How to Chat with Google News Using SerpApi & OpenAI
From Information Overload to Focused Insight
It is easier than ever to drown in news. Headlines, alerts, and feeds constantly compete for your attention, and staying informed can start to feel like a full-time job. If you are building a business, growing a project, or simply trying to protect your focus, manually scanning news sites is a huge time cost.
What if you could flip that around and let automation do the heavy lifting for you? Imagine asking a simple question, then receiving a clear, structured summary of the latest Google News results, grouped into topics and enriched with key links. No more endless scrolling, no more “I will read this later” tabs.
This is exactly what this n8n workflow template helps you achieve. By connecting SerpApi and OpenAI inside n8n, you can turn a stream of raw news into focused insight that supports better decisions and frees your time for higher-value work.
Adopting an Automation-First Mindset
Before we dive into the steps, it helps to shift how you think about your daily tasks. Any repetitive action you take to “check what is new” is a candidate for automation. When you automate that kind of routine work, you:
- Protect your attention for strategy, creativity, and deep work
- Stay consistently informed without manual effort
- Build reusable systems that grow with your business or projects
This Google News chat workflow is not just a one-off trick. It is a starting point, a template you can adapt, extend, and connect to other tools. As you walk through the setup, keep asking yourself: “Where else could I apply this approach?”
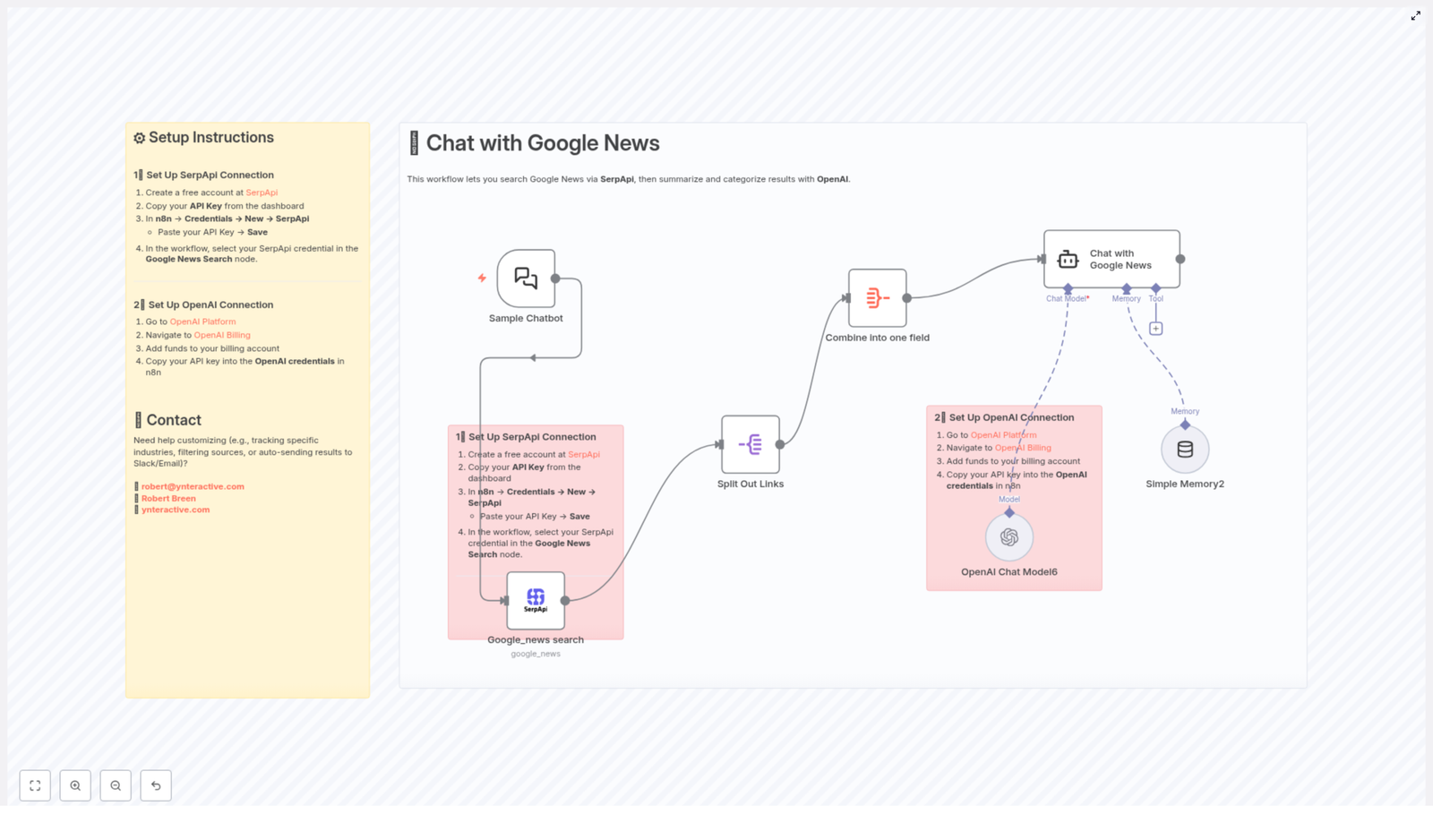
What This n8n Workflow Actually Does
At its core, the workflow turns a simple chat-style question into a curated overview of the latest news. Here is what happens behind the scenes:
- Sample Chatbot Trigger – You start the workflow with a user query, just like asking a chatbot a question.
- Google News Search via SerpApi – SerpApi queries Google News for your topic and returns structured results.
- Split Out Links – Each news result is separated so it can be processed individually.
- Combine Into One Field – All titles and links are merged into a single field that is easy for OpenAI to process.
- Chat with Google News (Using OpenAI) – OpenAI receives the combined data, then summarizes and categorizes the news into topics, including key article links.
- Simple Memory – A lightweight memory layer keeps session context so your “conversation” with the news feels more natural.
The result is a conversational experience: you ask, “What is happening in AI regulation today?” and the workflow returns structured insights instead of a chaotic list of headlines.
Key Building Blocks: SerpApi and OpenAI
SerpApi: Your Reliable Window Into Google News
SerpApi is an API that lets you access search engine data, including Google News, in a structured format. Instead of manually browsing Google News, you can programmatically request:
- Latest articles related to a specific topic
- Headlines, URLs, and metadata in a consistent structure
- Filtered results for particular industries or sources
In this workflow, SerpApi is the engine that fetches the raw news data that OpenAI will later transform.
OpenAI: Turning Raw Headlines Into Insight
OpenAI provides advanced language models, such as GPT, that can understand and generate natural language. When paired with SerpApi, OpenAI becomes your intelligent editor. It:
- Summarizes multiple articles into concise, readable overviews
- Groups related stories into categories or themes
- Returns structured text with links to the original sources
This combination means you no longer just “see” the news. You get a guided explanation of what matters and why, in a format that supports quick decisions.
Setting Up the Workflow in n8n
You do not need to be a full-time developer to put this to work. With n8n, you connect the pieces visually and configure a few credentials. Once it is running, it will keep working in the background while you focus on more meaningful tasks.
Step 1 – Connect SerpApi to n8n
- Create a free account at SerpApi.
- From your SerpApi dashboard, copy your API key.
- In n8n, open Credentials > New > SerpApi.
- Paste your SerpApi API key and save the credential.
- In the workflow, open the Google News Search node and select the SerpApi credential you just created.
With this in place, your workflow can now request live Google News data on demand.
Step 2 – Connect OpenAI to n8n
- Visit the OpenAI Platform and log in.
- Go to OpenAI Billing and make sure you have funds available in your account.
- Create or copy your OpenAI API key.
- In n8n, open Credentials and create a new OpenAI credential.
- Paste your API key, save, and then select this credential in the OpenAI node used for the “Chat with Google News” step.
Now your workflow has both the data source (SerpApi) and the intelligence layer (OpenAI) ready to work together.
How the Workflow Runs, Step by Step
Once your connections are configured, the workflow comes to life. Here is what happens when you send a query to the chatbot trigger:
- You ask a question in the Sample Chatbot Trigger, such as “What is new in renewable energy?”
- SerpApi searches Google News for that topic and returns a set of relevant articles.
- The workflow splits the results in the “Split Out Links” node so each article can be handled separately.
- All titles and links are combined into a single field in the “Combine Into One Field” node. This creates a compact input for OpenAI.
- OpenAI processes the combined data in the “Chat with Google News” step. It:
- Categorizes the news into five groups or topics
- Summarizes the key points from each group
- Returns structured text with relevant URLs for deeper reading
- Simple Memory tracks context so follow-up questions feel more natural within the same session.
From your perspective, it feels like chatting with a well-informed assistant that has just read the latest Google News for you and distilled it into what you actually need to know.
Turning a Template Into Your Own Automation System
This n8n template is a powerful starting point, but it is also an invitation to experiment. As you get comfortable with it, you can adapt it to match your goals, workflows, and tools.
Customization Ideas
- Adjust categories and depth
Modify the prompts in the OpenAI node to change how the news is grouped or how detailed the summaries should be. You can increase or decrease the number of categories or ask for specific angles, such as risks, opportunities, or market impact. - Control how much news you process
Update the SerpApi node parameters to change how many results you fetch. You can focus on a small, curated set of articles or broaden the scope for more comprehensive overviews. - Filter by industry or source
Use SerpApi filters to target certain industries, locations, or news sources. This is especially powerful if you monitor niche markets or competitors. - Send insights where you work
Connect additional n8n nodes to deliver the summarized news to Slack, email, Notion, or other platforms. For example, you could:- Receive a daily Slack message with categorized news on your key topics
- Send a weekly email digest to your team
- Log summaries in a knowledge base for future reference
Each small improvement you make turns this template into a tailored system that fits the way you and your team actually work.
Why This Workflow Is a Stepping Stone, Not a Finish Line
Automating your news consumption is more than a convenience. It is a concrete example of how you can reclaim time and mental energy with n8n, SerpApi, and OpenAI. Once you see how easily this template transforms scattered information into structured insight, you will likely spot other opportunities:
- Monitoring competitors or trends across multiple topics
- Feeding summarized news into dashboards or reports
- Combining this workflow with others for research, content creation, or decision support
Use this template as your proof of concept. Let it show you what is possible when you treat automation as a partner, not a luxury. Then keep iterating.
Need Help Extending or Customizing It?
If you want to push this workflow further, integrate it with other tools, or tailor it for a specific use case, you do not have to figure it out alone. You can reach out for support or collaboration:
- Email: robert@ynteractive.com
- LinkedIn: Robert Breen
- Website: ynteractive.com
Start Your Automation Journey Today
This workflow combines the reach of Google News with the intelligence of OpenAI, all orchestrated by n8n, to give you a smarter way to stay informed. Instead of chasing information, you design a system that brings the right insights to you, in a format that respects your time and attention.
Set up the template, run your first query, and experience what it feels like to chat with the news instead of scrolling through it. Then keep building from there, one automation at a time.
Ready to turn information overload into clarity and focus? Start setting up your Google News chat workflow today and let automation handle the updates while you focus on what truly moves you forward.