Two Way Sync Between Pipedrive and MySQL Using n8n
Every growing business eventually hits the same wall: customer data is scattered across tools, never quite matching, and always a little out of date. Your CRM says one thing, your internal database says another, and you end up spending precious time chasing down the truth instead of serving customers or building your product.
That tension is often a signal that you are ready for a new level of automation. Instead of treating data updates as manual chores, you can turn them into a reliable, always-on process that quietly works in the background while you focus on higher-value work.
This is where a two-way sync between Pipedrive and MySQL using n8n becomes a powerful stepping stone. With a single workflow, you can keep your CRM and database in harmony, reduce errors, and create a foundation for more advanced automation across your business.
From Manual Updates To An Automated Mindset
Before we get into nodes and queries, it helps to look at the bigger picture. Every time you copy and paste contact details between Pipedrive and MySQL, you are doing work that a workflow can do for you. The cost is not just the minutes spent updating records, it is the mental load of remembering to do it and the risk of missing something important.
Adopting automation is less about tools and more about mindset. You are choosing to:
- Protect your time by removing repetitive tasks
- Trust systems to handle routine updates
- Build a clean, consistent source of truth for your customer data
The n8n template for a two-way sync between Pipedrive and MySQL is designed exactly for this shift. It runs on a schedule, compares records, and keeps both sides aligned without constant supervision. Once you set it up, you can refine it, extend it, and use it as a model for future automations.
What This n8n Workflow Template Actually Does
At its core, the workflow connects your Pipedrive CRM and your MySQL database, then regularly checks for differences. Whenever it finds new, missing, or updated contacts, it syncs those changes in the right direction so both systems stay in step.
- Sources: Pipedrive (as your CRM) and MySQL (as your internal database).
- Trigger: A scheduled trigger that runs at set intervals, such as hourly or daily.
- Matching key: Contacts are matched by the
emailfield. - Actions: Create or update contacts in either Pipedrive or MySQL, depending on where the newest data lives.
This is not just a one-time import. It is a true two-way sync that keeps evolving with your data. As your team adds or edits contacts in either system, the workflow ensures that both sides are updated accordingly.
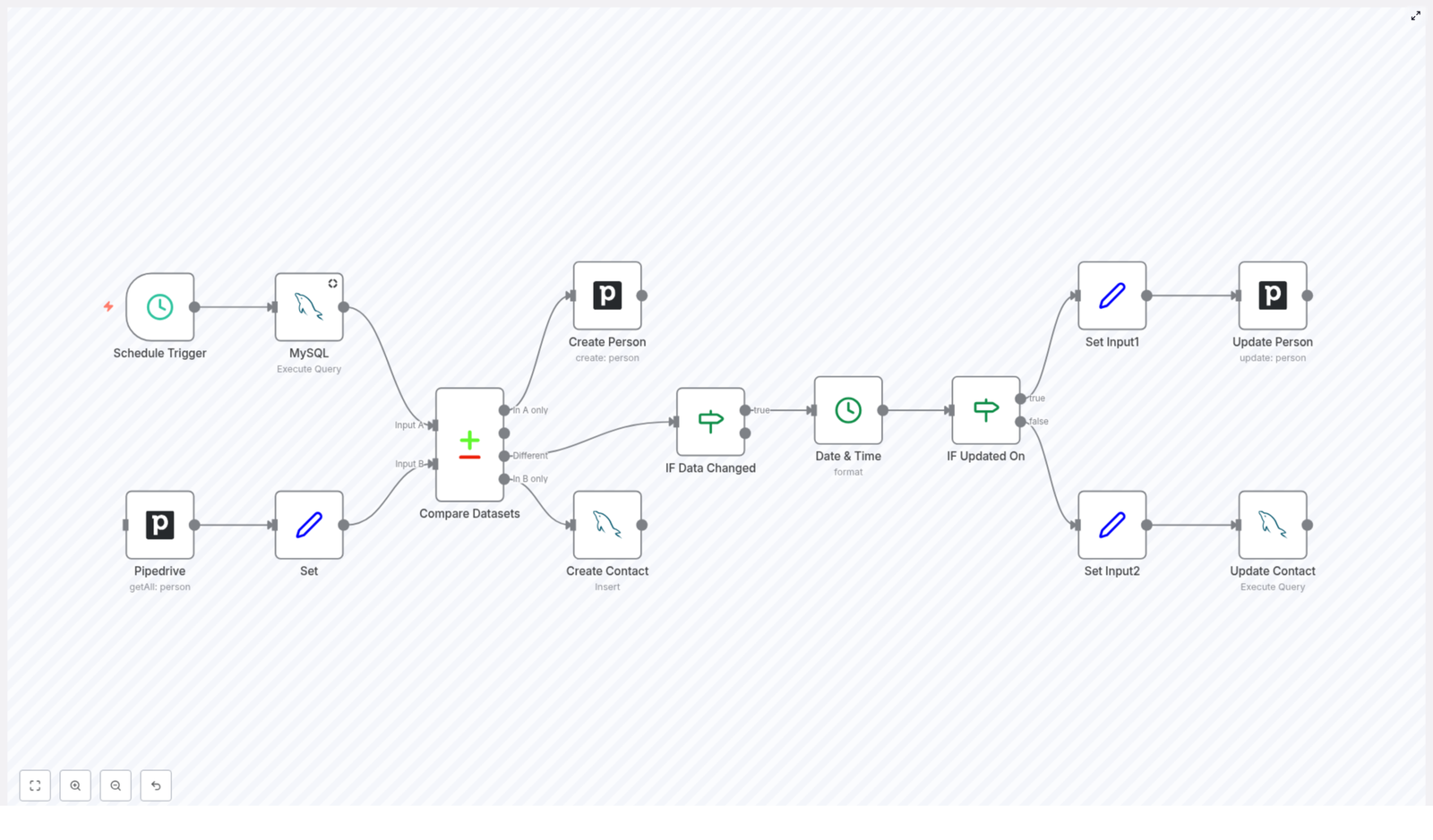
The Journey Of A Sync: How The Workflow Flows
To understand the power of this template, it helps to walk through the journey your data takes. Each n8n node plays a specific role, and together they create a robust, automated feedback loop between Pipedrive and MySQL.
1. Schedule Trigger Node – Let The Workflow Run For You
Everything begins with a Schedule Trigger node. Instead of relying on someone to remember to sync data, you define when the workflow should run.
For example, you can set it to run:
- Every hour for near real-time updates
- Once or twice a day for a lighter load
From that point on, the sync becomes an automatic routine. You no longer need to think about it, which is exactly the point.
2. MySQL Read Query – Pulling Contacts From Your Database
Next, the workflow reaches into your MySQL database to fetch the current list of contacts. The query targets your contact table and retrieves essential fields such as:
idnameemailphoneupdated_ontimestamp
This snapshot represents how your internal systems currently see each contact. It becomes one side of the comparison that drives the sync.
3. Pipedrive Fetch Contacts – Getting The CRM View
At the same time, the workflow uses the Pipedrive API to fetch all person records. This gives you a live view of your CRM contacts, including the fields you want to keep consistent with MySQL.
Now you have two datasets: one from MySQL and one from Pipedrive. The next step is to bring them into a comparable format.
4. Set Node – Preparing Pipedrive Data For Comparison
Raw data from APIs is not always structured in the exact way you need. The Set node is where you shape and format the Pipedrive data so that it lines up cleanly with your MySQL dataset.
In this step, you map fields and ensure that the data structure is compatible with the comparison node that follows. It is a small but important transformation that makes the rest of the workflow more reliable.
5. Compare Datasets – Finding New, Missing, And Changed Contacts
Now comes the heart of the sync: the Compare Datasets node. Using the email field as the unique key, n8n compares the contacts from MySQL and Pipedrive, then separates them into four clear outcomes:
- In A only: Contacts that exist in MySQL but not in Pipedrive. These trigger the creation of new persons in Pipedrive.
- In B only: Contacts that exist in Pipedrive but not in MySQL. These trigger the creation of new contacts in MySQL.
- Different: Contacts that exist in both systems but have mismatched data. These go through an update decision process.
- Same: Contacts that are identical in both systems. No action is needed, which keeps the workflow efficient.
This single node turns a messy comparison task into a structured decision tree that the rest of the workflow can act on.
Deciding What To Update And Where
Not every difference should be synced blindly. To keep your data accurate, the workflow needs to understand what changed and which system has the most recent version. This is where the conditional logic and timestamp handling come in.
6. Conditional Node – IF Data Changed
Within the Different path from the comparison, the workflow uses an IF node to check whether key fields have actually changed. Typically, this includes fields such as:
namephone
If those values differ between Pipedrive and MySQL, it signals that an update is needed. This protects you from unnecessary writes and keeps the workflow focused only on meaningful changes.
7. Date & Time Formatting – Aligning Timestamps
To decide which system has the most up to date information, the workflow needs consistent timestamps. The Date & Time node formats the updated_on field so that both sides can be compared reliably.
By standardizing these timestamps, you give the workflow a clear way to judge which record is newer.
8. Conditional Node – IF Updated On
Once timestamps are aligned, another IF node compares the updated_on values. This step determines the direction of the sync for each contact that has changed:
- If Pipedrive has the more recent update, the workflow pushes those changes into MySQL.
- If MySQL has the newer data, the workflow updates the corresponding person in Pipedrive.
This is what makes the integration truly two way. Neither system is always the source of truth. Instead, the most recent edit wins, regardless of where it happened.
Applying The Updates To Pipedrive And MySQL
After the workflow decides which side should be updated, it moves into the final step: actually writing the changes back into each system.
9. Set Input1 And Update Person (Pipedrive)
When Pipedrive is the system with the latest information, the workflow prepares that data for an update using a Set node. This node structures the fields so they are ready for the Pipedrive update operation.
Then the Update Person node sends the changes back into Pipedrive, keeping the CRM record aligned with the most current version of the data. Your sales and customer facing teams can trust that they are always seeing the latest details.
10. Set Input2 And Update Contact (MySQL)
If MySQL holds the most recent changes, a separate Set node prepares the data for an SQL update. The workflow then runs an Update Contact operation against the MySQL database.
This step ensures that your internal systems, dashboards, or reporting tools that rely on MySQL always reflect the latest contact information from Pipedrive when appropriate.
Why This Integration Matters For Your Growth
Automating a two-way sync between Pipedrive and MySQL is not just a technical improvement. It can reshape how your team works and how confidently you make decisions based on your data.
- Data consistency: Eliminate conflicting records and outdated contact details between your CRM and database.
- Efficiency: Remove repetitive manual data entry and updates, so your team can focus on selling, supporting, and building.
- Centralized view: Give every department access to synchronized customer information, no matter which tool they use.
- Scalability: Start with core contact fields, then extend the workflow to include more fields or additional systems as your needs grow.
Most importantly, this template can be the first of many automations. Once you experience the relief of having one piece of your data flow fully automated, it becomes easier to spot other areas you can streamline with n8n.
Using This Template As Your Launchpad
The beauty of n8n is its visual workflow editor. You are not locked into a rigid integration. Instead, you get a clear, editable map of how your data moves and transforms.
With this two-way sync template you can:
- Start quickly with a working Pipedrive-MySQL integration
- Customize fields, conditions, and timing to match your processes
- Experiment safely, improve over time, and build more complex automations as you grow
Think of this template as a foundation. Today it keeps your contacts in sync. Tomorrow it might trigger follow up workflows, analytics updates, or notifications based on those same contacts, all within the same n8n environment.
Take The Next Step Toward Smarter Automation
This two-way sync between Pipedrive and MySQL is a practical, high impact starting point for anyone serious about automation. It protects your data quality, frees your team from tedious updates, and opens the door to a more focused, automated way of working.
If you are ready to streamline your data workflows, explore this n8n template, connect your Pipedrive and MySQL instances, and let the workflow handle the sync for you. As you see the time and errors it saves, you will be inspired to keep building and refining your automation stack.