How Maya Built a Chatbot, Voice Agent and Phone Agent With Voiceflow, n8n and RAG
Maya was the kind of operations lead every fast-growing company relies on. She juggled support tickets, internal documentation, customer calls, and a calendar full of demos. Her team sold electronics online, and business was booming. Unfortunately, so were the repetitive questions.
“Where is my order?” “Can I book a call for tomorrow afternoon?” “What is your return policy for defective products?” These questions came through chat, email, and phone, at all hours. The information lived in different places: Google Drive docs, Google Calendar, a backend order tracking API, and a growing internal knowledge base. Every answer required context, and every context lived in a different tool.
Maya knew she needed automation, but not just any chatbot. She wanted a smart assistant that could talk, type, and even pick up the phone, all while pulling accurate answers from her company’s documents. That is when she discovered a workflow template built around Voiceflow, n8n, Google Calendar, Qdrant, OpenAI, and Twilio, using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to keep responses grounded in real knowledge.
The Problem: Fragmented Knowledge, Frustrated Customers
On a Monday morning, Maya watched her support dashboard spike again. Customers were asking for order updates, trying to schedule appointments, and hunting for basic product info. Her team was drowning in repetitive work while complex tickets waited in the queue.
She had already tried a basic FAQ chatbot on the website, but it failed whenever the question required live data or referenced internal documents. It could not read Google Calendar, it did not know anything about their updated warranty policy on Google Drive, and it definitely could not check order status from the backend API.
What she needed was a single automation layer that could:
- Hold natural conversations in chat, voice, or phone
- Pull answers from a real knowledge base using RAG
- Create and read appointments from Google Calendar
- Check order status via an internal API
She wanted a system that separated concerns, used the best tools for each task, and still felt like one unified assistant to the customer.
The Discovery: A Modular Voiceflow + n8n + RAG Architecture
While researching automation tools, Maya came across an n8n workflow template titled “Voiceflow Chatbot, Voice & Phone Agent with RAG.” It promised exactly what she was imagining: a chat, voice, and phone agent that could answer knowledge questions, track orders, and manage appointments.
The architecture clicked for her immediately. Each tool did what it was best at:
- Voiceflow handled conversational design and deployment to chat widgets, voice, and phone channels (including Twilio numbers).
- n8n acted as the orchestration layer, running webhooks, integrating with APIs, and connecting LangChain-style LLM nodes.
- OpenAI provided LLM capabilities for intent parsing, response generation, and embeddings.
- Qdrant served as a vector database that powered Retrieval-Augmented Generation so answers could reference actual documents.
- Google Calendar managed appointments created directly from conversations.
Instead of trying to force one platform to do everything, this stack let each piece specialize. Voiceflow talked to customers, n8n coordinated the logic, Qdrant remembered the documents, and OpenAI turned context into fluent answers.
The Plan: One Conversation, Three Webhooks, Many Capabilities
Maya sketched the high-level flow on a whiteboard. A customer would interact with a Voiceflow experience, either on the website chat widget or via a phone number. Voiceflow would collect what the customer wanted and call an n8n webhook. From there, n8n would decide what to do.
The architecture boiled down to a few key steps:
- The user talks or types into Voiceflow (chat, voice widget, or phone call).
- Voiceflow sends the captured data to n8n through a specific webhook, depending on the intent:
n8n_orderfor order trackingn8n_appointmentfor calendar bookingsn8n_ragfor knowledge questions handled with RAG
- n8n runs the correct branch of the workflow:
- Create or read Google Calendar events
- Call the backend order tracking API
- Run RAG retrieval from Qdrant and call the LLM agent
- n8n returns a plain response back to Voiceflow.
- Voiceflow continues the conversation and replies to the user in chat or voice.
The template Maya found already implemented this pattern. All she had to do was adapt it to her company’s data and rules. The real work would start with the knowledge base.
Rising Action: Teaching the Agent the Company’s Knowledge
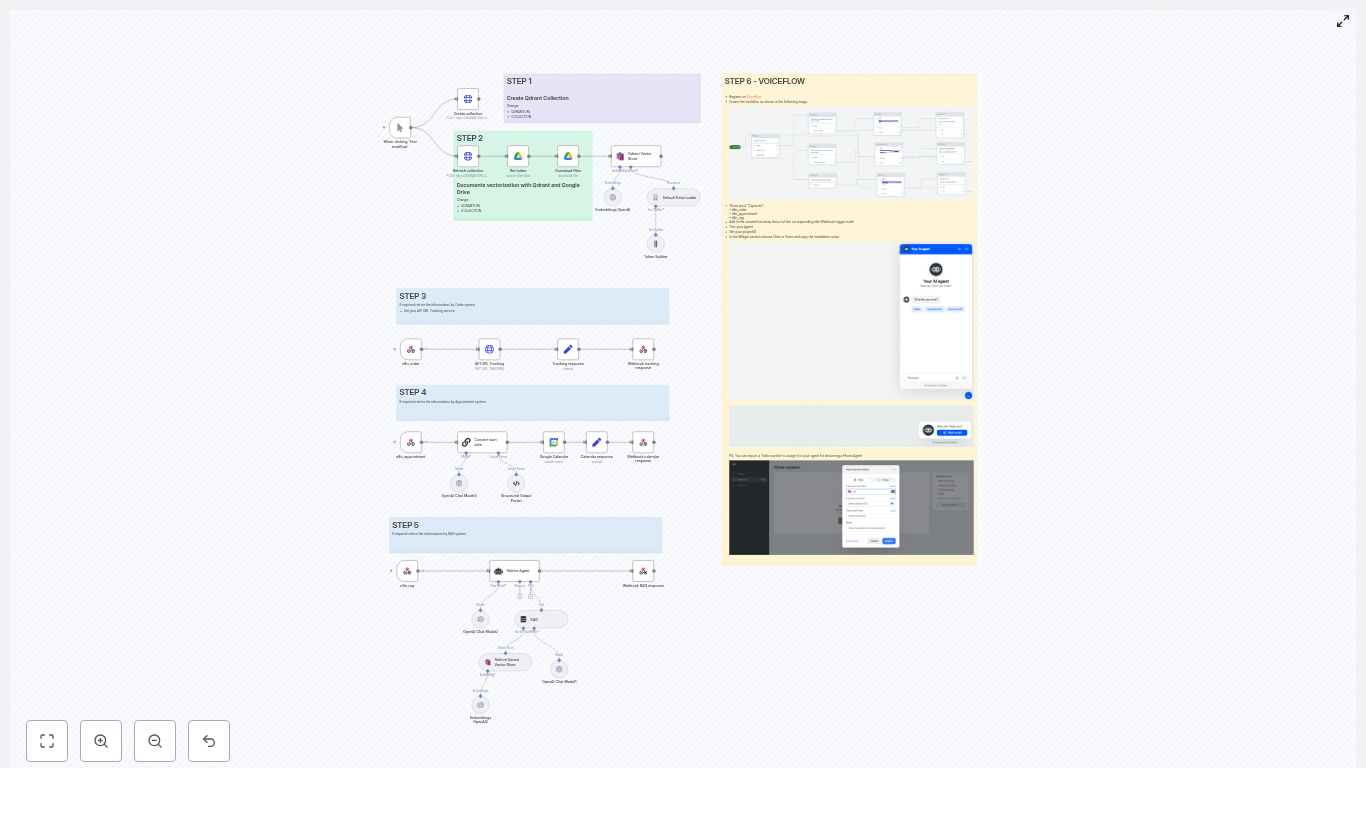
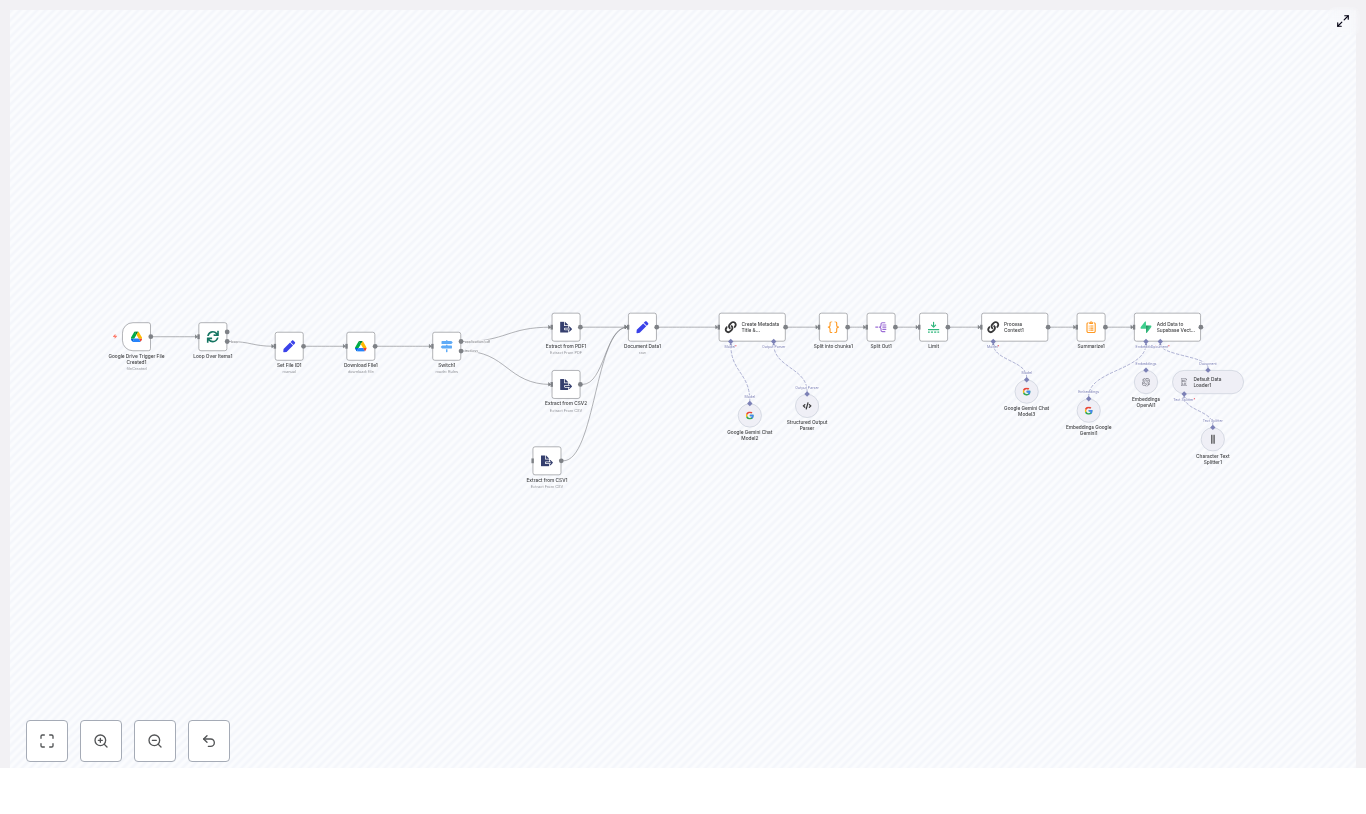
Step 1 – Creating a Qdrant Collection
Maya knew that RAG depends on a solid vector store. The template guided her to start with Qdrant. She set up a Qdrant collection that would store embeddings of her company’s documents: return policies, warranty terms, product guides, and onboarding manuals.
Using n8n’s HTTP Request nodes, she automated the collection setup. The workflow could create or refresh the collection as part of a setup routine, so she did not have to manage Qdrant manually. Whether hosted herself or through a managed Qdrant provider, the pattern stayed the same: a clean collection ready to receive vectors.
Step 2 – Ingesting Documents From Google Drive to Qdrant
Next, she turned her scattered Google Drive into a searchable memory. The template included a pipeline that:
- Used Google Drive nodes to list files in a folder and download them.
- Converted Google Docs into plain text so the LLM could read them.
- Split long documents into smaller chunks using a Text Splitter, based on tokens or characters, for better retrieval granularity.
- Called the OpenAI Embeddings node to convert each chunk into a vector.
- Inserted those vectors into the Qdrant Vector Store.
For the first time, her policies and product docs were not just static files. They became a living, searchable knowledge base that the agent could use in real time. This would be the backbone of RAG-powered answers later.
Parallel Challenge: Order Tracking Without Human Handoffs
While the knowledge base was coming together, support tickets kept piling up with one recurring theme: “Where is my order?” Maya wanted the agent to answer that without a human stepping in every time.
Step 3 – Wiring Order Tracking Into n8n
She created an n8n webhook named n8n_order. Voiceflow would call this webhook whenever a customer gave an order number or asked about order status. Inside n8n, the workflow received the order number, then called the company’s backend tracking API.
The workflow then transformed the raw API response into a human-friendly message, something like “Your order #12345 is on its way and expected to arrive on Friday.” That response was sent back to Voiceflow, which delivered it in natural language, whether via chat or voice.
For the customer, it felt like a helpful agent. For Maya, it meant dozens fewer tickets per day.
The Turning Point: Letting the Agent Book Real Appointments
One afternoon, a sales rep pinged Maya: “The bot is great for FAQ and orders, but can it book demos for us?” That question became the turning point. If the agent could schedule appointments directly into Google Calendar, it would close the loop between interest and action.
Step 4 – Appointment Handling With Google Calendar
Maya extended the template’s appointment flow. In Voiceflow, she created an appointment capture block that collected the user’s preferred date, time, and email. This block called the n8n_appointment webhook.
On the n8n side, the workflow used an LLM node to normalize natural language like “next Tuesday at 3 pm” into a Google Calendar compatible format. The template relied on a structured output parser to ensure that the LLM always returned valid fields for start and end.
The JSON that the Google Calendar node expected looked like this:
// Example JSON expected by Google Calendar node
{ "start": "2025-10-21T14:00:00Z", "end": "2025-10-21T15:00:00Z", "summary": "Event title with user@example.com", "description": "Created via Voiceflow agent"
} The workflow automatically added an hour to the end time, built a meaningful summary that included the user’s email, and created the event in the correct calendar. When the event was confirmed, n8n sent a success message back to Voiceflow, which replied to the user with a friendly confirmation.
Suddenly, the assistant was not just answering questions. It was filling the team’s calendar with qualified appointments.
The Heart of the System: RAG-Powered Knowledge Answers
With order tracking and appointments running smoothly, Maya returned to the original vision: an agent that could answer nuanced questions grounded in real documentation.
Step 5 – Running the RAG Pipeline
Whenever a user asked a knowledge question, Voiceflow routed it to the n8n_rag webhook. From there, the RAG pipeline kicked in:
- The workflow embedded the user’s question using the OpenAI Embeddings node.
- It queried Qdrant for the top-k most relevant document chunks.
- It combined those retrieved snippets with the original question and sent them to a conversational LLM agent node in n8n.
- The agent used a carefully designed system prompt that defined the domain, tone, and fallback behavior.
- The final answer, enriched with citations or references when appropriate, went back to Voiceflow.
A typical webhook payload from Voiceflow to n8n for a knowledge query looked like this:
{ "query": { "Question": "How do I return a defective product?", "Email": "user@example.com" }
} Thanks to RAG, the assistant could now explain the exact return policy for defective products, referencing the same Google Docs the legal team maintained, without hallucinating or guessing.
Voiceflow as the Front Door to Every Capability
To tie the whole experience together, Maya configured three capture blocks in Voiceflow, each pointing to a different n8n webhook URL:
n8n_orderfor order tracking flowsn8n_appointmentfor calendar eventsn8n_ragfor knowledge queries
Each block sent structured data to n8n, then parsed the response and continued the conversation accordingly. If the company wanted a phone agent, all they had to do was connect a Twilio number in Voiceflow’s project settings and enable the phone channel. The same workflows would power web chat, voice, and phone calls.
System Prompts: Teaching the Agent How to Behave
Maya quickly learned that the system message was as important as the data. The template shipped with an example system prompt tailored to an electronics store, which she adapted to her brand’s voice and policies.
She followed a few key guidelines:
- Always instruct the agent to cite or reference retrieved documents when giving RAG answers, if it makes sense.
- Require honesty when the knowledge base does not contain the answer, and tell the agent to offer next steps like contacting support or escalating to a human.
- Keep the tone friendly and professional, using minimal jargon unless the user explicitly asks for technical detail.
With a clear system prompt, the agent felt consistent and safe, even as it pulled information from a growing number of documents.
Testing, Tuning, and Trusting the Workflow
Before rolling out the agent to all customers, Maya spent a week testing every path.
Testing and Validation
She used the Voiceflow test console to simulate user conversations and the n8n manual trigger nodes to run workflows step by step. She checked that:
- Webhook payloads from Voiceflow were parsed correctly in n8n.
- Google Calendar events had the right timezone, start time, and one-hour duration.
- RAG retrieval returned relevant context, and the LLM referenced sources where needed.
Whenever something looked off, she adjusted chunk sizes, retrieval parameters, or the system prompt until the answers felt natural and reliable.
Keeping It Safe and Sustainable: Security, Monitoring, and Costs
Security
Maya knew that automation without security was a risk she could not take. She secured webhooks using shared secrets or tokens so only trusted calls could trigger workflows. API keys for OpenAI, Qdrant, Google, and Twilio were stored in n8n and Voiceflow secrets, never in plaintext inside nodes or scripts. Qdrant access was limited with network rules and API keys to protect the knowledge base.
Monitoring
To keep an eye on behavior, she logged webhook requests and responses, as well as LLM outputs, for debugging and auditing. She added alerts using n8n and external monitoring so that failed integrations or unusual error rates would trigger notifications before customers felt the impact.
Cost Awareness
Finally, she tracked costs across the stack:
- OpenAI usage for both LLM calls and embeddings
- Qdrant hosting fees
- Voiceflow paid plans, especially for phone channels
- Twilio phone number and call usage
- n8n hosting or infrastructure costs
To keep things efficient, she designed caching strategies where possible and limited unnecessary RAG retrievals. Only questions that truly required document context triggered the more expensive steps.
When Things Go Wrong: How Maya Troubleshoots
Even with a robust setup, edge cases appeared. Over time, Maya built a simple troubleshooting playbook.
- Incorrect calendar times: She checked timezone handling in the LLM parser and verified that Google Calendar credentials and settings matched the company’s default timezone.
- Weak or off-topic RAG answers: She experimented with a higher top-k value for retrieval, tried different embedding models, refined document chunking, and cleaned up source documents to remove irrelevant sections.
- Webhook failures: She validated network reachability, confirmed that Voiceflow function nodes used the correct HTTP method and headers, and reviewed n8n logs for error details.
Best Practices She Learned Along the Way
By the time the assistant was live, Maya had a short list of best practices she would recommend to any team:
- Use structured output parsing in n8n when you need strict schemas, especially for dates, start and end times, or numeric values.
- Keep system prompts concise but very specific, including instructions for citations and fallback paths.
- Design conversation flows with graceful error handling and clear escalation paths to human agents.
The Resolution: From Overwhelmed Support to a Unified AI Agent
Within a few weeks of launch, the impact was obvious. The new Voiceflow + n8n + RAG agent handled a large share of order tracking questions, booked appointments directly into Google Calendar, and answered detailed policy questions by referencing internal documents stored in Qdrant.