AI Agent to Chat with YouTube: Build This n8n Workflow
Imagine being able to ask questions like “What are people really saying about this channel?” or “Which thumbnails are actually working?” and getting clear, organized answers without manually digging through YouTube. That is exactly what this n8n workflow helps you do.
In this guide, you will learn how to build an AI agent that chats about YouTube videos and channels using n8n, OpenAI, Apify, and the YouTube Data API. It can analyze comments, review thumbnails, transcribe videos, and store insights so you can focus on strategy instead of repetitive research.
We will walk through what the template does, when to use it, and how to set it up step by step. Think of it as your YouTube research assistant that never gets tired.
What this n8n YouTube AI agent actually does
This workflow is built around two main ideas:
- A conversational AI agent that you can “chat” with about YouTube content
- A set of tools behind the scenes that handle all the heavy lifting with APIs and processing
When you send a message to the agent, it decides which tools to call. It can:
- Pull channel and video details from YouTube
- Search for videos and filter out Shorts if you only want long-form content
- Grab comments and summarize what viewers are really saying
- Send thumbnails to OpenAI for design critique and CTR improvement ideas
- Transcribe videos using Apify or another transcription service
- Store results in Postgres so you can track trends over time
All of this is orchestrated inside n8n, so you can tweak, extend, or connect it to other tools later.
When should you use this workflow?
This template is ideal if you:
- Create YouTube content and want deeper insights into what your audience cares about
- Work in marketing and need quick, structured research from YouTube without hours of manual review
- Are on a product or growth team and want to mine comments for feature requests, bugs, or feedback
It is especially helpful when you:
- Need to repurpose video content into blogs, shorts, or social posts
- Want to test and refine thumbnails with data-backed feedback
- Have to monitor multiple channels or videos at scale
Instead of juggling tabs and spreadsheets, you get a single AI agent you can ask questions like “Summarize the main complaints in the last 200 comments” or “How could I improve this thumbnail?”
Core tools and services behind the workflow
Here is what powers the AI agent under the hood:
- n8n – your automation and orchestration layer. It handles the webhook trigger, routing logic, HTTP requests, and data flow.
- OpenAI – used for natural language processing, comment summarization, insight extraction, and thumbnail analysis through its image endpoint.
- YouTube Data API (Google Cloud) – provides channel details, video metadata, search results, and comments.
- Apify – runs a transcription actor to convert video audio into text, which you can then analyze or repurpose.
- Postgres (optional but recommended) – stores chat memory and historical data so you can run trend analysis later.
Before you start: setup checklist
Before importing the n8n template, make sure you have these pieces ready:
- A Google Cloud project with the YouTube Data API enabled and an API key
- An OpenAI API key for GPT models and image analysis
- An Apify API key for the transcription actor, or another transcription API you prefer
- An n8n instance where you can import the workflow and add credentials
- (Optional) A Postgres database if you want persistent chat memory and long-term storage
Once those are in place, you are ready to connect everything inside n8n.
How the YouTube AI agent workflow runs (high-level)
Let us zoom out for a second and look at the full journey of a single chat message:
- You send a message to the chat webhook in n8n.
- The AI agent, powered by an OpenAI chat model, reads your request and decides which tools it needs.
- Based on that plan, n8n routes the request to specific tool workflows, such as channel lookup, video search, comment fetching, thumbnail analysis, or transcription.
- HTTP Request nodes call the YouTube Data API to get channel details, video lists, descriptions, statistics, and comments.
- If needed, the workflow sends thumbnail URLs to OpenAI for image analysis, and video URLs to Apify for transcription.
- All results are combined, summarized, and returned as a structured response to your chat.
- Optionally, the workflow saves data to Postgres so you can reuse it or analyze it over time.
The magic is that you interact with it in natural language, while n8n quietly coordinates all the technical steps in the background.
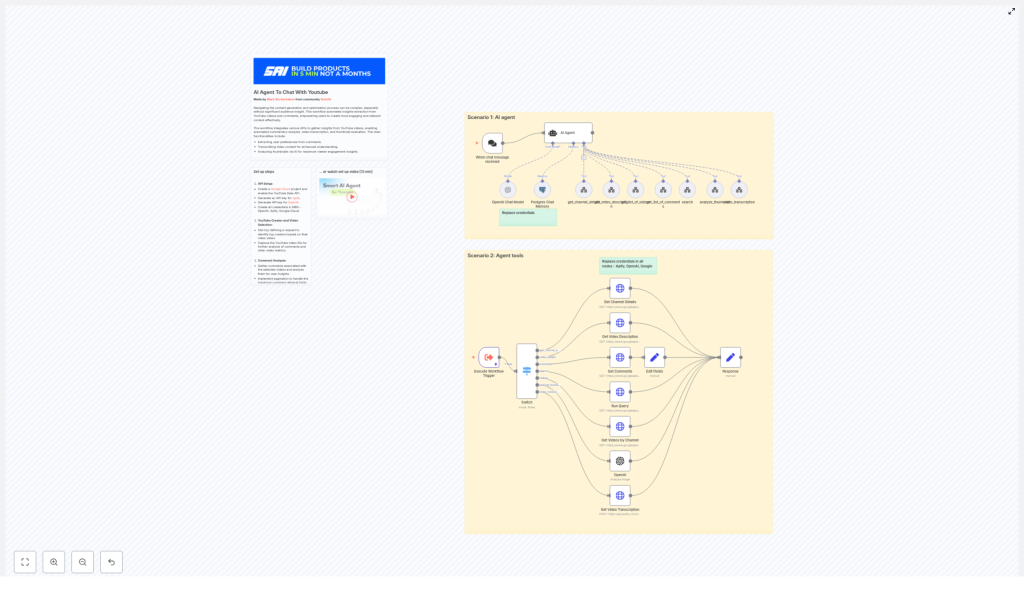
Step-by-step: mapping the n8n nodes
1. Webhook trigger for chat
You start by adding a chat trigger node in n8n. The template uses a “When chat message received” node.
Whatever the user types becomes the instruction for the AI agent. For example, “Find the top 5 videos on this channel and summarize the comments” is passed through this trigger into the workflow.
2. Agent orchestration with OpenAI
Next comes the agent node. This is configured with an OpenAI chat model and a system message that explains the agent’s role.
In that system message, you can tell the agent to:
- Plan which tools to call based on the user request
- Use the YouTube tools to fetch channel, video, and comment data
- Filter out Shorts (anything under 60 seconds) when detailed analysis or transcription is requested
- Ask clarifying questions if the user’s prompt is vague or missing details
The agent does not call APIs directly. Instead, it emits commands that n8n routes to the right tool workflows.
3. Routing agent commands with a Switch node
To interpret the agent’s tool calls, the workflow uses a Switch node. This node looks at the command name and sends the flow to the correct branch.
Each command corresponds to one of the tools, such as:
get_channel_detailsvideo_detailscommentssearchvideosanalyze_thumbnailvideo_transcription
This structure keeps things modular. You can add or adjust tools without breaking the whole agent.
4. Calling the YouTube Data API with HTTP Request nodes
The YouTube-related tools use HTTP Request nodes to talk to the YouTube Data API. Here are the main endpoints you will configure:
/channels– retrieves thechannel_id, title, and description, usually by channel handle or ID./search– finds videos for a channel or keyword. You can sort results bydate,viewCount, orrelevance./videos– gets full video details such as description,contentDetails(including duration), and statistics like views and likes./commentThreads– fetches comments and top-level replies for a given video.
These nodes give the agent the raw data it needs to answer your questions. OpenAI then turns that data into human-friendly summaries and insights.
5. Thumbnail analysis with OpenAI image models
For thumbnails, the workflow sends the high-resolution thumbnail URL to OpenAI’s image analysis endpoint.
In your prompt to the image model, you can ask for things like:
- Design critique and overall first impression
- Color contrast and text readability
- What elements draw attention first
- Specific suggestions to improve click-through rate
The agent can then combine this feedback with performance data to recommend changes like clearer text, stronger contrast, or more focused visuals.
6. Video transcription with Apify (or another service)
To turn video audio into text, the workflow sends the video URL to an Apify transcription actor using an HTTP Request node.
There are a couple of practical things to keep in mind:
- Long videos can take time to process and may cost more, depending on your provider.
- You might want to limit transcription to certain durations or sample segments for quick analysis.
Once the transcription is ready, it can be summarized, tagged, or repurposed into other content formats directly inside the workflow.
Making sense of noisy comments: tips for better insights
YouTube comments can be messy, repetitive, or full of spam. The workflow helps you clean this up and extract real insights by combining LLM analysis with good data handling.
Here are some strategies you can use:
- Aggregate comments across multiple videos, then send them in batches to an LLM for sentiment analysis and topic extraction.
- Use pagination with the YouTube API to pull as many comments as allowed, then deduplicate and normalize the text before analysis.
- Separate constructive feedback (feature requests, bug reports, content ideas) from generic praise or clear spam.
The result is a clear picture of what viewers actually want, not just a wall of comments.
Filtering out Shorts and choosing the right videos
By default, the YouTube API returns all kinds of video content, including Shorts. That is not always useful if you want deep analysis or long-form transcriptions.
Inside the video_details step, you can check contentDetails.duration. Use that to:
- Filter out videos shorter than 60 seconds when you need in-depth insights
- Focus your analysis on full-length content that has more context and viewer engagement
This simple filter keeps your transcription and analysis budget focused on the videos that matter most.
Storing data and scaling your analysis
If you are just testing, you can run the workflow and read the results directly. But once you start using it regularly, you will probably want a database.
The example workflow uses Postgres for this. You can store:
video_id- Title and description
- Publish date
- View count and other stats
- Thumbnail URL
- Transcription text or summary
- Comment summaries and sentiment tags
With that data in place, you can start doing trend analysis, compare performance across time, or feed it into dashboards and BI tools.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
As powerful as this setup is, there are a few gotchas you should watch out for:
- API quota limits
Both YouTube Data API and OpenAI have quotas. Use pagination carefully, cache results where it makes sense, and batch requests instead of calling endpoints one by one. - Transcription costs
Long videos add up. Consider sampling, using a cheaper ASR model for first drafts, or only fully transcribing your highest value content. - Credential security
Replace all example keys in the workflow with your own, and store them securely using n8n credentials or environment variables. Never hardcode keys in plain text where they can leak.
Real-world use cases for this YouTube AI agent
So what can you actually do with this workflow once it is running? Here are a few practical examples:
- Marketing teams can mine top creators’ comments to uncover pain points, objections, and language to use in ad copy and landing pages.
- Creators can quickly turn long videos into blog posts, shorts, and social snippets using transcriptions and AI-generated topic breakdowns.
- Product teams can monitor multiple channels for mentions of features, bugs, and common requests, then feed that into product roadmap discussions.
Once you see how flexible the agent is, you will probably think of more use cases tailored to your niche.
Ideas to extend and customize the workflow
The template gives you a solid foundation, but you can absolutely build on top of it. Some ideas:
- Generate thumbnail A/B test ideas based on historical CTR compared with thumbnail features and styles.
- Sync insights to tools like Airtable or Notion for content planning, editorial calendars, or publishing pipelines.
- Connect Postgres to Grafana or your favorite BI tool to visualize sentiment trends, top topics, or performance over time.
Because everything runs in n8n, you can plug this agent into other automations you already use.
Security, privacy, and compliance
Since you are working with user-generated content, it is worth being intentional about privacy and terms of service.
Good practices include:
- Avoid storing personally identifiable information unless you truly need it.
- Respect YouTube and API provider terms when collecting and storing data.
- If you share insights publicly, sanitize comments, remove usernames where appropriate, and attribute quotes carefully.
This keeps your automation useful, sustainable, and respectful of viewers.
Quick start checklist
Ready to get your own YouTube AI agent up and running? Here is a condensed checklist you can follow:
- Create and secure your API keys for Google (YouTube Data API), OpenAI, and Apify.
- Import the n8n workflow template into your instance.
- Replace all placeholder credentials in the relevant nodes with your own secure keys.
- Test with a single channel and one or two videos to make sure the data and responses look right.
- Tune your prompts for thumbnail and comment analysis so they match your KPIs and style.
- Once you are happy, scale up by batching channels and writing results into Postgres for long-term trend analysis.
Wrapping up
With this n8n workflow, you are essentially giving yourself an AI research assistant for YouTube. It handles channel discovery, video details, comment mining, transcription, and thumbnail evaluation, all orchestrated through a single conversational agent.
As you refine prompts, watch costs, and keep your credentials secure, this setup can become a powerful part of your content strategy, marketing research, or product feedback loop.
Try the template
If you are ready to see it in action, import the workflow into your n8n