n8n RSS to Telegram Workflow Template: Automated, Filtered Alerts
Use this n8n workflow template to continuously monitor multiple RSS feeds and push only relevant, non-duplicate items into specific Telegram channels. The workflow implements scheduled polling, item-level deduplication, URL-based routing, and keyword-based classification so that IT and security teams receive focused alerts instead of noisy, redundant updates.
1. Technical Overview
This n8n automation is designed for teams that consume updates from several technology and security RSS feeds and want to:
- Poll multiple RSS feeds at a fixed interval
- Process each feed sequentially to avoid concurrency issues
- Filter out already-processed items using a persistent deduplication store
- Route alerts to different Telegram channels based on:
- Patterns in the item URL (for example, specific hostnames)
- Security-related keywords in the item title
The workflow uses n8n’s built-in scheduling, RSS reading, conditional routing, and Telegram integration. Static workflow data is used as a simple, persistent cache for deduplication across runs.
2. Workflow Architecture
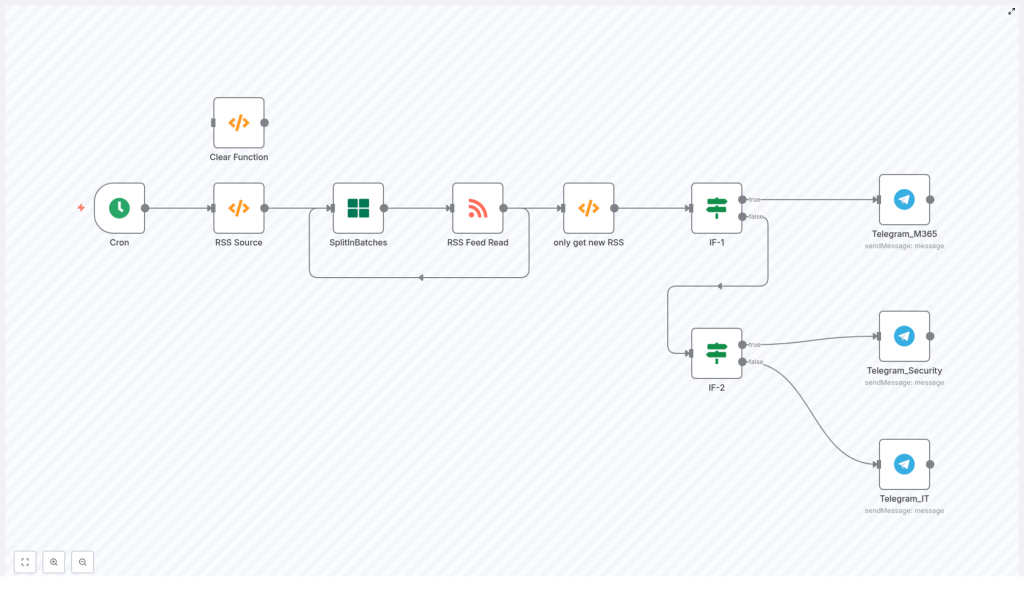
The workflow is organized as a linear pipeline with branching for routing and an optional maintenance utility. At a high level, the node sequence is:
- Cron – Scheduled trigger (for example, every 10 minutes)
- RSS Source (Function) – Defines the list of RSS feed URLs to poll
- SplitInBatches – Iterates through feeds one at a time
- RSS Feed Read – Fetches and parses items from the current feed
- only get new RSS (Function) – Deduplicates items using workflow static data
- IF-1 – URL-based routing (for example, Microsoft Tech Community)
- IF-2 – Title keyword-based routing (security vs general IT)
- Telegram_* nodes – Sends formatted messages into specific Telegram chats
- Clear Function – Optional utility to reset the deduplication cache
The main processing path is:
Cron → RSS Source (Function) → SplitInBatches → RSS Feed Read → only get new RSS (Function) → IF-1 (URL-based) → Telegram_M365 (if URL match) → IF-2 (if no URL match) → Telegram_Security (if keyword match) → Telegram_IT (if no keyword match)
The Clear Function node is not part of the regular run path. It is used manually when you need to clear the stored IDs (for testing or when changing the deduplication strategy).
3. Node-by-Node Breakdown
3.1 Cron (Schedule Trigger)
Purpose: Start the workflow periodically.
- Trigger type: Cron
- Typical configuration: Every 10 minutes
Set the execution interval based on:
- How often the monitored RSS feeds are updated
- Telegram API rate limits and your expected message volume
For higher-volume feeds, you may want a shorter interval. For low-frequency feeds, you can reduce the schedule to every 30 or 60 minutes to reduce load.
3.2 RSS Source (Function)
Purpose: Provide the list of RSS feed URLs that the workflow should poll.
This is a JavaScript Function node that outputs one item per RSS feed URL. Example implementation from the template:
return [ { json: { url: 'https://feeds.feedburner.com/UnikosHardware' } }, { json: { url: 'http://www.ithome.com.tw/rss.php' } }, { json: { url: 'http://feeds.feedburner.com/playpc' } }, { json: { url: 'https://lab.ocf.tw/feed/' } }, { json: { url: 'https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/plugins/custom/...'} }
];
Key points:
- Each item in the returned array is a separate feed, with the URL stored under
json.url. - You can add or remove feeds by editing this array.
- Keep the structure consistent so downstream nodes can always read
urlfromitem.json.url.
3.3 SplitInBatches
Purpose: Process one feed URL at a time.
- Batch size: 1
By setting batchSize: 1, the workflow ensures that each feed is processed sequentially. This has two benefits:
- Reduces the chance of hitting multiple remote RSS endpoints concurrently, which can be helpful if certain feeds are rate-limited or slow.
- Makes the deduplication logic easier to reason about, since each batch corresponds to a single feed URL.
Downstream, the RSS Feed Read node obtains the current feed URL from this node’s output.
3.4 RSS Feed Read
Purpose: Fetch and parse RSS items from the current feed.
This is the n8n RSS Feed Read node. It is configured to read the URL dynamically from the previous node:
url = {{$node["SplitInBatches"].json["url"]}}
Typical output fields per item include:
title– RSS item titlelink– URL of the itemisoDate– Published date in ISO format (used by default for deduplication)
These fields are used later for deduplication, routing, and message formatting.
3.5 only get new RSS (Function) – Deduplication
Purpose: Filter out items that have already been processed in previous workflow runs.
This Function node uses n8n’s workflow static data in global scope to maintain a list of previously seen IDs across executions. The core logic from the template is:
const staticData = getWorkflowStaticData('global');
const newRSSIds = items.map(item => item.json['isoDate']);
const oldRSSIds = staticData.oldRSSIds;
if (!oldRSSIds) { staticData.oldRSSIds = newRSSIds; return items;
}
const actualNewRSSIds = newRSSIds.filter(id => !oldRSSIds.includes(id));
const actualNewRSS = items.filter(data => actualNewRSSIds.includes(data.json['isoDate']));
staticData.oldRSSIds = [...actualNewRSSIds, ...oldRSSIds];
return actualNewRSS;
How it works:
- Reads the global static data object via
getWorkflowStaticData('global'). - Builds an array of IDs from the current batch using
item.json["isoDate"]. - On the first run (no
oldRSSIdsyet), it:- Initializes
staticData.oldRSSIdswith the current IDs - Returns all items as “new”
- Initializes
- On subsequent runs:
- Compares the current IDs against
oldRSSIds - Filters out items whose IDs are already stored
- Updates
staticData.oldRSSIdswith the union of:actualNewRSSIds(the IDs just seen for the first time)- Existing
oldRSSIds
- Returns only the subset of items with new IDs
- Compares the current IDs against
Important notes:
- Dedupe key: The template uses
isoDateas the identifier. This is simple, but:- Different feeds can have items with the same
isoDate. - Some feeds may not provide a stable
isoDatefor updates.
Prefer
guidorlinkif available and unique. - Different feeds can have items with the same
- Persistence: Global static data is persisted across workflow runs on the same n8n instance, so deduplication continues to work between scheduled executions.
- Growth:
staticData.oldRSSIdswill grow over time unless you implement a trimming strategy.
3.6 IF-1 – URL-Based Routing
Purpose: Route items to a dedicated Telegram channel if the URL matches a specific host or pattern.
This is an IF node that checks whether the RSS item’s link contains a certain hostname, for example:
techcommunity.microsoft.com
Behavior:
- True branch: Items whose link contains the specified host are routed directly to a dedicated Microsoft 365 Telegram node, for example
Telegram_M365. - False branch: All other items are passed to IF-2 for further classification based on title keywords.
You can adjust the URL condition to route other vendors or domains to their own Telegram channels.
3.7 IF-2 – Title Keyword Filter
Purpose: Classify items by scanning the title for security-related keywords using a regular expression.
This second IF node runs only for items that did not match the URL-based rule in IF-1. It uses a regex condition on title to look for security terms. Example keywords include:
- 資安
- 資訊安全
- 外洩
- 監控
- 威脅
- 漏洞
- 攻擊
- 入侵
- 隱私
- 騙
- phishing
- security
- Secure
Behavior:
- True branch: If the title matches the regex (contains any of the security-related keywords), the item is routed to
Telegram_Security. - False branch: If there is no keyword match, the item is treated as general IT content and routed to
Telegram_IT.
You can refine the regex for language coverage, case-insensitivity, or more granular topic routing.
3.8 Telegram Nodes (Telegram_M365, Telegram_Security, Telegram_IT)
Purpose: Deliver formatted messages to the appropriate Telegram channels or groups.
Each Telegram node is configured with its own credentials and target chat. The basic message template used in the workflow is:
{{$json["title"]}}
{{$json["link"]}}
Configuration notes:
- Credentials:
- Store your Telegram bot token in n8n’s credentials manager.
- Do not hardcode tokens in node parameters or Function nodes.
- Chat IDs:
- Use separate bots or separate chat IDs for different channels (for example, M365, security, general IT).
- Make sure the bot has permission to post in the target group or channel.
- Message formatting:
- You can switch to Markdown or HTML mode in the Telegram node if you want richer formatting.
- Extend the template to include additional fields such as description, author, or publication date.
3.9 Clear Function (Optional Utility)
Purpose: Reset the deduplication state by clearing staticData.oldRSSIds.
This is a utility Function node that you run manually when needed. It removes the stored IDs so that the workflow can treat all items as new again.
Typical use cases:
- Testing the workflow from scratch
- Changing the deduplication key (for example, from
isoDatetolinkorguid) - Backfilling older items intentionally
4. Configuration Notes and Best Practices
4.1 Choosing a Robust Deduplication Key
Using isoDate is convenient, but it is not always unique or stable across feeds. For more reliable deduplication:
- Prefer
guidif the feed provides a stable GUID per item. - Use
linkas a fallback, assuming each item URL is unique.
Example adjustment for link-based dedupe (see also section 7):
const newRSSIds = items.map(item => item.json['link']);
// The rest of the logic stays the same, using 'link' instead of 'isoDate'
4.2 Controlling Static Data Growth
The oldRSSIds array in global static data grows on every new item. For long-running workflows, consider:
- Storing only the last N IDs (for example, last 1000 or 5000) to limit memory usage
- Implementing a simple trimming step after updating
staticData.oldRSSIds
If you need very long-term or shared deduplication state, you can move this to an external database or cache instead of static data.
4.3 Telegram Rate Limiting and Message Volume
If your feeds are very active, you may send many messages per run. To avoid problems:
- Reduce the Cron frequency or add a delay between messages.
- Optionally batch multiple items into a single Telegram message (for example, a daily digest) instead of one message per item.
4.4 Credential Security
- Always store Telegram bot tokens in n8n Credentials, not in plain Function code.
- Use environment variables for chat IDs or other sensitive configuration if needed.
- Review Telegram bot privacy settings to ensure it can post in the intended chats.
4.5 Keyword and Language Tuning
The security keyword list in IF-2 is tailored for a mixed-language audience. You can adjust it to better match your context:
- Add or remove terms for your language or domain.
- Use case-insensitive regex flags to avoid missing matches due to capitalization.
- Consider multiple IF nodes or a Switch node if you want separate channels per topic, severity, or language.
4.6 Error Handling and Monitoring
To harden the workflow for production:
- Add a global error workflow or a Catch node to capture failures from:
- RSS feed read errors (network issues, invalid feeds)
- Telegram API errors (invalid token, blocked bot, wrong chat ID)
- Send error notifications to an admin Telegram channel or log them to