Build a Visa Requirement Checker with n8n, Weaviate and Embeddings
Imagine never having to manually dig through visa rules again. With a simple n8n workflow, a vector database, and an LLM, you can turn all those dense policy documents into a friendly, automated visa assistant.
In this guide, we will walk through how the Visa Requirement Checker n8n template works, why it uses vector search and embeddings, and how you can wire up each node step by step. By the end, you will have a clear picture of how to deploy a reliable, privacy-aware visa lookup service that your users can actually trust.
What this Visa Requirement Checker actually does
At a high level, this workflow takes a user question like:
“Does a US passport holder need a visa for Brazil for tourism?”
Then it:
- Receives the question via a Webhook
- Searches your visa policy documents using embeddings and Weaviate
- Uses an LLM Agent to read the relevant snippets and craft a clear answer
- Optionally logs everything to Google Sheets for analytics or audits
The result is a small, self-contained visa guidance service that you can plug into a website, internal tool, or API.
When should you use this n8n template?
This workflow is a great fit if you:
- Run a travel platform and want to give users instant visa guidance
- Work in a corporate mobility or HR team that supports employees who travel a lot
- Are a travel agent or service provider who needs a consistent, auditable way to answer visa questions
If you are tired of manually checking consulate pages, or you want a system that can scale beyond one or two experts, this template will feel like a huge relief.
Why vector search and embeddings make visa guidance easier
Visa rules are messy. They are long, full of exceptions, and written in language that users do not always copy exactly. Someone might ask about “business travel,” “work trip,” or “attending a conference,” and they all map to similar rules.
Traditional keyword search struggles with this. That is where embeddings and a vector store like Weaviate shine.
Key benefits of using embeddings for visa checks
- Semantic search over policy documents – find the right passages even if the user does not use the exact same wording as the document.
- Easy updates – you can add or replace documents in your vector store without retraining a model.
- Scalable and fast – combine vector search with an LLM chat agent to deliver answers quickly, even as your document set grows.
In short, embeddings help you match “what the user means” rather than just “what they typed.”
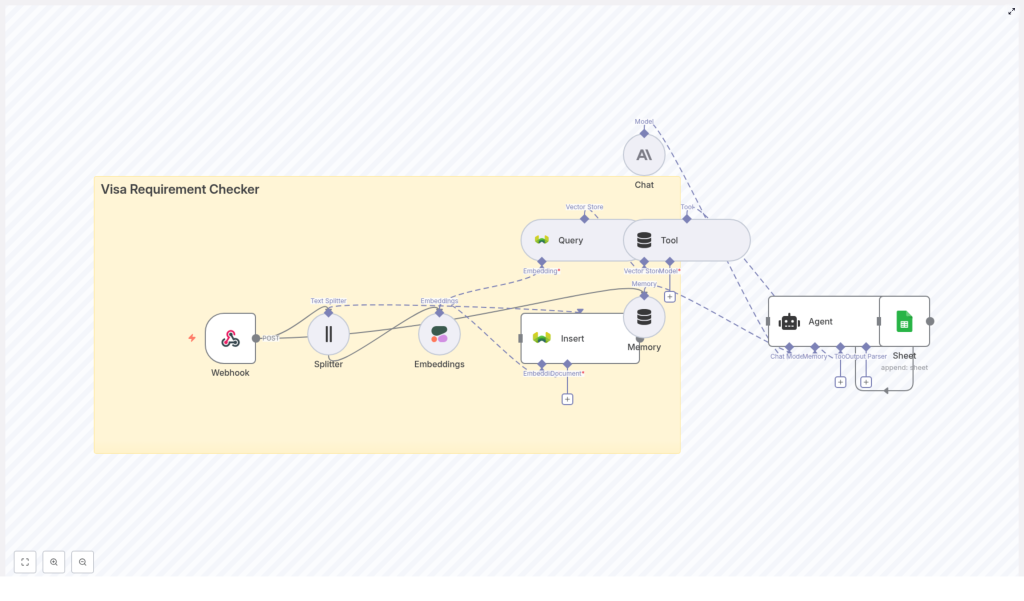
How the n8n workflow is structured
The Visa Requirement Checker template is built as a set of connected n8n nodes that each handle a specific part of the flow. Here is the big picture:
- Webhook – receives questions from your app or frontend
- Text Splitter – breaks long visa documents into smaller pieces
- Embeddings – converts each text chunk into a vector
- Weaviate Insert & Query – stores and retrieves those vectors
- Tool + Agent – lets the LLM use those retrieved snippets as context
- Memory – keeps short-term context between related questions
- Google Sheets – logs questions, answers, and matched passages
Let us go through each part in a more conversational way so you can see how it all fits together.
Step-by-step: Node-by-node walkthrough
1. Webhook – the front door of your visa checker
Everything starts with a simple HTTP POST request. In the template, you create a Webhook node with an endpoint like:
/visa_requirement_checkerYour UI or API client sends a request there with the user question. For example:
“Does a US passport holder need a visa for Brazil for tourism?”
This node is the entry point, so any app that can make an HTTP POST can use your visa checker.
2. Text Splitter – preparing your policy documents
Visa policy documents are usually long. If you try to embed the entire document as a single chunk, you lose precision and waste tokens. The Text Splitter node solves that.
In this template, the splitter is configured with:
chunkSize = 400characterschunkOverlap = 40characters
The overlap is important. It keeps some context between chunks so that sentences that span boundaries still make sense to the embedding model.
In practice, you feed your raw visa policy text into this node, and it outputs a list of smaller, overlapping text chunks that are ready for embedding.
3. Embeddings – turning text into vectors
Next, each of those chunks goes through an Embeddings node. The template uses Cohere as the embeddings provider, but you can plug in another provider if you prefer.
The model is set to default in the template. For production, you might choose a specific model that is tuned for semantic retrieval or multilingual support, depending on your use case.
The output of this node is a dense vector for each text chunk, which is exactly what Weaviate needs to store and search your documents efficiently.
4. Insert into Weaviate – building your visa knowledge base
Now that you have vectors, it is time to store them. The Weaviate Insert node takes each embedded chunk and saves it into a vector index, along with helpful metadata.
A typical setup includes:
- An index or class name such as
visa_requirement_checker - The embedding vector for each chunk
- The original text of the chunk
- Metadata like country, visa type, and timestamps
That metadata is crucial for filtering and auditing later. More on that in a bit.
5. Query + Tool – finding the most relevant policy snippets
When a user asks a question, the workflow embeds the question in a similar way and sends it to Weaviate for a nearest neighbor search.
The Weaviate Query node returns the chunks that are closest in vector space to the user query. In plain language, that means “the pieces of your documents that are most likely to answer the question.”
Those retrieved passages are then passed into a Tool node. The Tool exposes this retrieval function to the Agent so that your LLM can pull in real policy text whenever it needs it, rather than hallucinating an answer from scratch.
6. Memory & Chat – handling follow-up questions
Users rarely ask just one question. They might say:
- “Do I need a visa for tourism?”
- Then: “What about for work?”
To make that feel natural, the workflow uses a short-window Memory node that stores recent interactions. This allows the Agent and Chat nodes to keep context across messages so the LLM knows what “what about work visas?” is referring to.
The Chat node itself connects to an LLM provider. In the template, it is configured to use Anthropic, but you can adapt it to another LLM if needed. The LLM takes the retrieved passages plus the conversation history and generates a friendly, grounded answer.
7. Agent & Google Sheets – orchestrating and logging
The Agent node is the conductor of this whole setup. It decides when to call the retrieval Tool, how to use memory, and how to structure the final response.
Once the Agent has produced the answer, the workflow can optionally log everything to Google Sheets. A typical row might include:
- The original user question
- The passages that were retrieved from Weaviate
- The final LLM response
- A timestamp
This gives you a lightweight audit trail and a simple way to review how well the system is performing.
Designing your metadata for smarter search
Good metadata makes your vector store far more powerful. When you store each vector in Weaviate, add fields that reflect how you think about visa rules in real life.
Useful metadata keys include:
country– destination country for the rulevisa_type– tourism, business, work, transit, etc.document_url– link to the official source or PDFlast_updated– when the policy was last refreshed
With these fields, you can filter queries, for example to only return recent rules or to focus on a specific visa type.
Getting chunking right
Chunking might sound like a small detail, but it has a big impact on quality and cost.
Some practical tips:
- Keep chunks semantically coherent. Try to split along sentence or paragraph boundaries rather than in the middle of a thought.
- Use overlap to avoid cutting important context, but do not overdo it. Too much overlap means more storage and higher embedding costs.
- Group shorter notes or bullet points into a single chunk so each embedding represents a meaningful idea.
The template’s values of 400 characters for chunkSize and 40 for chunkOverlap are a solid starting point, and you can tweak from there based on your documents.
Prompting the LLM so it stays grounded
Even with good retrieval, the LLM needs clear instructions so it does not “make things up.” Prompt engineering here is all about grounding the answer in the actual policy text.
Best practices:
- Ask the model to cite which passages it used.
- Have it include a link to the official consulate or government source whenever possible.
- Encourage it to express uncertainty and ask follow-up questions if the rules are unclear.
A simple prompt pattern that works well looks like this:
Given these policy passages, answer whether a traveler with [passport_country] traveling to [destination_country] for [purpose] needs a visa. Cite the passages used and provide a link to the official source. If unclear, ask a clarifying question. This kind of instruction reduces hallucinations and makes your answers more trustworthy.
Privacy, logging, and compliance
Visa questions can sometimes include personal details, so it is worth thinking about privacy from the start.
Guidelines to keep in mind:
- Avoid storing sensitive personal data in embeddings or logs.
- Use the Google Sheets log for non-sensitive analytics only, or protect it with proper access control.
- For GDPR compliance, do not persist user-identifiable PII unless you have a lawful basis and a clear retention policy.
In many cases, you can design the system so that only the question text and high-level context are stored, without names or passport numbers.
Testing your visa checker before going live
Before you roll this out to real users, it is worth spending time on thorough testing. Try to “break” the system with tricky questions.
Test scenarios might include:
- Ambiguous phrasing or typos in country names
- Different passport origins for the same destination
- Multi-leg trips or transit through third countries
- Special cases like diplomatic passports or visa waiver programs
Each time, check that the retrieved passages actually support the LLM’s answer. If something feels off, adjust your chunking, metadata, or prompts.
Scaling and keeping costs under control
As usage grows, most of your costs will come from embedding new documents and calling the LLM. A few tweaks can help keep things efficient.
- Reduce the number of chunks where possible by merging small notes into coherent sections.
- Cache frequent queries, especially common passport-destination-purpose combinations.
- Limit LLM token usage by using concise prompts and setting reasonable maximum output lengths.
These optimizations let you serve more users without sacrificing quality.
Monitoring and ongoing maintenance
Visa rules change. APIs occasionally fail. To keep your checker reliable, you will want some basic monitoring and a maintenance routine.
Suggestions:
- Monitor API errors for Weaviate, your embeddings provider, and your LLM.
- Refresh your vector store whenever official documents change, and keep a simple changelog of updates.
- Re-embed only the documents that have changed rather than everything at once.
A bit of regular housekeeping goes a long way in keeping your answers accurate.
Ideas for extending the workflow
Once the basic visa checker is running, you can layer on more advanced features without rewriting everything.
- Multi-language support – embed translated versions of your documents or add a translation step before embedding and answering.
- Role-based answers – provide a simple explanation for travelers and a more detailed, technical view for internal teams or immigration specialists.
- Automated updates – scrape official government or consulate pages, detect changes, and re-ingest updated passages automatically.
Because the core is built on n8n, you can add these pieces as new branches in the workflow instead of rebuilding everything from scratch.
Why this template makes your life easier
Manually checking visa rules is tedious, error-prone, and hard to scale. This n8n-based Visa Requirement Checker gives you:
- A no-code automation backbone that is easy to maintain
- Semantic search over complex policy documents
- LLM-powered answers that are grounded in real text, not guesswork
- An auditable trail of how each answer was generated
It is a practical solution for travel platforms, corporate mobility teams, and travel agents who need accuracy and transparency, without building a whole AI stack from scratch.
Ready to try the Visa Requirement Checker?
If you want to see this in action, you can start right away:
- Import the n8n workflow template into your n8n instance.
- Connect your Cohere, Weaviate, and Anthropic (or chosen LLM