How to Generate XML from SQL Data with XSLT in n8n
What You Will Learn
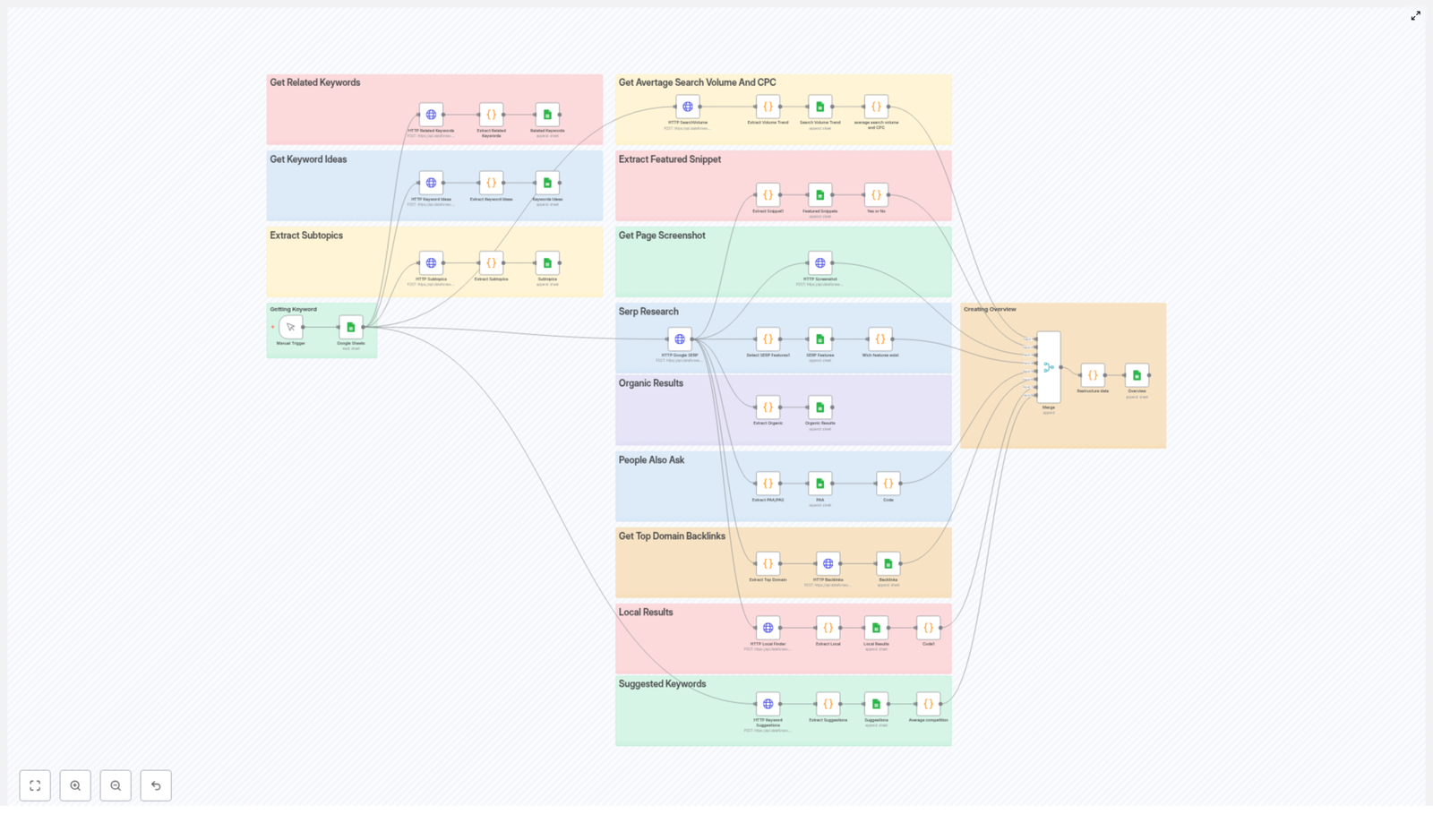
In this tutorial you will learn how to build an n8n workflow that:
- Fetches product data from a MySQL database with an SQL query
- Transforms the data into structured JSON, then into XML
- Links the XML to an XSLT stylesheet for visual formatting
- Serves both the XML and the XSLT through n8n webhooks
- Handles CORS requirements so modern browsers can load the stylesheet correctly
By the end, you will understand each node in the workflow and how they work together to deliver styled XML over HTTP.
Key Concepts Before You Start
n8n Workflow Basics
n8n lets you connect different services and data sources using nodes. In this workflow you will use:
- Webhook nodes to receive and respond to HTTP requests
- MySQL or similar SQL nodes to run queries on your database
- Set, Concatenate Items, and Convert to XML nodes to shape and transform data
- Move Binary Data to set the correct MIME type for the XML response
From SQL to XML with XSLT
- SQL data is tabular, with rows and columns.
- XML is a markup format that represents data in a tree structure.
- XSLT is a stylesheet language that lets you transform and style XML for display, for example in a browser.
In this tutorial, you will:
- Load product data from SQL.
- Convert it to JSON, then to XML.
- Attach an XSLT stylesheet reference in the XML declaration.
- Serve both XML and XSLT from the same n8n instance to satisfy browser CORS rules.
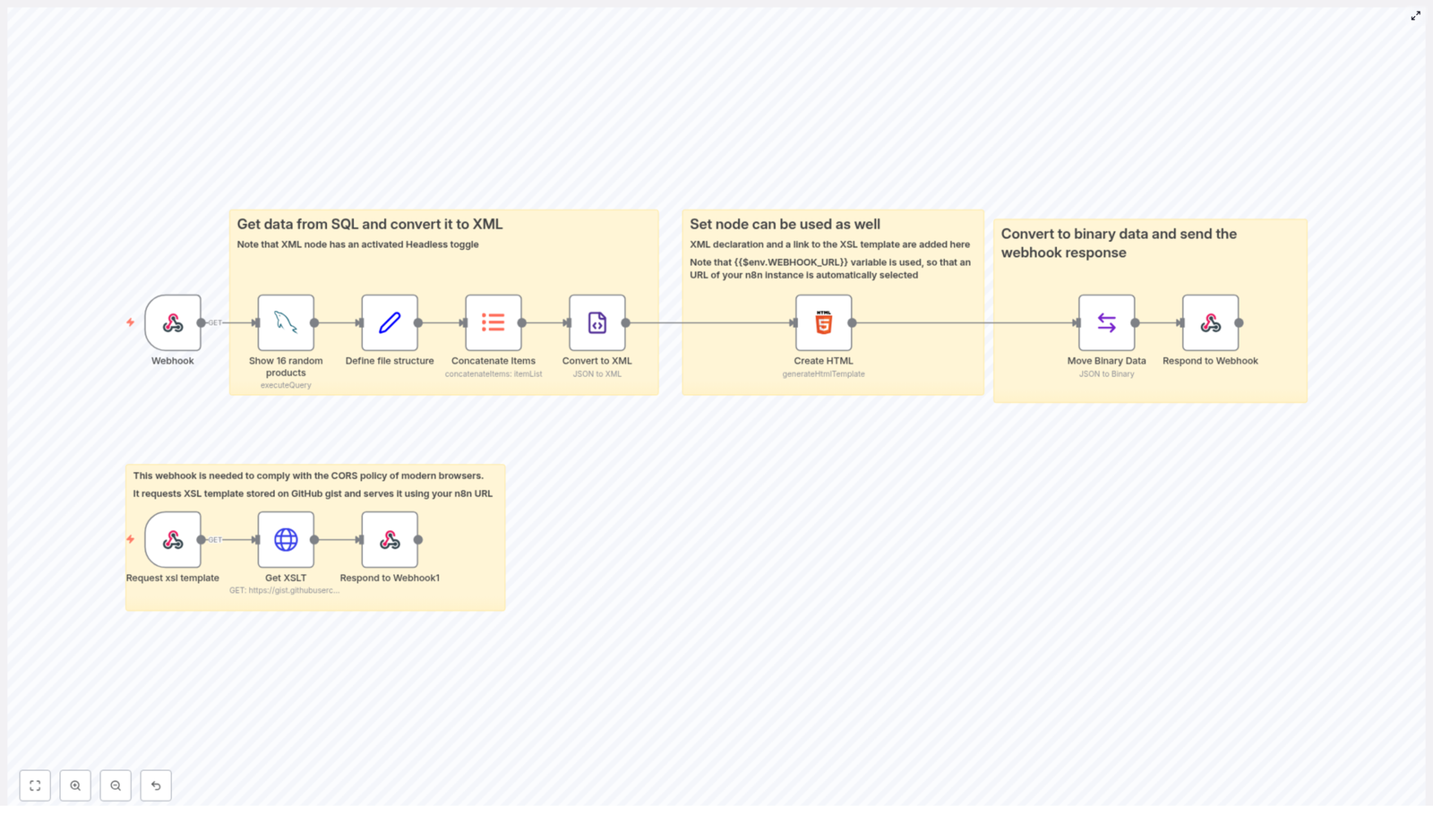
Step 1 – Trigger the Workflow and Fetch SQL Data
1.1 Set up the Webhook trigger
The workflow starts with a Webhook node that listens for an HTTP GET request. When a client calls this webhook URL, the workflow runs and prepares the XML response.
- Method: GET
- Use case: A browser, script, or external system can request your generated XML by calling this webhook URL.
1.2 Query random products from the database
Next, use a node such as Show 16 random products that runs an SQL query on your products table. This node is typically configured as a MySQL node (or another SQL-compatible node) with a query similar to:
- Select 16 random rows from the
productstable.
The query returns product records that include key fields such as:
codenamelinescaleprice
These fields will later be mapped into a consistent JSON structure before converting to XML.
Step 2 – Structure the Data and Convert It to XML
2.1 Normalize the product data with a Set node
After the SQL query, insert a Set node, often named something like Define file structure. This node ensures that each product item has a predictable and clean JSON shape.
In the Set node, you typically:
- Create fields such as
code,name,line,scale, andprice. - Map each field to the corresponding data from the SQL query result.
The goal is to have a uniform JSON object for each product, which makes the XML conversion step straightforward.
2.2 Combine all products into one array
Next, add a Concatenate Items node. This node aggregates all individual product items into a single JSON array.
This step is important because the Convert to XML node will take this combined JSON array and produce one coherent XML document instead of multiple separate XML fragments.
2.3 Convert JSON to XML
Now use the Convert to XML node to transform the aggregated JSON array into XML.
- Input: the JSON array from Concatenate Items.
- Output: an XML string that represents all 16 random products.
In this node, the Headless toggle is enabled. That means the node does not include the standard XML declaration line at the top, such as:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
You skip this here on purpose because you will add a custom XML declaration later that also includes a link to the XSLT stylesheet.
Step 3 – Add XML Declaration and Link the XSLT Stylesheet
3.1 Create the final XML wrapper
Once you have the raw XML from the Convert to XML node, you use a Create HTML node to construct the final XML output string.
Despite the name, this node can be used to build any text content, including XML. In this node you:
- Prepend an XML declaration to the converted XML.
- Insert a processing instruction that points to the XSLT stylesheet.
3.2 Use a dynamic URL for the XSLT template
The XSLT reference in the XML declaration uses the environment variable {{$env.WEBHOOK_URL}}. This allows you to generate a dynamic URL that points to the XSL template served by your own n8n instance.
Your final XML header will look similar to this pattern (simplified):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="<dynamic-n8n-xsl-url>"?> <products> ... </products>
By using {{$env.WEBHOOK_URL}}, the href in the stylesheet instruction always points to the correct n8n webhook URL for the XSLT file, even if your deployment URL changes.
Step 4 – Convert to Binary and Return the XML in the Webhook
4.1 Prepare XML as binary data
Browsers and HTTP clients expect XML to be served with the correct content type. To achieve this, add a Move Binary Data node after Create HTML.
In this node you:
- Move the XML string into the binary section of the item.
- Set the MIME type to
text/xml.
This ensures that when n8n sends the response, the client recognizes it as XML and can apply the XSLT stylesheet correctly.
4.2 Send the response from the Webhook
Finally, use the Respond to Webhook node to send the XML back to the caller of the initial webhook.
In this node you typically configure:
- Response body: the binary XML data produced by Move Binary Data.
- Content-Type header:
text/xml. - Appropriate CORS headers so that browsers can access the resource from different origins.
With these settings, your workflow now returns a fully styled XML response that a browser can render using the linked XSLT.
Step 5 – Serve the XSLT Template and Handle CORS
5.1 Why CORS matters for XML and XSLT
Modern browsers enforce strict Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) rules on resources like stylesheets. When your XML document references an XSLT file, the browser checks whether it is allowed to load that stylesheet from the specified origin.
If the XSLT is served from a different domain or without the correct headers, the browser can block it, which prevents your XML from being styled.
5.2 Use a second webhook to serve the XSLT
To avoid CORS issues, this workflow includes a separate webhook whose job is to serve the XSL template from the same n8n instance.
This auxiliary workflow typically:
- Receives a request for the XSLT via a webhook URL.
- Fetches the XSL template from a remote source, such as a GitHub gist.
- Returns the XSLT content through the n8n webhook URL, with appropriate headers.
Because the XSLT is now served from the same origin as the XML (or at least from a controlled n8n endpoint), the browser can safely load it without triggering CORS errors.
This design keeps your XSLT source in GitHub while still complying with browser security policies.
Recap – How the n8n Workflow Fits Together
To summarize, the full pipeline looks like this:
- Webhook node receives an HTTP GET request to generate XML.
- Show 16 random products node runs an SQL query to fetch random product data from the database.
- Set node (Define file structure) maps raw SQL fields into a consistent JSON format.
- Concatenate Items node aggregates all product items into a single JSON array.
- Convert to XML node turns that JSON array into XML, with the Headless option enabled.
- Create HTML node builds the final XML string, adding the XML declaration and the XSLT stylesheet reference that uses
{{$env.WEBHOOK_URL}}. - Move Binary Data node converts the XML string to binary and sets the MIME type to
text/xml. - Respond to Webhook node sends the XML back to the client with correct headers and CORS settings.
- A separate webhook workflow fetches the XSL template from a GitHub gist and serves it via n8n to satisfy CORS requirements.
With this pattern you can customize the SQL query, the XML structure, and the XSLT styling to present any database data in a rich, browser-friendly way.
FAQ
Can I change the number of products returned?
Yes. Adjust the SQL query in the Show 16 random products node. For example, change the limit from 16 to any number that fits your use case.
Do I have to use MySQL?
No. You can use any n8n SQL node that connects to your database, as long as it returns product-like records that you can map in the Set node.
Can I reuse this pattern for other data types?
Absolutely. Replace the products table and fields with any other dataset. The key steps – SQL fetch, JSON normalization, XML conversion, and XSLT styling – remain the same.
Why is the XSLT hosted through a webhook instead of directly from GitHub?
Serving the XSLT through n8n lets you control headers and origin, which helps satisfy browser CORS policies. Direct loading from GitHub can result in blocked stylesheets due to stricter cross-origin rules.
Try This n8n XML + XSLT Workflow Yourself
This workflow is a practical example of how n8n can combine SQL data retrieval, XML generation, XSLT styling, and webhook-based delivery into a single automated pipeline.
Implement it in your own n8n instance to:
- Serve dynamic XML feeds from your database
- Apply custom XSLT styles for rich visual presentations
- Experiment with more advanced automation patterns and data formats
For more in-depth automation tutorials and workflow ideas, subscribe to our newsletter or explore additional guides on our blog.