatedly uploading large audio files during development, the workflow includes a node that provides a fixed transcripted text as an example.
Purpose
- Serve as a predictable text input for downstream ChatGPT examples.
Usage
- Enable this node when you want to test summarization, translation, or image generation without running Whisper-1 each time.
- Disable Whisper-1 or other heavy nodes during rapid iteration to speed up testing.
3. ChatGPT Example 1.1 & 1.2: Tl;dr and Translation
These two nodes demonstrate basic text processing with ChatGPT using separate calls for summarization and translation.
3.1 Tl;dr Summarization (Example 1.1)
- Input: Transcript from Whisper-1 or the static text node.
- Model: ChatGPT (for example, gpt-3.5-turbo, depending on your n8n version and credentials).
- Prompt strategy: Instruct ChatGPT to produce a concise tl;dr style summary.
The node returns a short, high-level summary that can be used as the basis for further processing, such as prompt construction for image generation.
3.2 Translation to German (Example 1.2)
- Input: Original text or the tl;dr summary, depending on your desired behavior.
- Model: ChatGPT.
- Prompt strategy: Ask ChatGPT to translate the text into German.
Running summarization and translation as separate nodes keeps the responsibilities clear and makes it easier to reuse each step independently.
4. ChatGPT Example 2: System Instructions + User Content
This node illustrates how to use system and user roles in ChatGPT to control behavior.
Purpose
- Showcase flexible prompt engineering using role-based messages.
- Apply general instructions globally through system content.
Configuration Pattern
- System message: High-level instructions, such as writing style, tone, or constraints.
- User message: The actual content or question that should be processed.
This pattern is useful when you want consistent behavior across multiple user inputs, for example enforcing a specific output format or language.
5. ChatGPT Example 3.1: Programmatic Multi-turn Conversations
In this part of the workflow, you build an array of messages programmatically, then send it to the ChatGPT API via an HTTP Request node.
Purpose
- Model multi-turn conversations with explicit
system,user, andassistantroles. - Maintain conversation history in a structured format.
Typical Implementation
- Use a Function or Set node to construct an array of messages, for example:
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant." }{ role: "user", content: "User question or statement..." }{ role: "assistant", content: "Previous assistant reply..." }(optional for multi-turn)
- Pass this array into an HTTP Request node configured to call the ChatGPT chat completions endpoint.
- Parse the response and route it to subsequent nodes as needed.
Benefits
- Fine-grained control over the full conversation context.
- Easier integration with custom logic that appends or modifies messages before each call.
6. ChatGPT Example 3.2 & DALLE-2 Example 3.3: Image Generation Pipeline
These examples show a two-step pipeline where ChatGPT first generates a creative prompt, then DALLE-2 uses that prompt to produce images.
6.1 Prompt Generation with ChatGPT (Example 3.2)
- Input: Typically the summarized text from the tl;dr node.
- Model: ChatGPT.
- Prompt strategy: Ask ChatGPT to create a detailed, imaginative prompt suitable for DALLE-2. For example, specify “comic-style” or a particular visual mood.
The output is a descriptive text prompt that captures the essence of the summary in visual form.
6.2 Image Generation with DALLE-2 (Example 3.3)
- Input: Prompt from the previous ChatGPT node.
- Model: DALLE-2.
- Operation: Image generation.
- Configuration: Generate multiple comic-style images related to the content.
The DALLE-2 node returns one or more image URLs or binary image data, depending on how you configure the node and the OpenAI integration in n8n.
7. ChatGPT Example 4: SVG HTML Code Generation
This example demonstrates how ChatGPT can generate HTML containing SVG code.
Purpose
- Automatically create dynamic visuals, such as SVGs with random shapes, colors, and styles.
- Use AI-assisted creative coding within your automation pipeline.
Behavior
- The node sends a prompt instructing ChatGPT to return valid HTML that includes inline SVG.
- ChatGPT responds with code that can be rendered in a browser or passed to a frontend system.
This is useful for generating simple, programmatically described visuals without manual coding each variation.
8. ChatGPT Example 5: Quick Replies Generator
The final example focuses on generating short email response suggestions.
Purpose
- Speed up email workflows by suggesting concise replies based on the original message.
Configuration Pattern
- Input: User-provided email text or message content.
- Prompt strategy: A short instruction telling ChatGPT to generate several brief, ready-to-use reply options.
The node returns multiple suggested responses that can be displayed to a user, sent via another integration, or filtered based on additional logic.
Configuration Notes & Best Practices
Model and Cost Considerations
- Prefer ChatGPT models over Davinci-003 for most text tasks to reduce costs and benefit from better instruction-following behavior.
- Use Whisper-1 for transcription instead of legacy audio handling to leverage improved accuracy and pricing.
Workflow Performance
- Disable or pause nodes that process large audio files or call slower external services when they are not required for a particular test run.
- Use the static text example node to test downstream chains (summarization, translation, image generation) without re-running transcription.
Prompt and Role Design
- Use system messages to define global behavior, tone, and constraints for ChatGPT.
- Keep user messages focused on the specific content or question.
- In multi-turn scenarios, include previous assistant messages in the message array to maintain context.
Integration and Error Handling
- Ensure your OpenAI credentials are configured correctly in n8n’s credentials section before activating the workflow.
- When using HTTP Request nodes, verify the endpoint URL and required headers (for example,
Authorization: Bearer <API_KEY>). - Consider using n8n error workflows or Continue On Fail options where appropriate to handle occasional API errors gracefully.
Advanced Customization Ideas
While this template focuses on core patterns, you can extend it in several ways:
- Chain multiple ChatGPT nodes to enforce step-by-step transformations, such as summarization, sentiment analysis, and then translation.
- Integrate the quick reply generator with your email provider nodes to send selected replies automatically.
- Store transcripts, summaries, and generated prompts in a database node for later analytics or reuse.
All of these customizations build on the same fundamental structure: input nodes, OpenAI processing nodes, and downstream integration nodes.
Next Steps
To start using these patterns, connect your OpenAI credentials in n8n and experiment with the ChatGPT and Whisper examples described above. Gradually adapt the prompts, models, and data flows to match your own automation requirements.
For full node parameter details, authentication configuration, and additional examples, refer to the official
n8n OpenAI documentation.